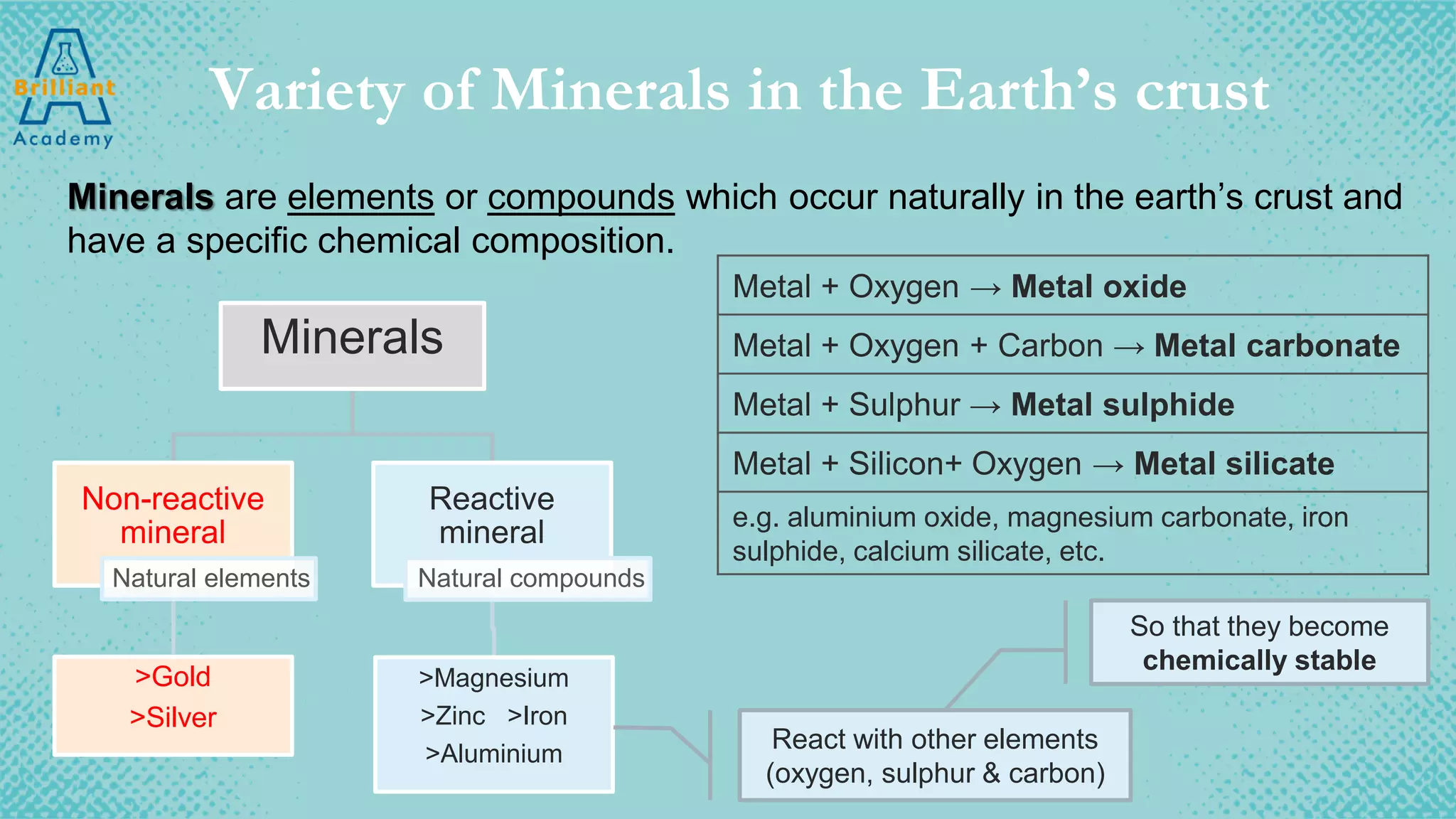
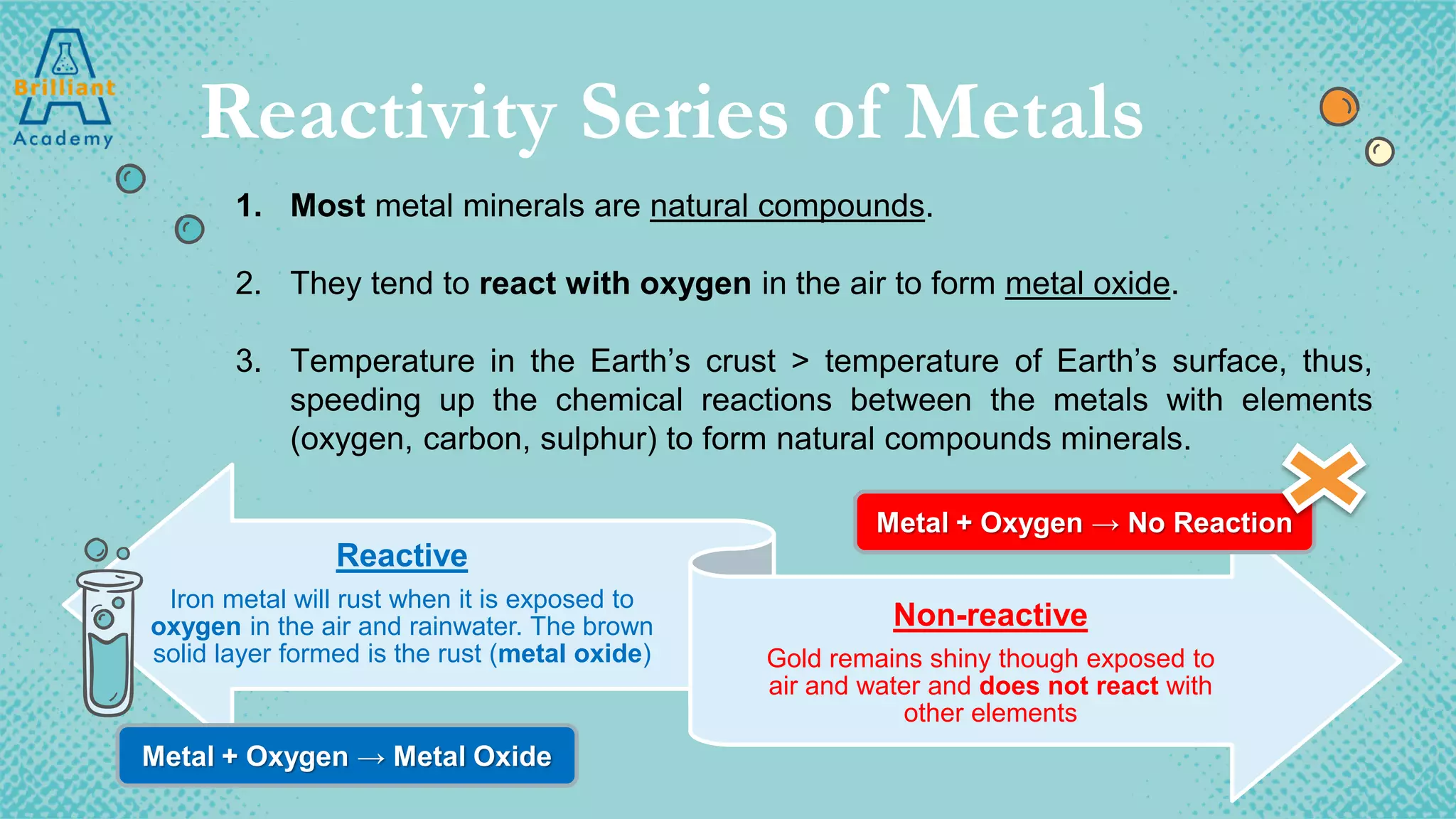
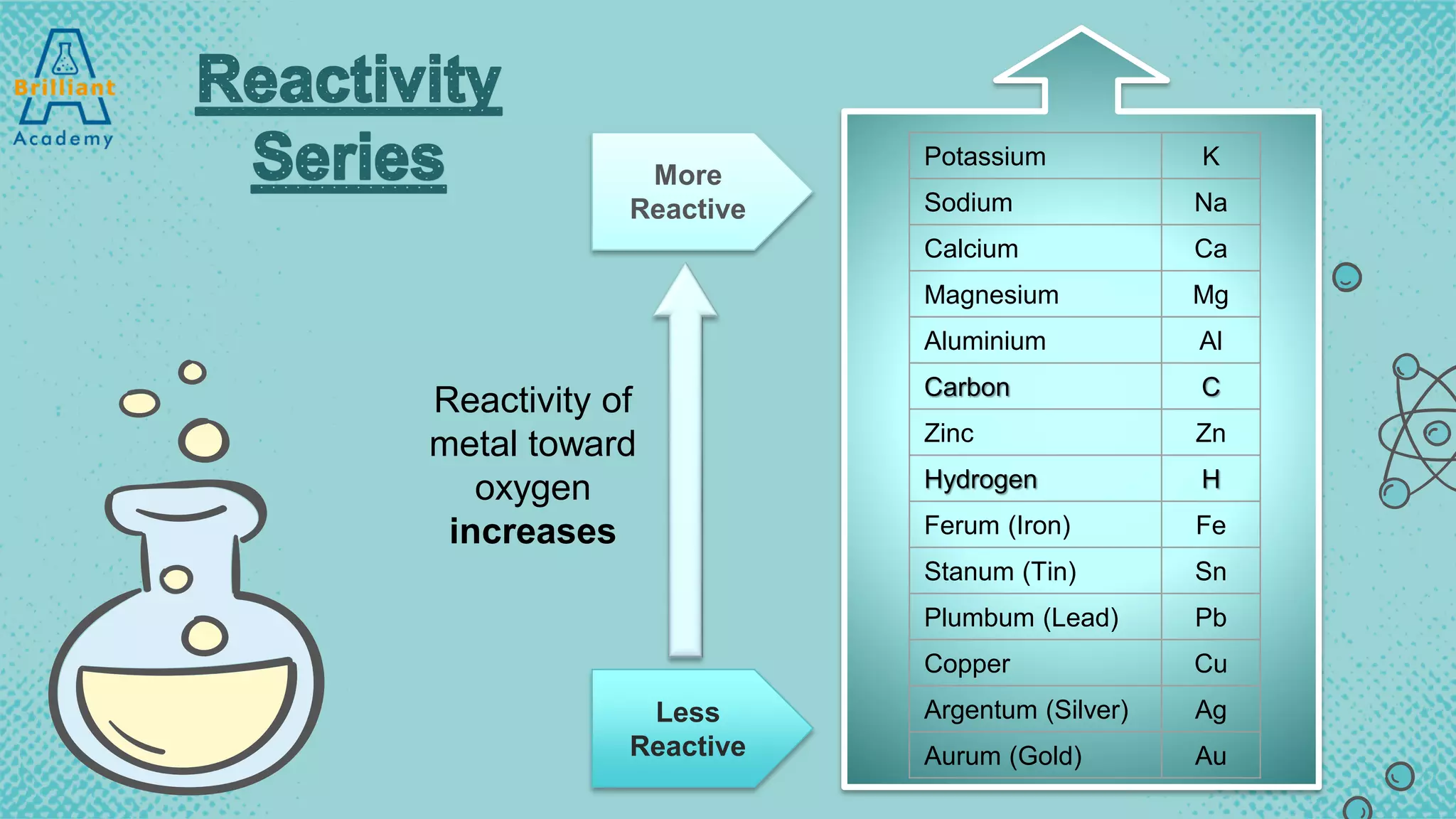
