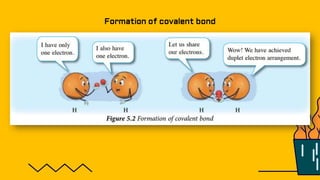
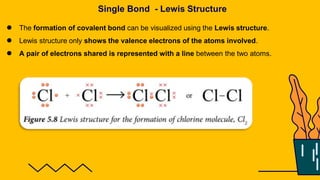
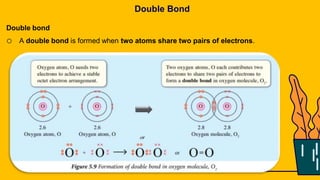
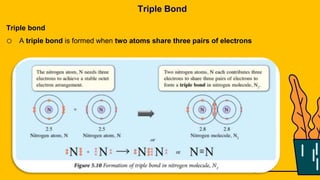
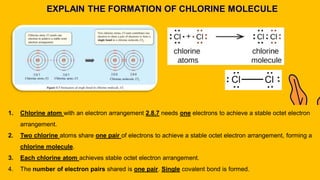
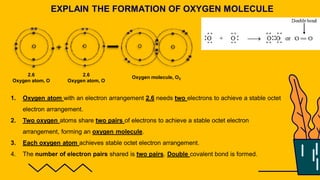
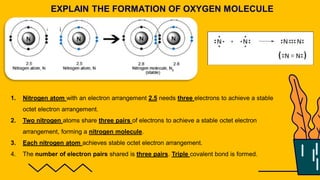
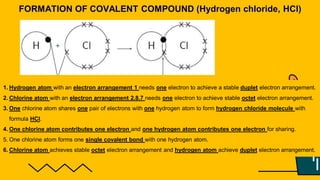
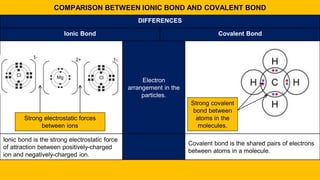
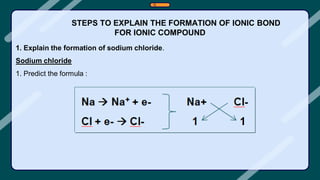
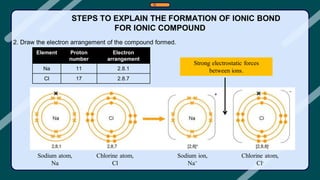
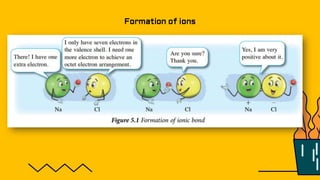
1. The document discusses the formation of chemical bonds through ionic bonds and covalent bonds. Ionic bonds involve the transfer of electrons between metal and non-metal atoms to form ions, while covalent bonds involve the sharing of electron pairs between non-metal atoms.
2. Key differences between ionic and covalent bonds are outlined, such as ionic bonds forming between metal and non-metal atoms that become oppositely charged ions, while covalent bonds form between non-metal atoms that share electrons.
3. Examples of ionic compounds such as sodium chloride and covalent compounds such as methane are given to illustrate the different types of bonds.









![Test Yourself 5.2, Textbook page 114
1. Aluminium atom, Al has 13 protons while fluorine atom, F has 9
protons
2. Muriate of Potash is a type fertiliser that has a high content of
potassium chloride compound. [Proton number : Cl = 17, K = 19]
a) Write the formulae of ions formed from the two atoms respectively.
b) Write half-equation for the formation of ions in (a).
a) Write the chemical formula for potassium chloride.
b) Describe the formation of ionic bonds in potassium chloride compound.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ionicbondcovalentbond-210625143405/85/IONIC-BOND-AND-COVALENT-BOND-18-320.jpg)