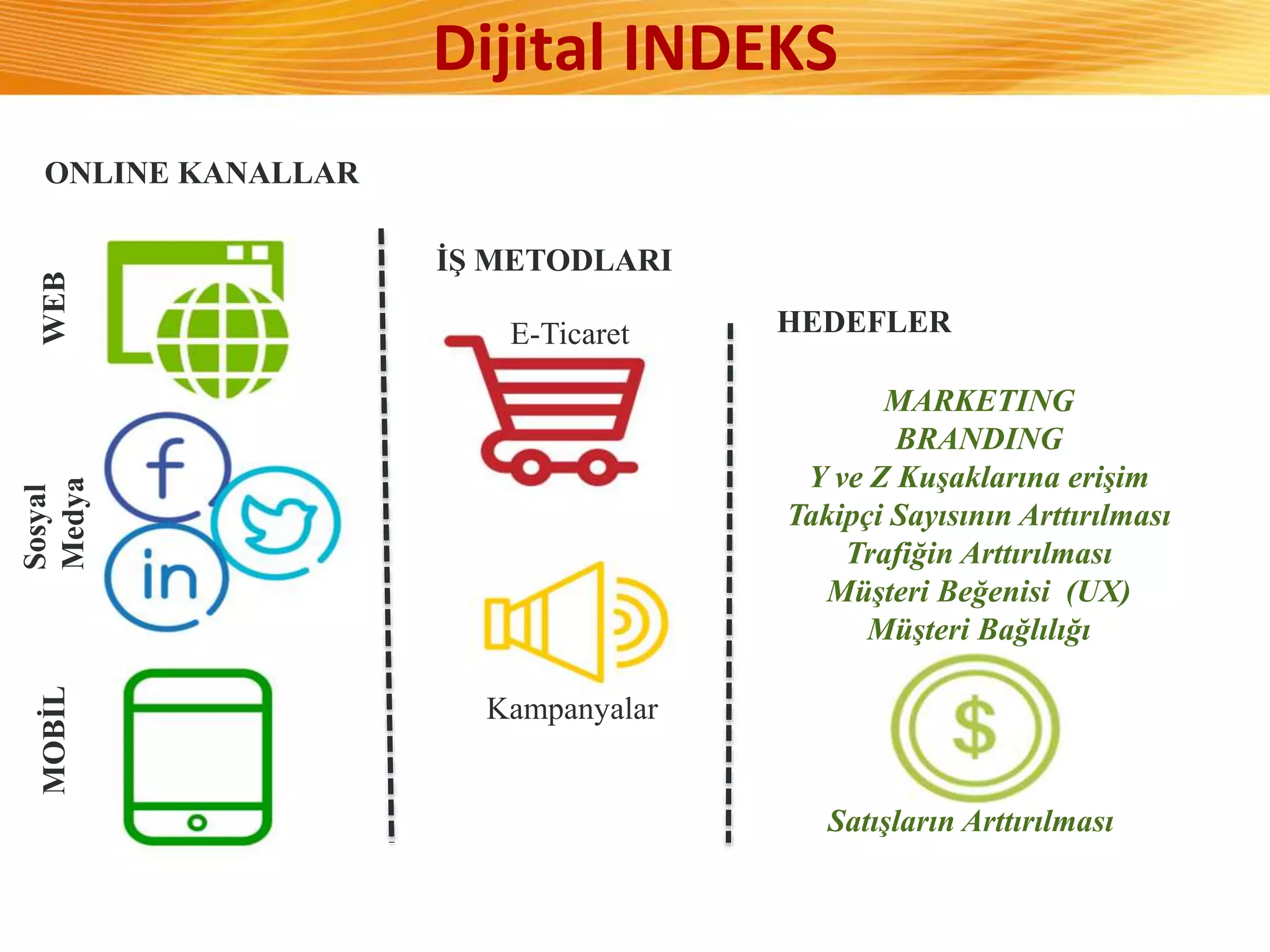
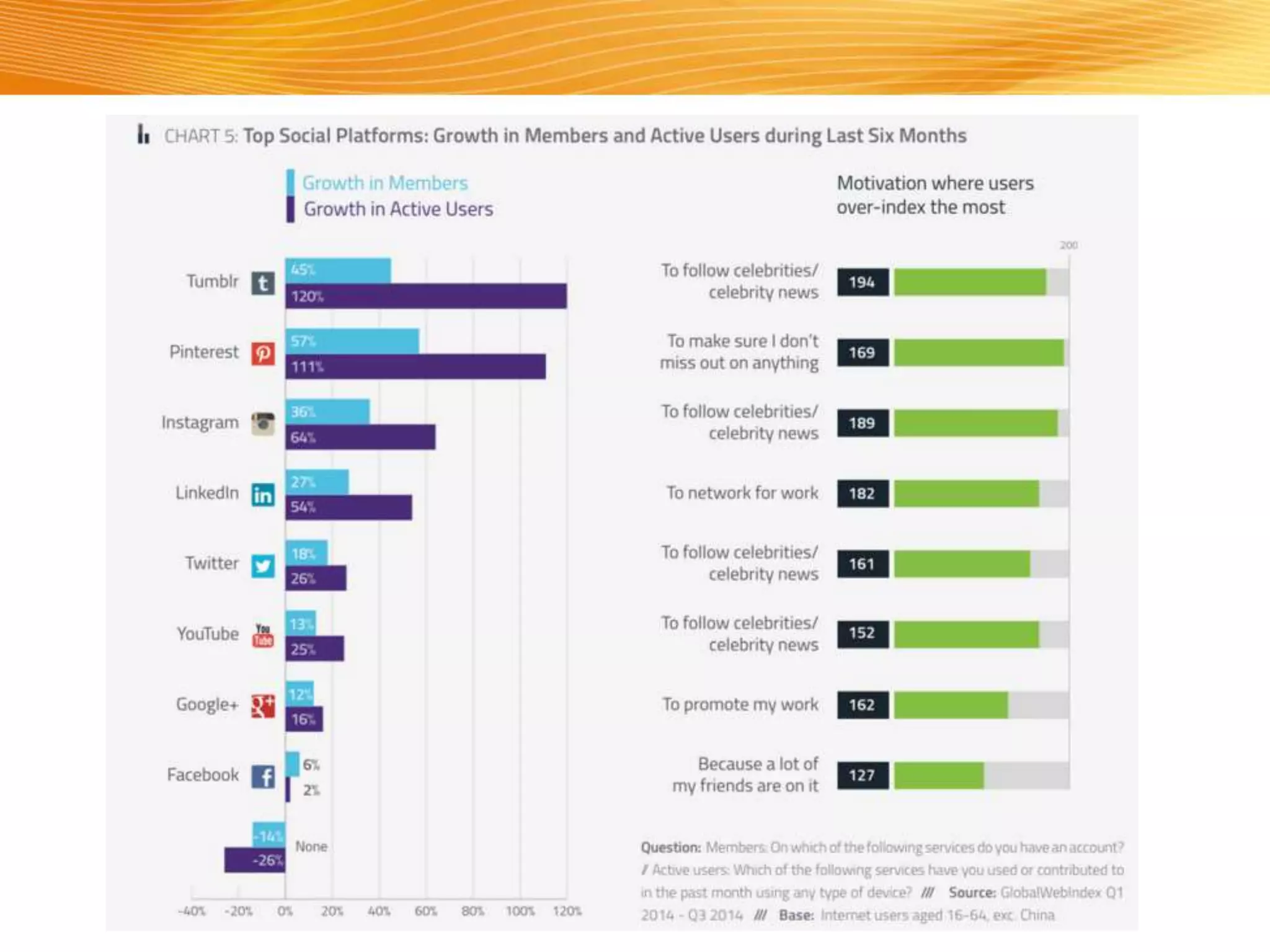
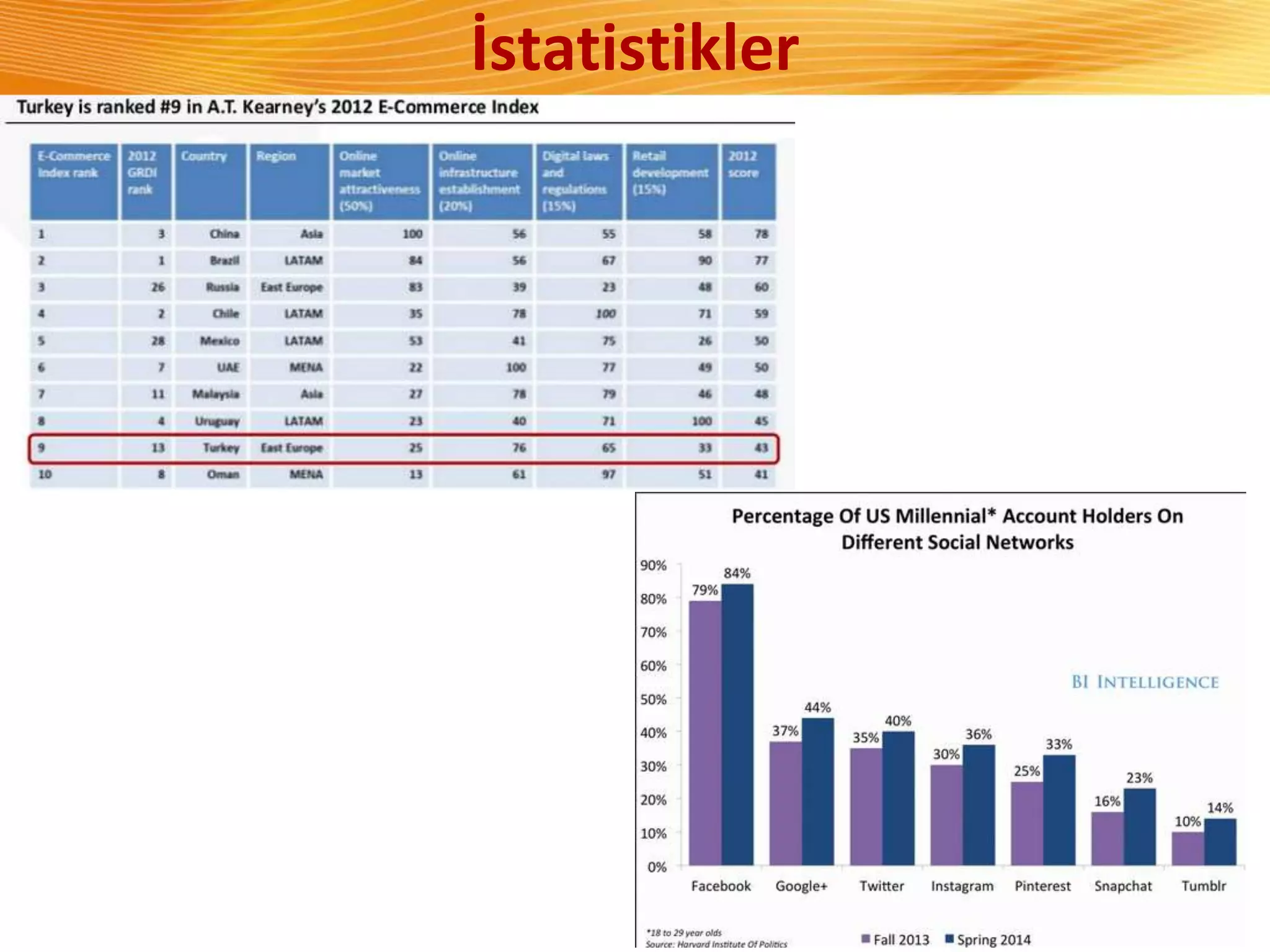