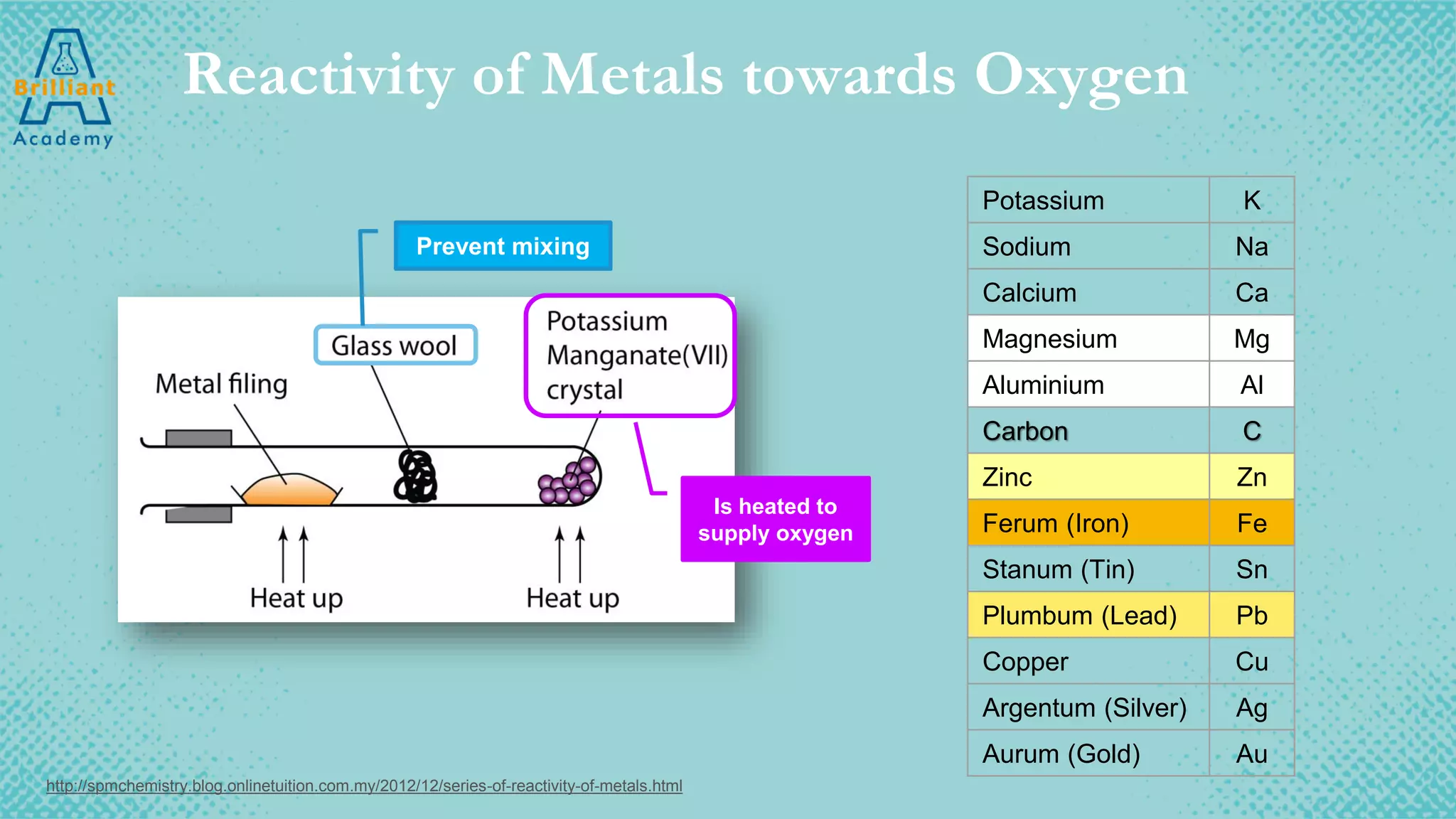
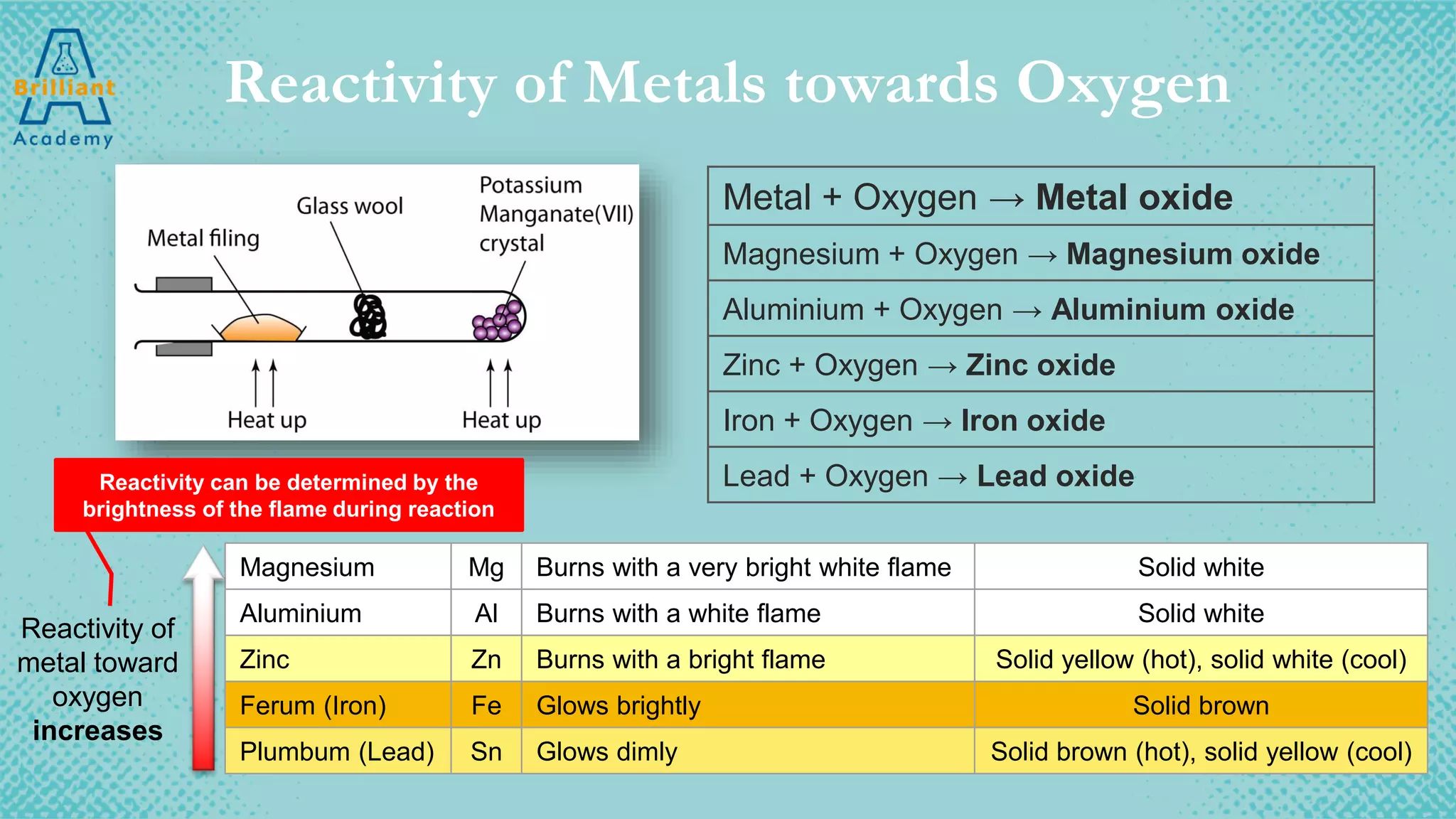
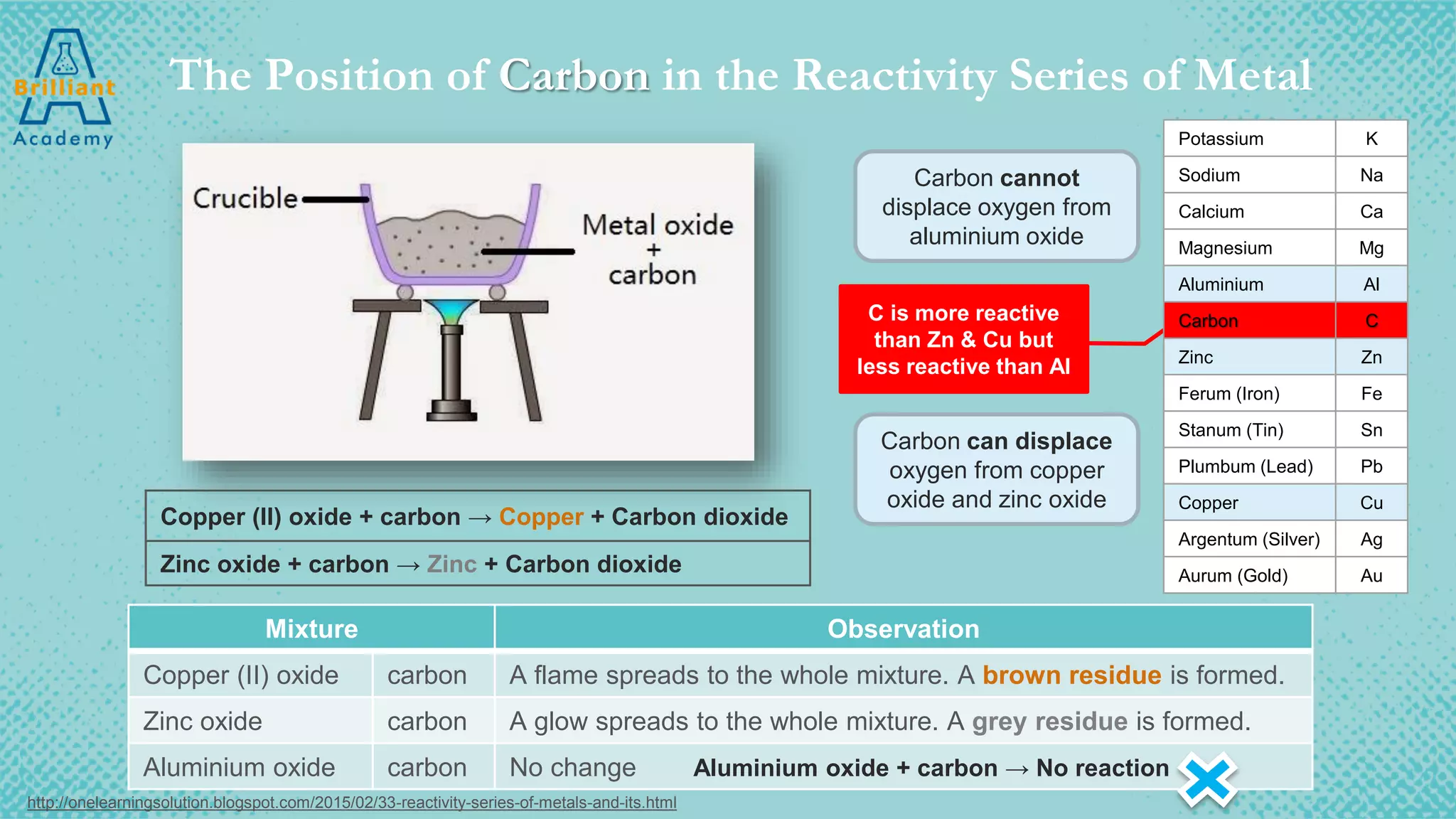
