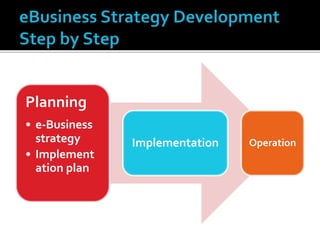
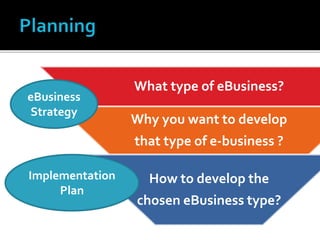
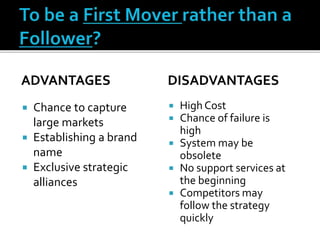
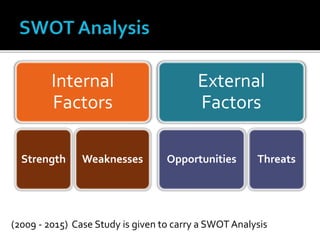
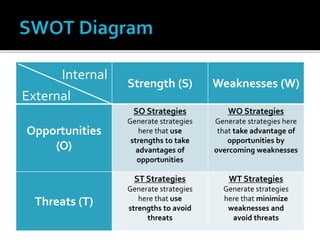
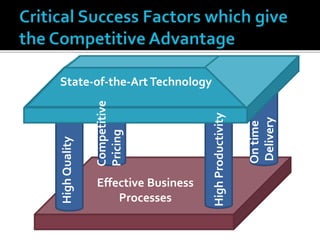
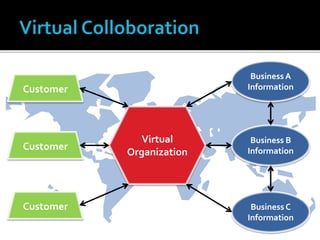
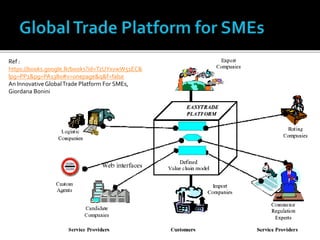
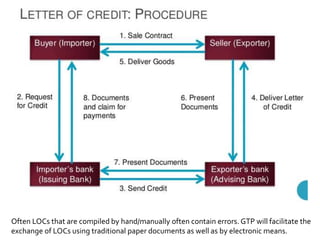
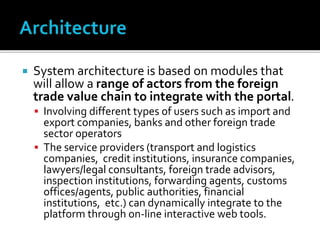
The document discusses e-commerce business strategies, highlighting the importance of strategic planning to enhance competitiveness, optimize resources, and ensure long-term growth. It emphasizes the need for specific implementation plans that focus on profitability, efficiency, and customer satisfaction, while also addressing potential advantages and disadvantages of e-business. Additionally, it describes an innovative global trade platform designed to assist SMEs in managing international trade processes effectively, ensuring data security, and reducing costs and errors associated with export/import activities.


















![ Need high security environment both physical & digital.
Digital security mechanisms should be properly in place
(protocols [HTTPS/ SSL], encrypted information
transmission, password protection, user id system, digital
signatures and acquire necessary digital certificates.)
CIA Features in Digital Security
Confidentiality – ensure that information is not accessed by
unauthorized parties
Integrity – ensure that information is not altered by
unauthorized people in a way not detectable by authorized users
Authentication – ensure that users are the people they claim to
be](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chap5-160806131141/85/eCommerce-Business-Strategies-31-320.jpg)