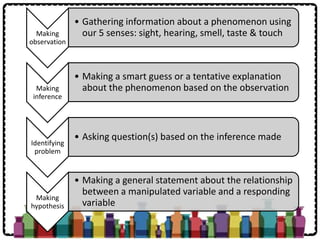
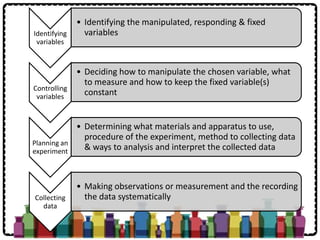
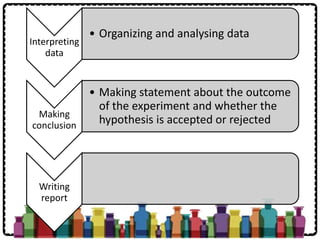
Chemistry is the study of the composition, structure, properties and interactions of matter. It involves investigating what chemicals are made of, how elements interact with each other, and how to produce useful new chemicals. Chemistry is important for fields like medicine, agriculture, materials science, and more. The scientific method is the systematic process used in chemistry and other sciences to solve problems, involving steps like making observations and inferences, identifying variables, designing experiments, collecting and analyzing data, and reporting findings.