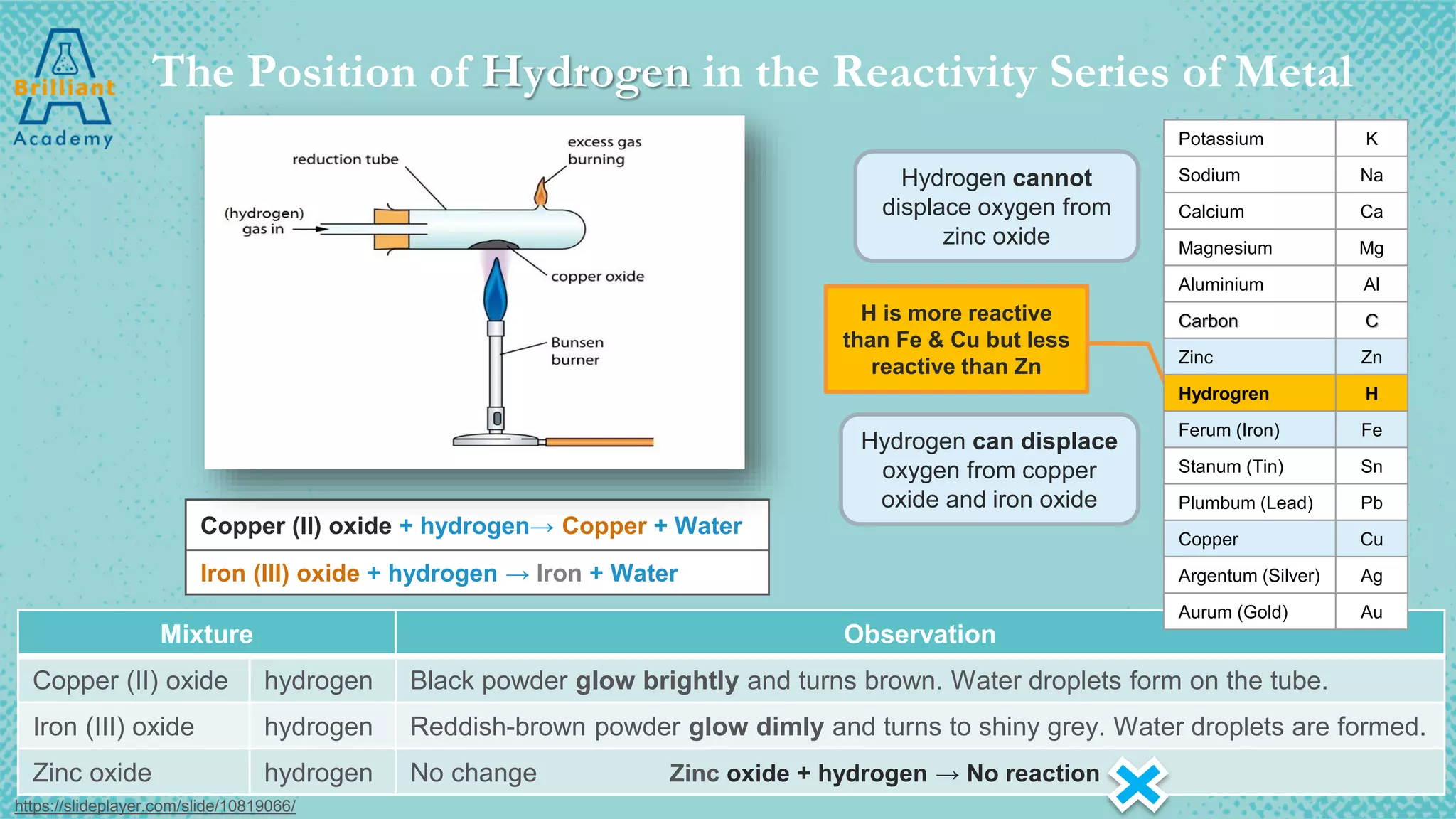
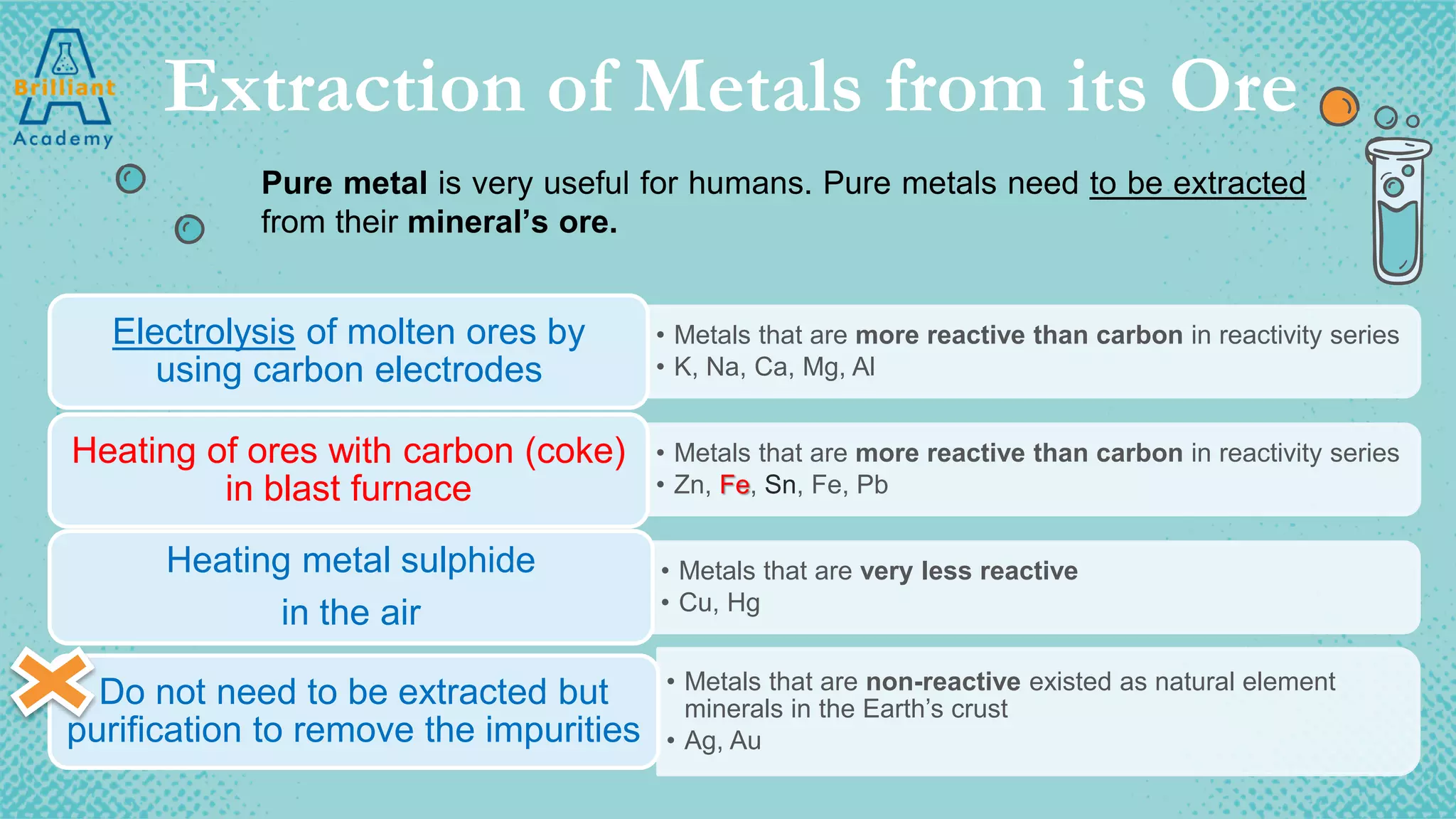
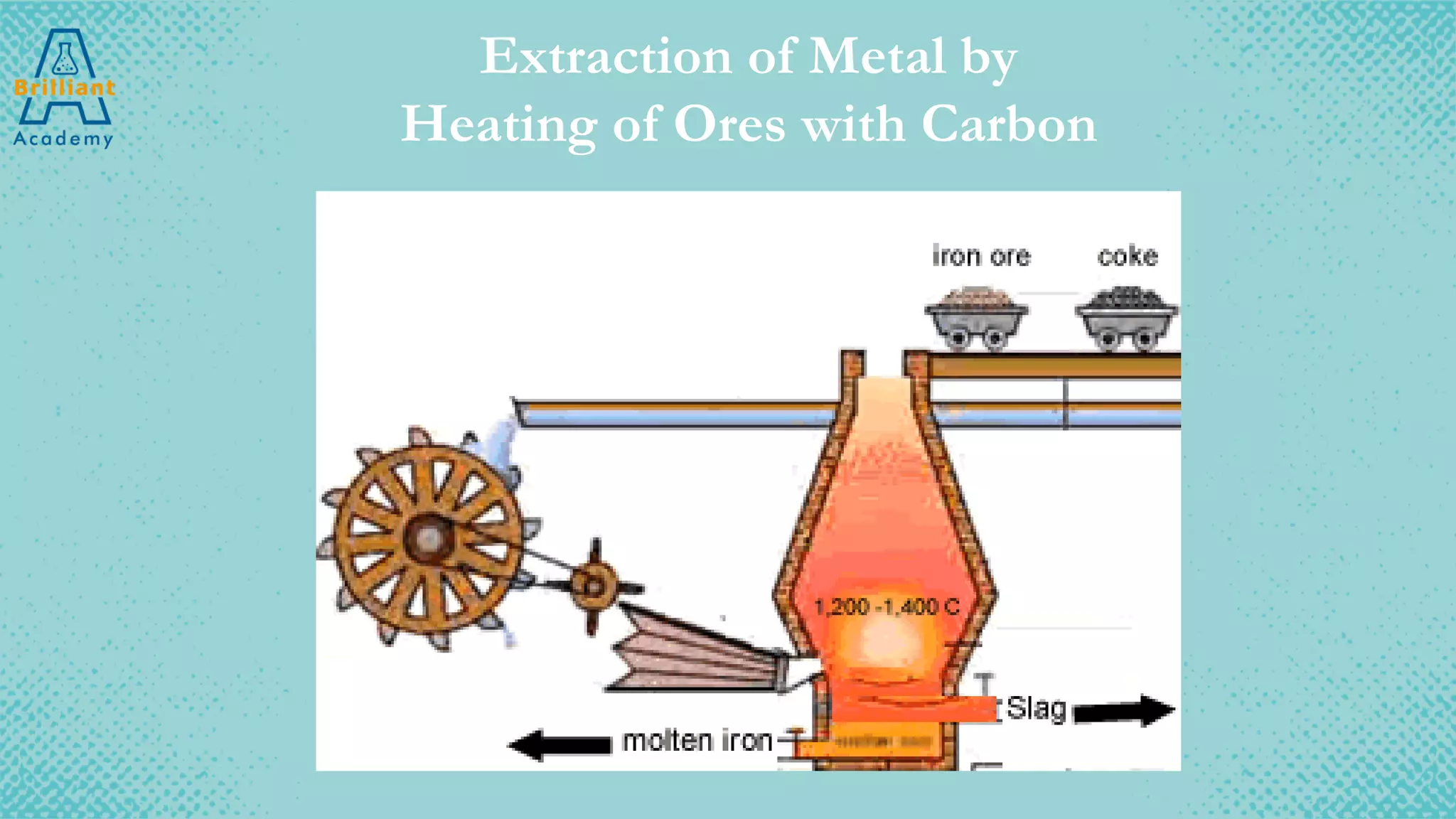
