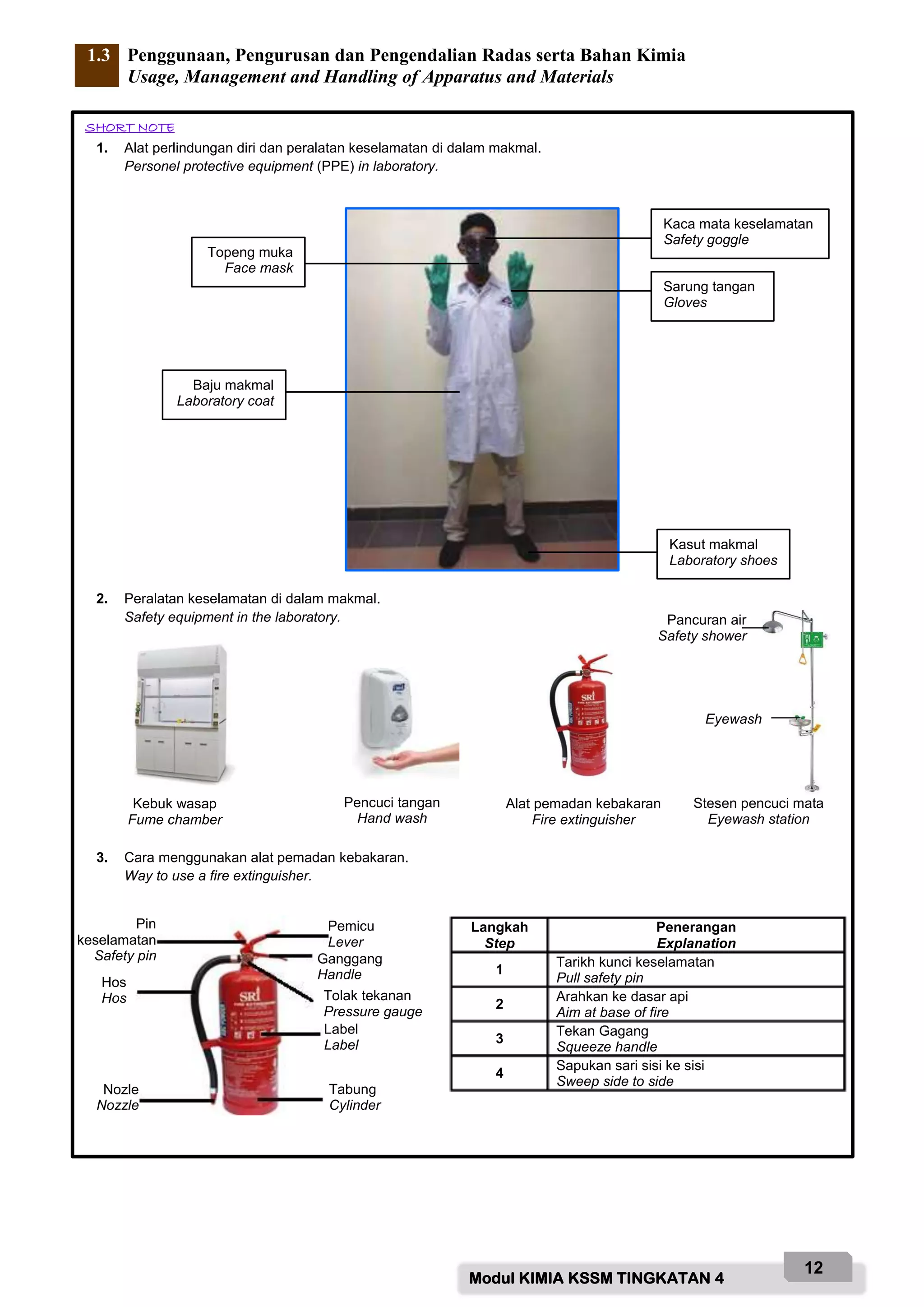
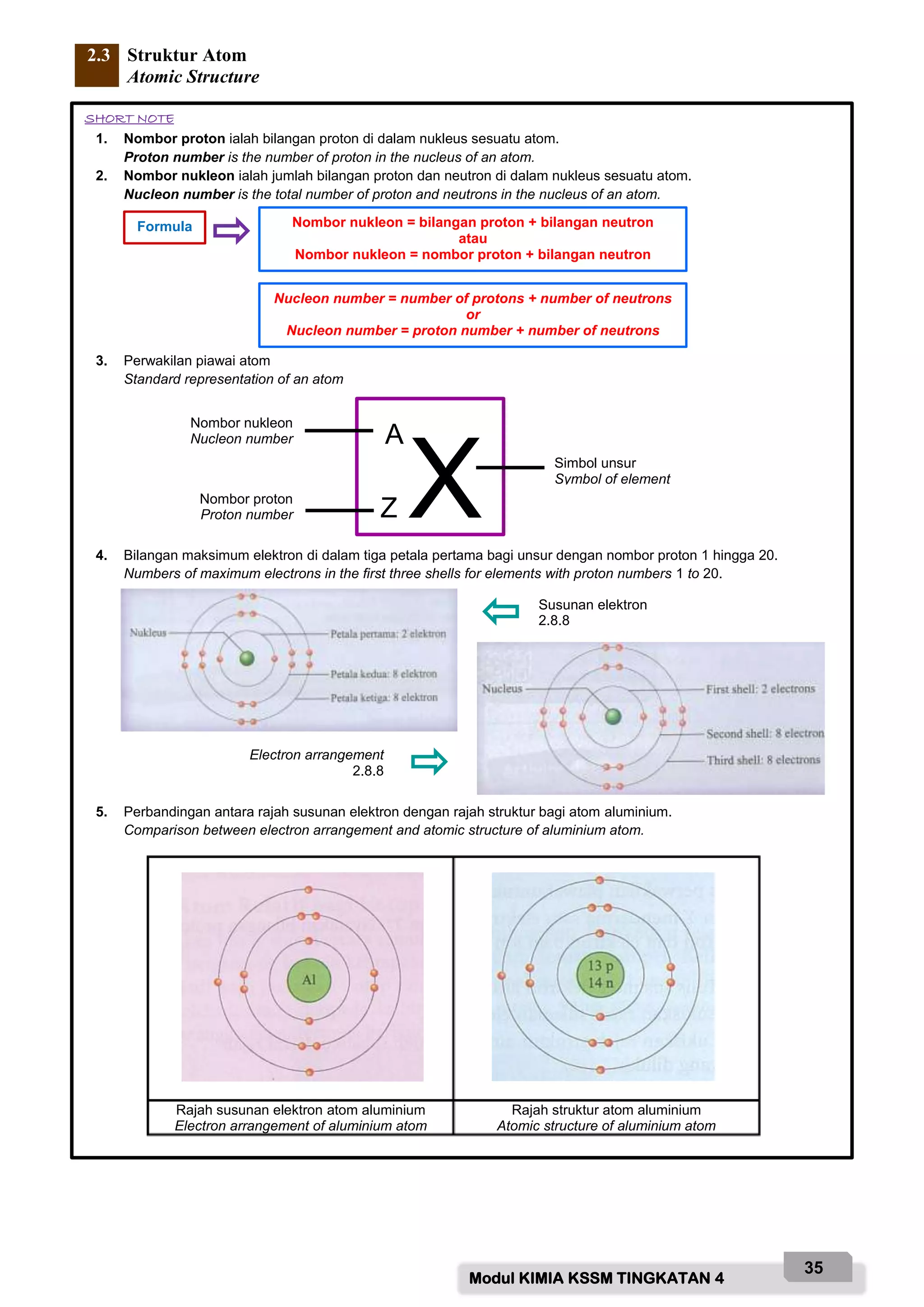
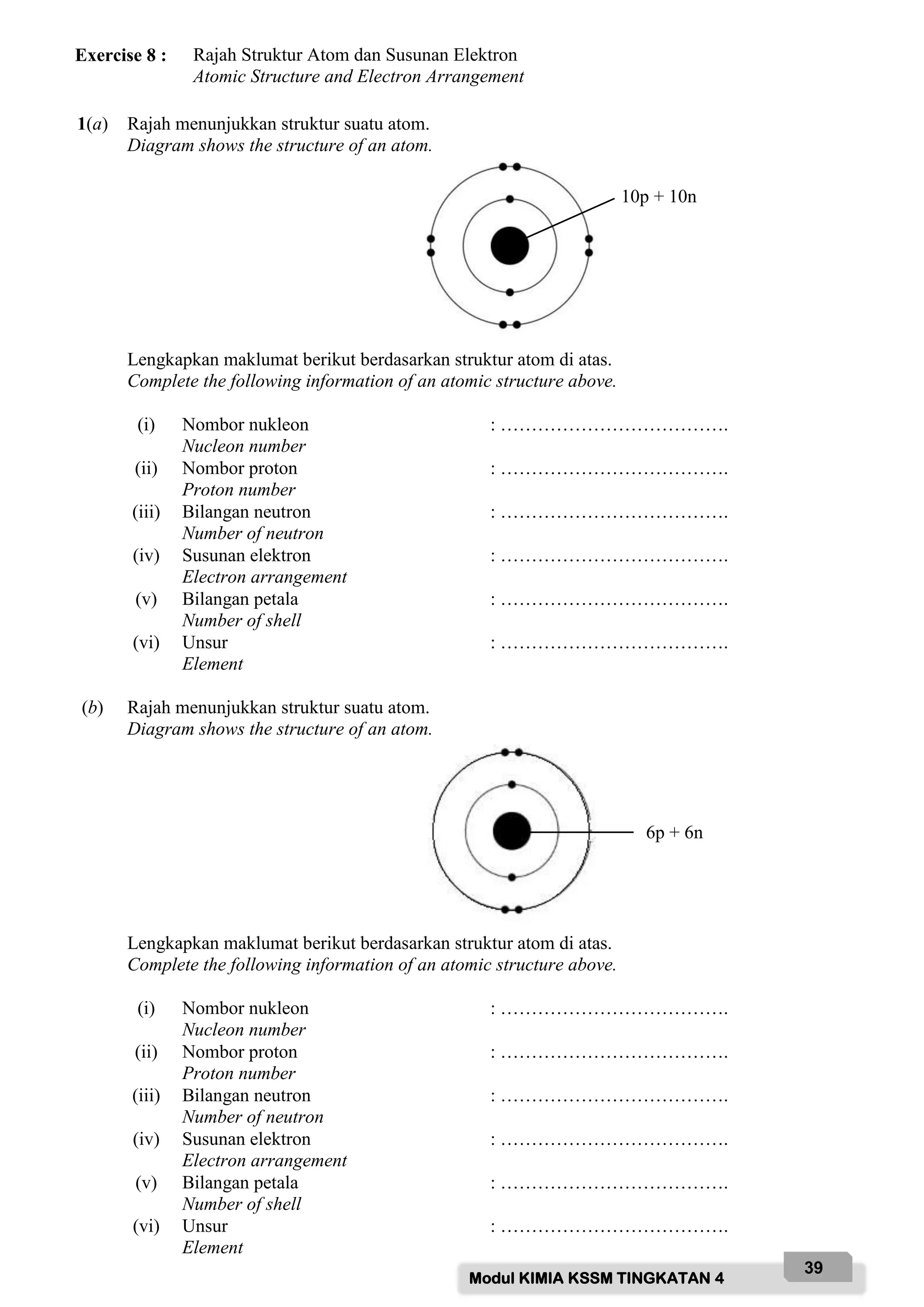
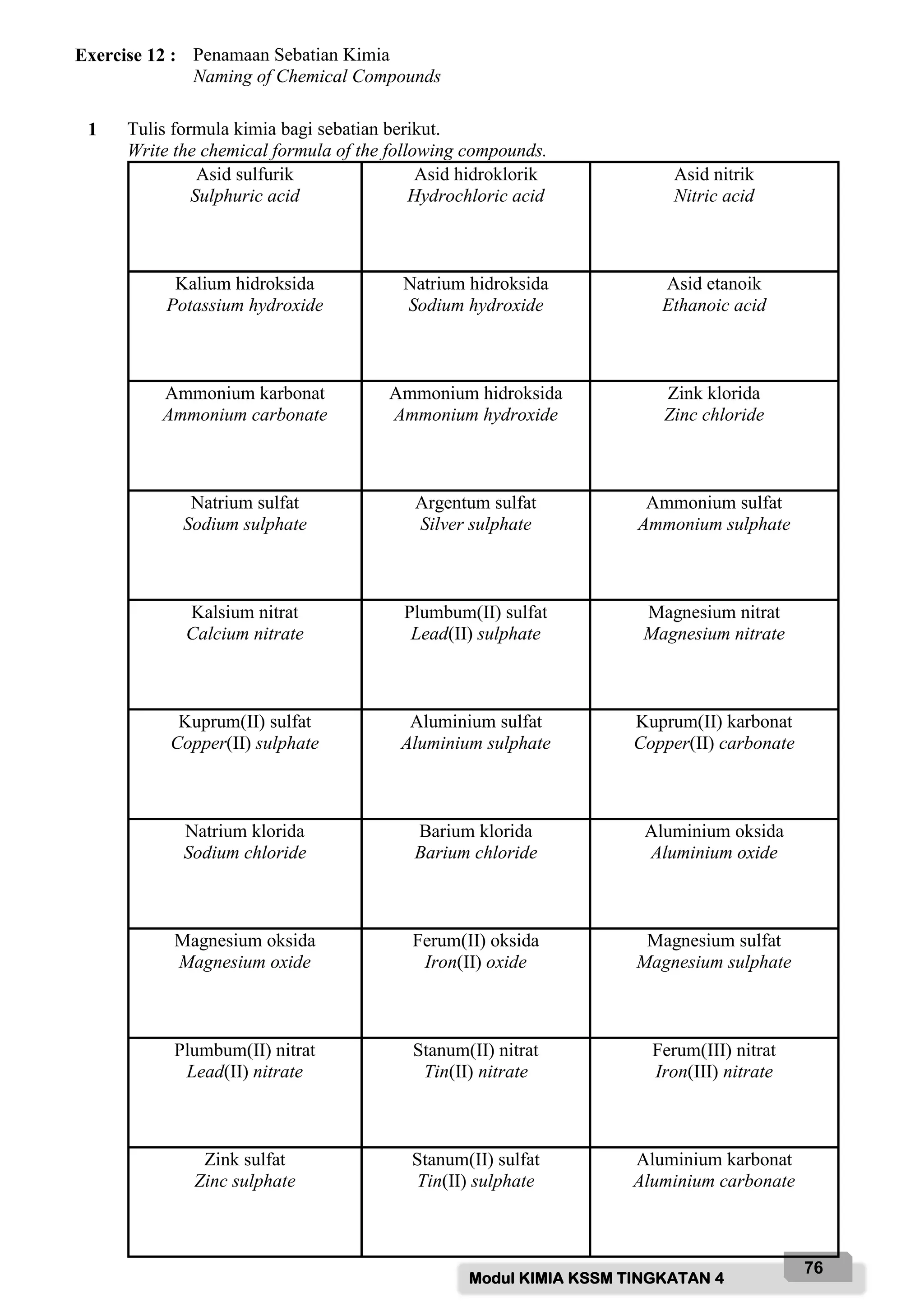
Based on the diagram above, name the labelled parts and state their functions:
A - Safety goggle
Function: To protect eyes from chemical splashes or flying objects.
B - Gloves
Function: To protect hands from chemicals and prevent skin contact with hazardous substances.
C - Laboratory coat
Function: To protect body from chemicals and prevent contamination of clothing.
D - Face mask
Function: To protect face and prevent inhalation of hazardous fumes/vapours.
E - Safety shoes
Function: To protect feet from chemicals, broken glass and prevent slips.
F - Fume chamber
Function: To contain and remove noxious fumes/vap













![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
19
Bahagian A
Section A
1(a) Rajah 1.1 menunjukkan alat pemadam kebakaran.
Diagram 1.1 shows fire extinguisher.
Rajah 1.1
Diagram 1.1
(i) Namakan label P, Q, R dan S dalam Rajah 1.1.
Name the labels P, Q, R and S in Diagram 1.1.
[2 markah]
[2 marks]
(ii) Nyatakan satu fungsi alat pemadam kebakaran.
State one function of fire extinguisher.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..
[1 markah]
[1 mark]
(iii) Nyatakan langkah penggunaan alat pemadam kebakaran ini dengan betul.
State the steps taken to use this fire extinguisher properly.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..
[3 markah]
[3 marks]
Paper 2 Questions
Tolok tekanan
Pressure gauge
Pemicu / Discharge lever
Panggang / Carrying handle
R : ………………………
S : ………………………
Pin keselamatan
Safety pin
P : ………………………
Q : ………………………](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-19-2048.jpg)
![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
20
(b) Rajah 1.2 menunjukkan peralatan keselamatan di dalam makmal.
