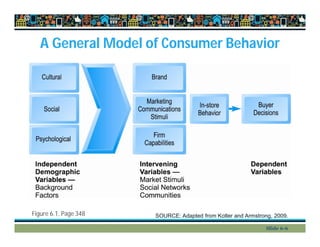
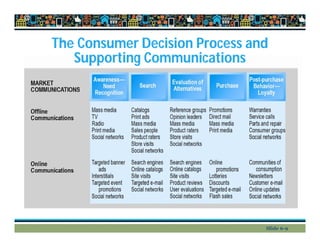
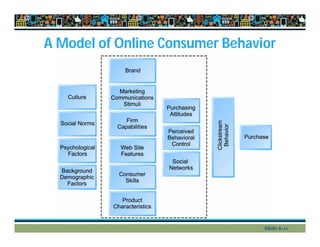
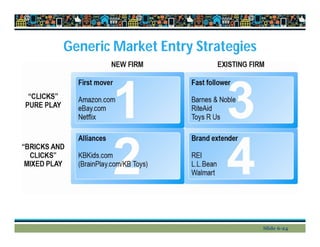
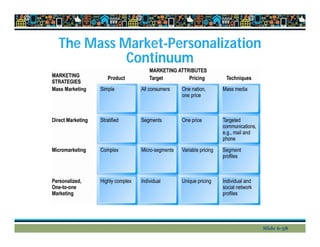
This document provides an overview of key concepts in e-commerce marketing, including social media marketing, mobile marketing, and local marketing. It discusses models of online consumer behavior and decision-making processes. It also outlines various digital marketing strategies and tools such as search engine optimization, display ads, email marketing, social media marketing on platforms like Twitter and blogs, viral marketing, mobile marketing, app marketing, and local marketing strategies like geotargeting. Finally, it touches on concepts like multi-channel marketing, customer retention, personalization, and net pricing strategies.