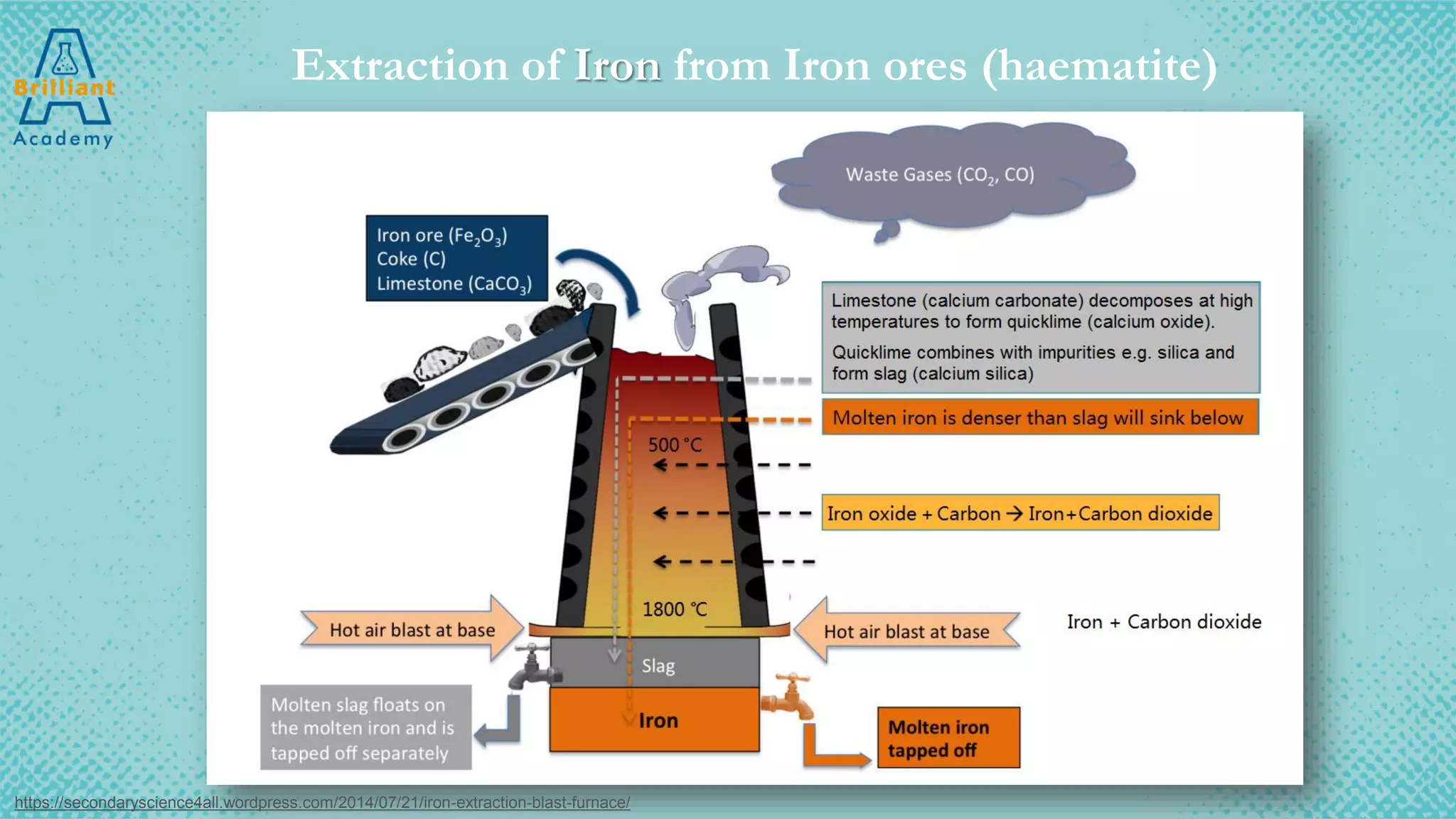
The document discusses the variety of minerals found in the Earth's crust, including both natural elements like gold and silver as well as natural compounds like bauxite and magnetite. It also covers the reactivity series of metals and how more reactive metals must be extracted from their ores using methods like heating with carbon or electrolysis, while less reactive metals can be found in purer form. A variety of everyday uses for common minerals are presented, along with the environmental impacts that can result from mining activities.