Diagram 1.2 shows safety equipment in the laboratory.
Rajah 1.2
Diagram 1.2
(i) Namakan peralatan keselamatan itu.
Name the safety equipment.
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..
[1 markah]
[1 mark]
(ii) Nyatakan fungsi bagi peralatan yang dinamakan di 1(b)(i).
State the function of the equipment named in 1(b)(i).
…………………………………………………………………………………………………..
[1 markah]
[1 mark]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-20-2048.jpg)
![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
21
Bahagian B
Section B
1(a) Jadual 1 menunjukkan radas yang digunakan dalam makmal.
Table 1 shows the apparatus used in the laboratory.
Nama radas
Name of apparatus
Radas
Apparatus
A
B
C
D
E
Jadual 1
Table 1
Namakan radas A, B, C, D dan E. Kemudian, nyatakan fungsinya.
Name the apparatus A, B, C, D and E. Then, state its function.
[10 markah]
[10 marks]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-21-2048.jpg)
![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
22
(b) Kebanyakan kerjaya dalam era perkembangan industri yang pesat ini memerlukan pengetahuan
dalam bidang kimia.
Nyatakan dua contoh kerjaya dalam setiap bidang yang berikut.
In the era of rapid industrial development, most careers require knowledge in chemistry.
State two examples of careers in each of the following fields.
Kosmetik
Cosmetics
Farmaseutikal
Pharmaceutical
Bioteknologi
Biotechnology
Nanoteknologi
Nanotechnology
Teknologi hijau
Green technology
[10 markah]
[10 marks]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-22-2048.jpg)
![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
23
Bahagian C
Section C
1(a) Apakah itu kimia?
What is chemistry?
[2 markah]
[2 marks]
(b) Semua bahan yang terdapat di sekeliling kita terdiri daripada bahan kimia. Aktiviti harian
