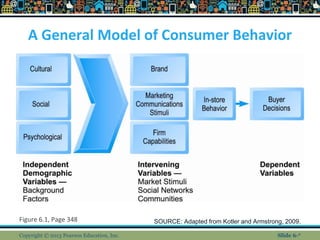
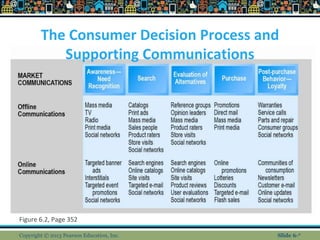
This document discusses concepts related to e-commerce marketing. It provides an overview of social, mobile and local marketing strategies. It discusses models of consumer behavior and decision making processes. It also outlines various digital marketing platforms and tools, including social media marketing, mobile marketing, search engine marketing, display ads, email marketing and more. The key aspects of developing an integrated multi-channel marketing strategy are also addressed.