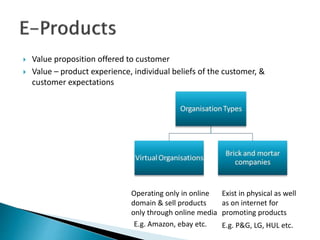
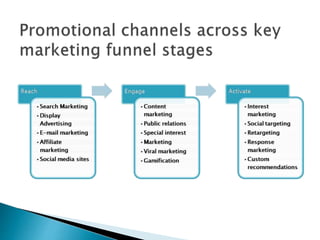
The document discusses the significant growth of online marketing and e-commerce in India, projecting a rise in internet users and e-commerce market value by 2026. It emphasizes the importance of understanding consumer behavior, segmentation strategies, and the online marketing mix, which includes product attributes, branding, co-creation, and distribution channels. Additionally, it highlights the need for effective promotion and marketing processes tailored to the digital landscape to enhance customer engagement and optimize service delivery.