yang kita lakukan turut melibatkan tindak balas kimia.
Nyatakan dua contoh bahan kimia yang lazim digunakan dalam
All substance around us made up of chemicals. The activities that we carry out daily involve
chemical reactions as well.
State two examples of chemicals commonly used in
Makanan
Food
Perubatan
Medicine
Pertanian
Agriculture
Industri
Industry
[8 markah]
[8 marks]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-23-2048.jpg)
![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
24
(c) Rajah 1 menunjukkan graf jisim garam kalium nitrat yang terlarutkan melawan suhu larutan.
Diagram 1 shows a graph of mass of dissolved potassium nitrate salt against solution
temperature.
Rajah 1
Diagram 1
Berdasarkan Rajah 1, huraikan satu eksperimen untuk membuktikan pernyataan graf di atas.
Jawapan anda haruslah mengandungi susunan radas, prosedur, keputusan dan kesimpulan.
Based on Diagram 1, describe an experiment to prove the graph statement above.
Your answer should include apparatus set-up, procedure, result and conclusion.
[10 markah]
[10 marks]
Suhu larutan (o
C)
Solution temperature
Jisim garam kalium nitrat yang terlarutkan (g)
Mass of dissolved potassium nitrate salt
10 20 30 40 50 60 70
0
m5 -
m4 -
m3 -
m2 -
m1 - X
X
X
X
X](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-24-2048.jpg)



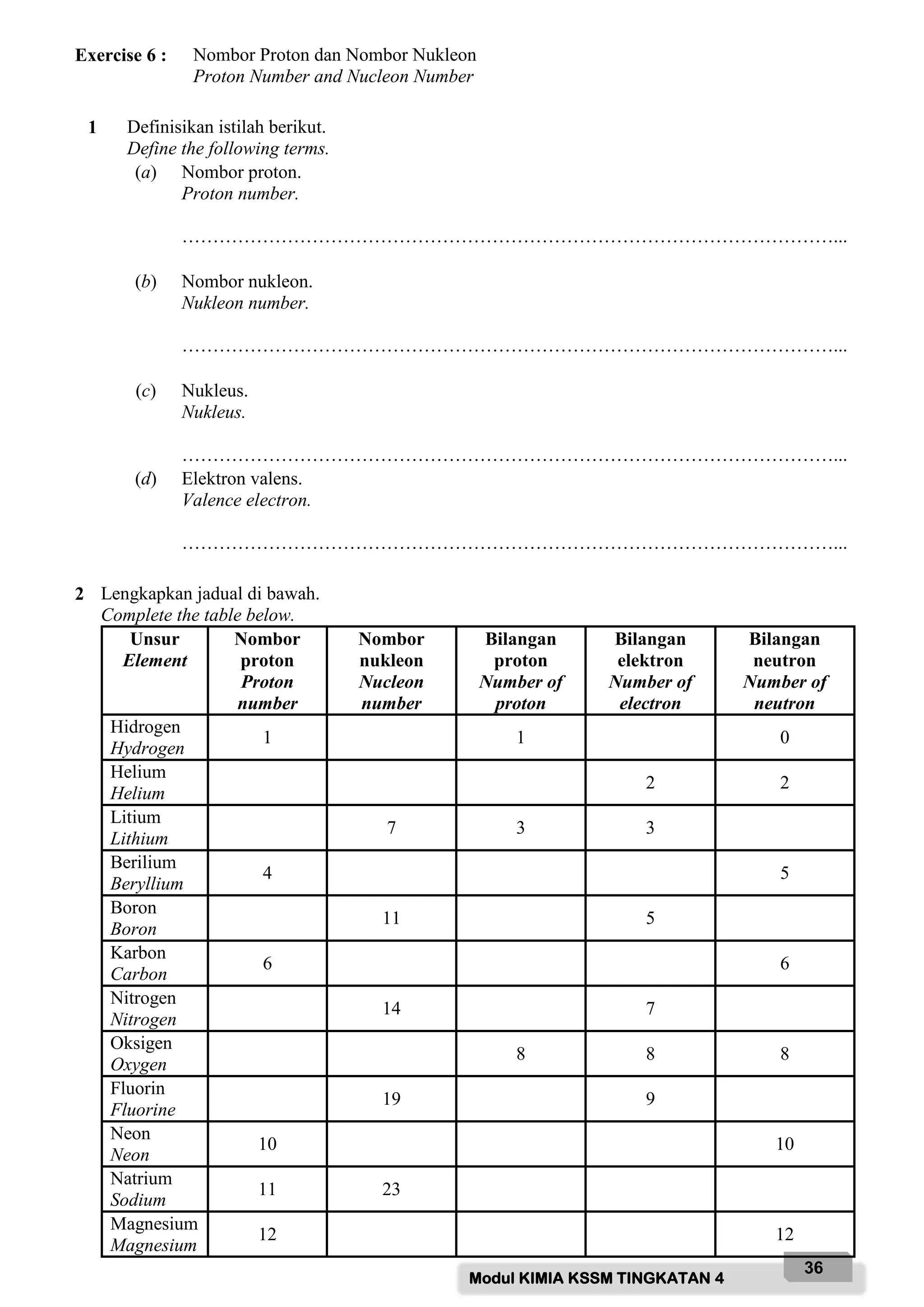
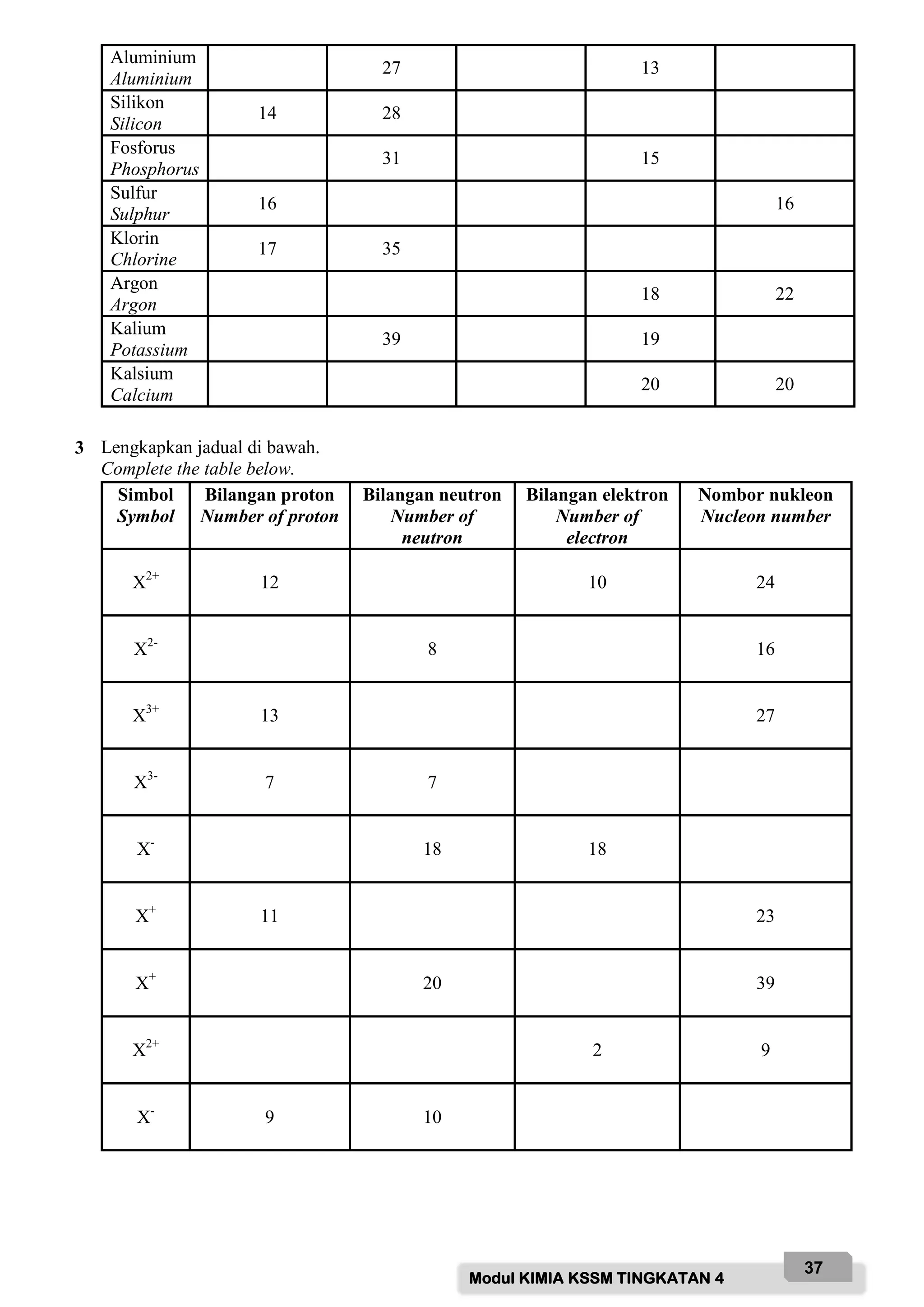
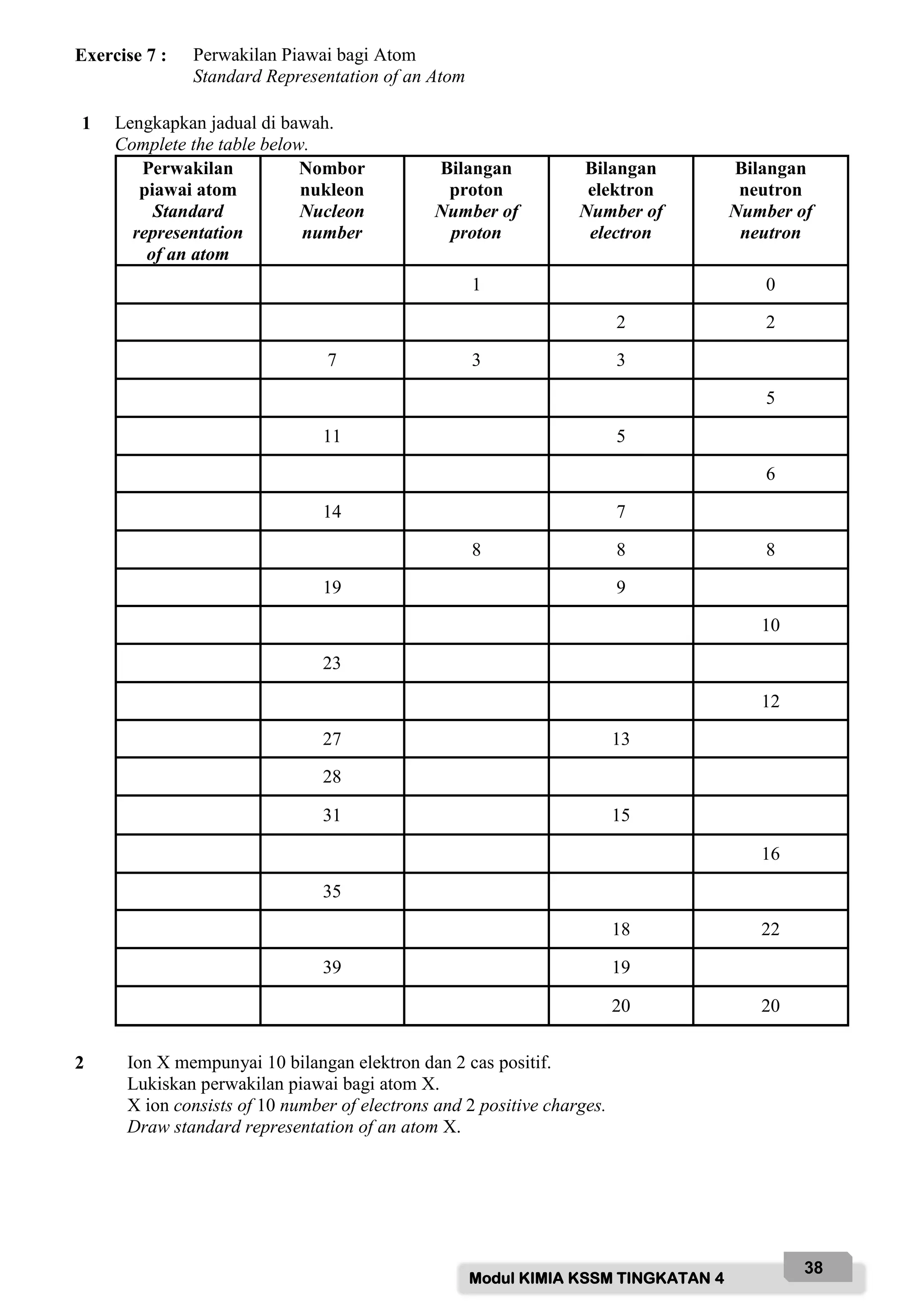


![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
44
Bahagian A
Section A
1(a) Jadual 1 menunjukkan tiga bahan dan formula kimianya.
Table 1 shows three substances and their chemical formulae.
Bahan
Substance
Formula kimia
Chemical formula
Litium
Lithium
Li
Oksigen
Oxygen
O2
Naftalena
Naphthalene
C10H8
Jadual 1
Table 1
Berdasarkan Jadual 1,
Based on Table 1,
(i) Apakah maksud formula kimia?
