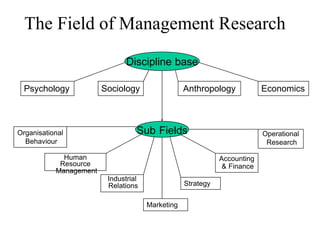
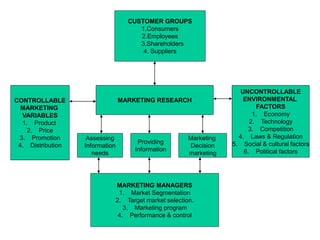
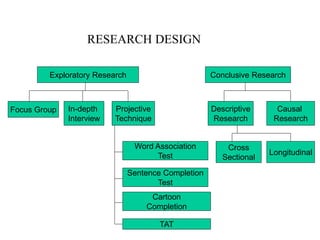
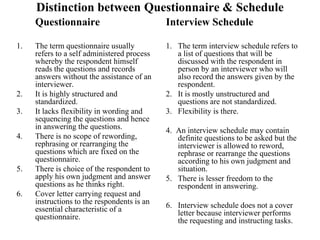
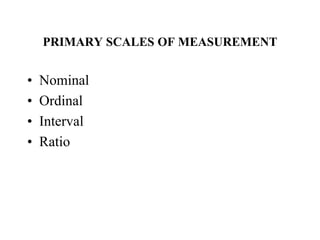
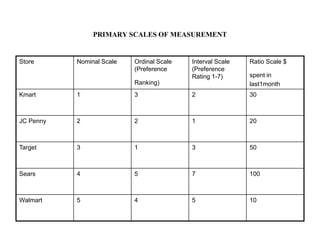
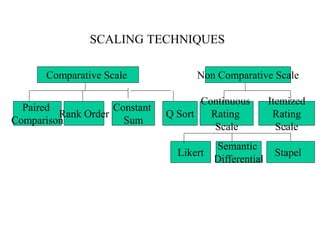
Marketing research involves the systematic design, collection, analysis and reporting of data to help solve specific marketing problems. It uses both primary and secondary data collected through various methods like questionnaires, interviews and observations. The data is then analyzed using statistical tools to help marketing managers make better decisions regarding segmentation, targeting, and developing effective marketing strategies and programs.