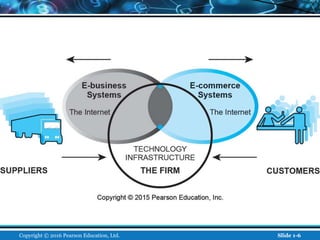
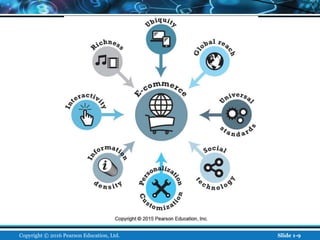
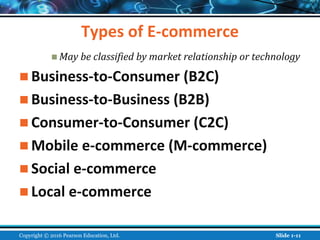
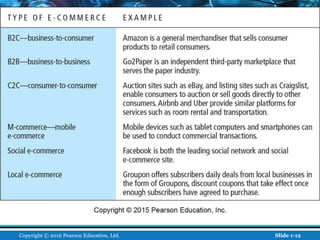
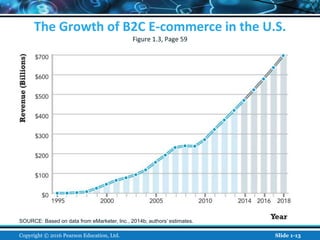
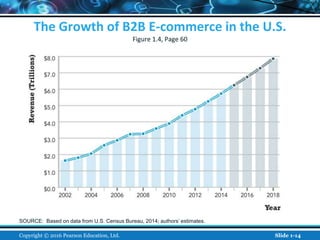
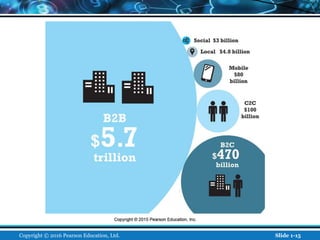
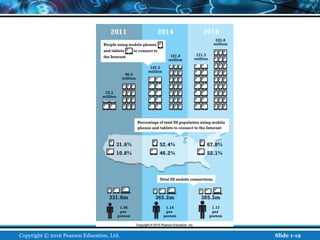
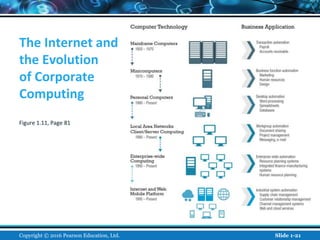
The document is an introductory chapter about e-commerce from a textbook. It defines e-commerce as digitally enabled commercial transactions over the Internet. It discusses how e-commerce differs from traditional commerce through its unique features such as ubiquity, global reach, and personalization. The chapter also outlines the growth of business-to-consumer and business-to-business e-commerce in the US, and introduces various types of e-commerce including mobile and social commerce. It frames e-commerce as an intersection of technology, business, and society.