What is meant by chemical formula?
……………………………………………………………………………………………………...
[1 markah]
[1 mark]
(ii) Nyatakan jenis zarah dalam oksigen.
State the type of particles in oxygen.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………...
[1 markah]
[1 mark]
(iii) Lukis rajah struktur bagi atom litium.
Draw atomic structure of lithium atom.
[1 markah]
[1 mark]
Paper 2 Questions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-44-2048.jpg)
![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
45
(iv) Tuliskan perwakilan piawai bagi unsur litium tersebut.
Write the standard representative for lithium element.
[1 markah]
[1 mark]
(b) Rajah 1 menunjukkan lengkung pemanasan bagi pepejal naftalena.
Diagram 1 shows the heating curve for solid naphthalene.
Rajah 1
Diagram 1
(i) Tentukan takat lebur bagi naftalena.
Determine the melting point of naphthalene.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………...
[1 markah]
[1 mark]
(ii) Terangkan mengapa lengkung graf pada suhu x tidak berubah.
Explain why curve of graph at the temperature of x remains constant.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………...
……………………………………………………………………………………………………...
[2 markah]
[2 marks]
Suhu
Temperature (O
C)
Masa
Time (s)
x](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-45-2048.jpg)
![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
46
(c) Jadual 2 menunjukkan magnesium secara semula jadi wujud dalam tiga isotop.
Table 2 shows magnesium exits naturally as three isotopes.
Unsur
Element
Nombor proton
Proton number
Peratusan (%)
Percentage
24
Mg 12 79.0
25
Mg 12 10.0
26
Mg 12 11.0
Jadual 2
Table 2
(i) Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan isotop bagi atom magnesium?
What is meant by isotope of magnesium atom?
……………………………………………………………………………………………………...
