Embed presentation
Downloaded 124 times


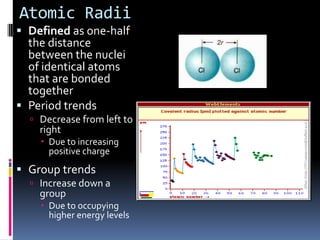

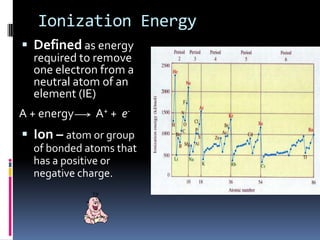

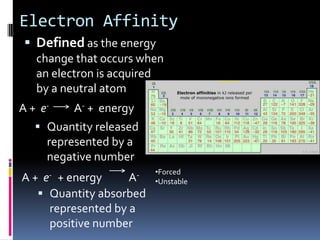

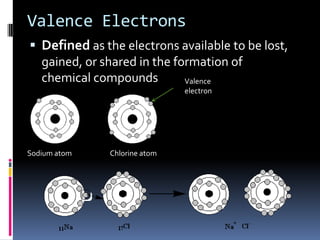
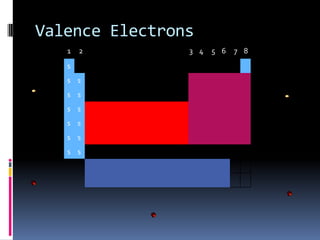

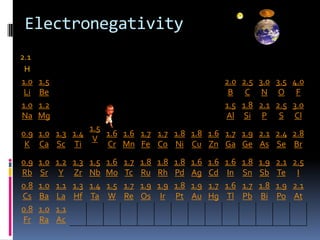
This document defines and compares various periodic properties including atomic radii, ionization energy, electron affinity, ionic radii, valence electrons, and electronegativity. It states that atomic radii decreases left to right and increases down a group. Ionization energy generally increases across a period and decreases down a group. Electron affinity is the energy released or absorbed when an atom gains or loses an electron. Ionic radii are smaller for cations and larger for anions. Valence electrons are those involved in bonding and their number varies by main group element. Electronegativity generally increases across a period and decreases down a group.