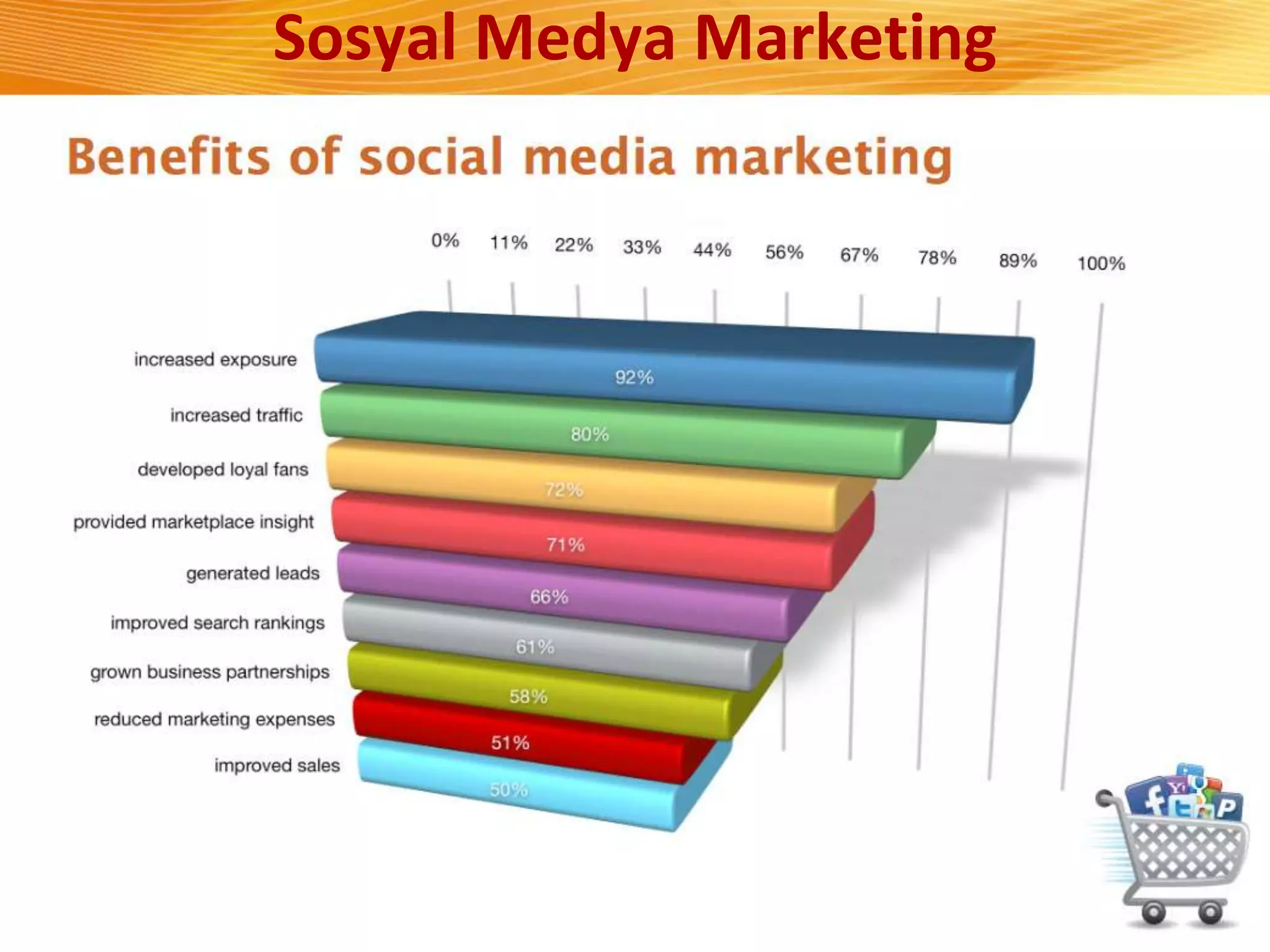
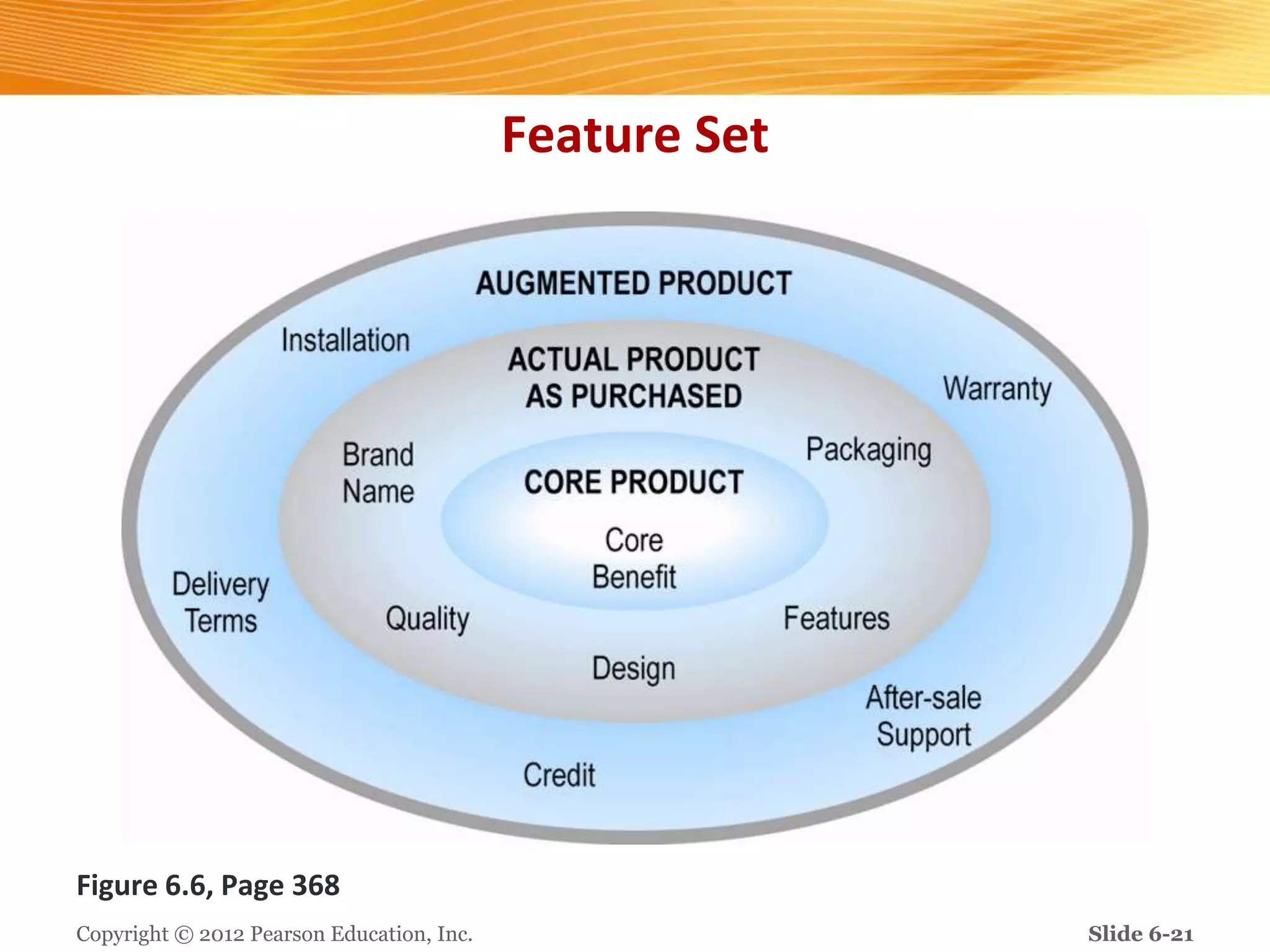
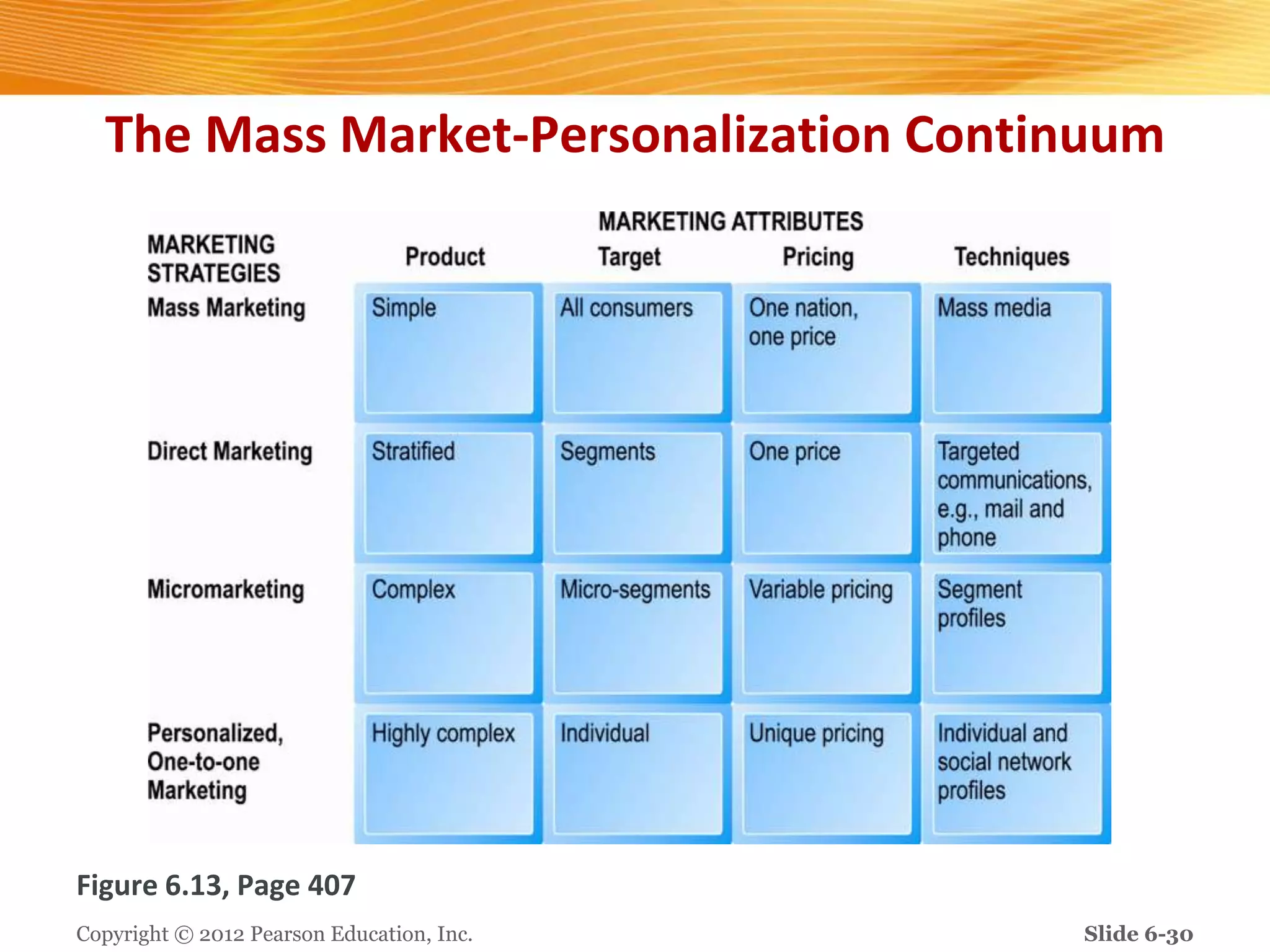
The document discusses how digital marketing and social media can improve customer relationships for businesses. It provides an overview of key digital marketing strategies and metrics that companies should focus on, such as increasing social media followers, website traffic, mobile app usage, and e-commerce sales. The document also outlines the importance of enhancing the customer experience through personalized marketing approaches using tools like customer relationship management systems and social media marketing.