[1 markah]
[1 mark]
(ii) Hitung jisim atom relatif magnesium.
Calculate the relative atomic mass of magnesium.
[3 markah]
[3 marks]
2 Rajah 2 menunjukkan perwakilan piawai bagi dua isotop atom karbon.
Diagram 2 shows the standard representation of two isotopes of carbon atoms.
Rajah 2
Diagram 2
(a) Nyatakan maksud isotop.
State the meaning of isotope.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………...
[1 markah]
[1 mark]
SPM 17’
C C
12
6
14
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-46-2048.jpg)
![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
47
(b) Berdasarkan Rajah 2,
Based on Diagram 2,
(i) Tentukan bilangan elektron dan neutron dalam jadual di bawah.
Determine the number of electrons and neutrons in the table below.
Zarah
Particle
C C
Bilangan elektron
Number of electron
Bilangan neutron
Number of neutron
[2 markah]
[2 marks]
(ii) Nyatakan satu kegunaan C dalam kehidupan seharian.
State one use of C in our daily life.
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
[1 markah]
[1 mark]
(c) P adalah satu bahan yang mempunyai takat lebur 51 o
C dan takat didih 305 o
C.
P is a substance that has a melting point of 51 o
C and a boiling point of 305 o
C.
(i) Lakar graf suhu melawan masa apabila bahan P dipanaskan daripada 30 o
C ke 90 o
C.
Skech a graph of temperature ahainst time when substance P is heated from 30 o
C to 90 o
C.
[2 markah]
[2 marks]
14
6
12
6
14
6
14
6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-47-2048.jpg)
![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
48
(ii) Apabila bahan P disejukkan, suhu berkurangan dan menjadi malar pada satu peringkat dan
kemudian berkurang semula.
When substance P is cooled, the temperature decreases and becomes constant at one stage
and then decreases again.
Ramalkan suhu yang malar itu.
Predict the constant temperature.
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
[1 markah]
[1 mark]
Terangkan mengapa suhu malar pada peringkat itu.
Explain why the temperature is constance at that stage.
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
[2 markah]
[2 marks]
3(a) Jadual 3.1 menunjukkan nombor proton dan nombor nukleon bagi atom P, Q dan R.
Table 3.1 shows the proton number and nucleon number of atoms P, Q and R.
Atom unsur
Atom of element
Nombor proton
Proton number
Nombor nukleon
Nucleon number
P 8 16
Q 9 19
R 8 17
Jadual 3.1
Table 3.1
(i) Pasangan atom manakah merupakan isotop?
Which pair of atoms are isotopes?
………………………………………………………………………………………………
[1 markah]
[1 mark]
(ii) Berikan sebab bagi jawapan anda di 3(a)(i).
Give the reason for your answer in 3(a)(i).
………………………………………………………………………………………………
[1 markah]
[1 mark]
(iii) Lukis gambar rajah susunan elektron bagi atom Q.
Draw the electron arrangement for atom Q.
[1 markah]
[1 mark]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-48-2048.jpg)
![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
49
(b) Bahan X adalah pepejal putih dan penebat elektrik.
Substance X is a white solid and an electrical insulator.
(i) Lukis susunan radas bagi menentukan takat lebur bahan X.
Draw the apparatus set-up used to determine the melting point of substance X.
[2 markah]
[2 marks]
(ii) Nyatakan jenis zarah bahan X.
State the type of particles of substance X.
………………………………………………………………………………………………
[1 markah]
[1 mark]
(iii) Huraikan keadaan bahan X apabila berada pada suhu 40 o
C dan 90 o
C dalam jadual di
bawah.
Describe the state of substance X when it is at 40 o
C and 90 o
C in the table below.
Suhu
Temperature
40 o
C 90 o
C
Susunan zarah
Arrangement of particles
Daya tarikan di antara
zarah
Force of attraction
between particles
[4 markah]
[4 marks]
Bahan X melebur pada 61 o
C dan meruap pada 301 o
C
Substance X melts at 61 o
C and evaporates at 301 o
C](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-49-2048.jpg)
![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
50
Bahagian B
Section B
1(a) Rajah 1.1 menunjukkan dua Model Struktur Atom.
Diagram 1.1 shows the Atomic Structure Model.
Saintis R
Scientist R
Saintis Q
Scientist Q
Rajah 1.1
Diagram 1.1
(i) Kenal pasti saintis R dan saintis Q.
Identify the scientist R and scientist Q.
(ii) Huraikan sejarah perkembangan model struktur atom bagi setiap ahli saintis tersebut.
Describe the history development of the atomic structure model for each of these scientists.
(iii) Berdasarkan sejarah perkembangan model struktur atom, salin dan kenal pasti maklumat
daripada ahli saintis bagi menentukan suatu unsur dalam atom magnesium dan atom oksigen
dalam jadual di bawah.
Based on the history development of the atomic structure models, copy and identify
information from scientists to determine an element in magnesium atom and oxygen atom in
the table below.
Unsur
Element
Maklumat
Information
Mg O
Saintis R
Scientist R
Saintis Q
Scientist Q
[10 markah]
[10 marks]
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
Elektron
Electron
Sfera yang bercas positif
Positively-charged sphere
+
Elektron
Electron
Petala
Shell
Nukleus yang mengandungi proton
Nucleus that contains protons](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-50-2048.jpg)
![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
51
(b) Jadual 1 menunjukkan nombor proton dan nombor nukleon bagi atom P, Q dan R.
Table 1 shows the proton number and nucleon number of atoms P, Q and R.
Atom unsur
Atom of element
Nombor proton
Proton number
Nombor nukleon
Nucleon number
J 8 16
K 11 23
L 19 39
Jadual 1
Table 1
Berdasarkan Jadual 1, kenal pasti atom unsur J, K and L dari segi
Based on Table 1, identify the atoms of the element J, K and L in terms of
(i) Bilangan neutron
Number of neutron
(ii) Bilangan petala
Number of shell
[6 markah]
[6 marks]
(c) Rajah 1.2 menunjukkan lengkung pemanasan bagi pepejal naftalena.
Diagram 1.1 shows the heating curve for solid naphthalene.
Rajah 1
Diagram 1
Huraikan lengkung dari bahagian I dan II, dalam huraian anda sertakan:
Describe the curve from the region of I and II, in your description include:
keadaan jirim
state of matter
pergerakan zarah-zarah
movement of the particles
[4 markah]
[4 marks]
Suhu
Temperature (O
C)
Masa
Time (s)
80
I
II
t1 t2 t3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-51-2048.jpg)
![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
52
Bahagian C
Section C
1 Rajah 1 menunjukkan perbualan antara pelajar dalam satu kumpulan untuk menentukan takat
beku.
Diagram 1 shows the conversation between students in a group to determine freezing point.
Rajah 1
Diagram 1
(a) Kenal pasti bahan X. Jelaskan maksud takat beku.
Identify the substance X. Explain the meaning of freezing point.
[4 markah]
[4 marks]
(b) Lukis graf lengkung bagi menunjukkan takat beku bahan X. Kemudian, terangkan perubahan
keadaan jirim bagi setiap perubahan suhu tersebut. Namakan proses perubahan keadaan jirim
yang terlibat.
Draw a graph of the curve to show the freezing point of substance X. Then, explain the
change in state of matter for each change in temperature. Name the process of change of
state of matter involved.
[6 markah]
[6 marks]
(c) Berdasarkan Rajah 1, huraikan satu eksperimen untuk membuktikan pernyataan daripada
perbualan di atas.
Jawapan anda haruslah mengandungi susunan radas, prosedur, keputusan dan kesimpulan.
Based on Diagram 1, describe an experiment to prove the statement from the above
conversation.
Your answer should include apparatus set-up, procedure, result and conclusion.
[10 markah]
[10 marks]
Apakah bahan X?
What is substance
X?
Bahan X terdiri
daripada molekul.
Substance X consists
of molecule.
Apakah takat beku
bahan X?
What is freezing
point of substance
X?
Takat beku bahan X
adalah 80 o
C.
Freezing point of
substance X is 80 o
C.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-52-2048.jpg)
![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
53
Bab 3
Chapter 3
Konsep Mol, Formula dan Persamaan Kimia
The mole Concept, Chemical Formula and
Equation
3.1 Jisim Atom Relatif dan Jisim Molekul Relatif
Relative Atomic Mass and Relative Molecular Mass
Exercise 1 : Jisim Atom Relatif, JAR
Relative Atomic Mass, RAM
Example : Tentukan jisim atom relatif bagi atom magnesium, Mg.
Determine the relative atomic mass of magnesium atom, Mg.
[JAR / RAM : Mg = 24]
= 24
1 Nyatakan maksud bagi jisim atom relatif.
State the meaning of relative atomic mass.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….
2 Lengkapkan jadual di bawah dengan menentukan jisim relatif bagi semua unsur atom.
Complete the table below with determine the relative atomic mass of all atom elements.
Unsur
Element
JAR
RAM
Unsur
Element
JAR
RAM
Hidrogen / Hydrogen , H Natrium / Sodium , Na
Helium / Helium , He Magnesium / Magnesium , Mg
Litium / Lithium , Li Aluminium / Aluminium , Al
Berilium / Beryllium , Be Silikon / Silicon , Si
Boron / Boron , B Fosforus / Phosphorus , P
Karbon / Carbon , C Sulfur / Sulphur , S
Nitrogen / Nitrogen , N Klorin / Chlorine , Cl
Oksigen / Oxygen , O Argon / Argon , Ar
Fluorin / Fluorine , F Kalium / Potassium , K
Neon / Neon , Ne Kalsium / Calcium , Ca
SHORT NOTE
1. Konsep ‘jisim atom relatif, JAR’ dengan membandingkan jisim atom sesuatu dengan jisim atom unsur lain yang
dipilih sebagai piawai.
The concept of ‘relative atomic mass, RAM’ by comparing the mass of atom of an element to the mass of atom
another element that is chosen as the standard.
2. Karbon-12 dipilih sebagai piawai:
Carbon-12 is chosen as the standard:
mudah dikendalikan memandangkan unsur ini merupakan pepejal pada suhu bilik
it is a solid at room temperature and thus can be handled easily
karbon-12 mudah bergabung dengan unsur-unsur lain
carbon-12 combines easily with other elements
karbon-12 mudah dijumpai dalam kebanyakan bahan
carbon-12 is found in most substances
jisim atom relatif karbon-12 adalah tepat 12.0
the relative atomic mass of carbon-12 exactly 12.0
3. Jisim molekul relatif, JMR sesuatu molekul ialah jisim purata molekul tersebut berbanding dengan
1
12
kali jisim satu
atom karbon-12.
The relative molecular mass, RMM of a molecule is the average mass of the molecule compared to
1
12
of the mass
of one carbon-12 atom.
4. Jisim relatif bahan ion dipanggil jisim formula relatif, JFR.
The relative mass of an ionic substance is called the relative formula mass, RFM.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-53-2048.jpg)
![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
54
3 Berikan tiga sebab mengapa karbon-12 digunakan sebagai piawai untuk menentukan jisim atom
relatif dan jisim molekul relatif.
Give three reasons why carbon-12 is used as a standard to determine the relative atomic mass
and relative molecular mass.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….
4 Jisim suatu atom adalah sangat kecil. Oleh itu, ahli kimia menentukan jisim atom dengan
membandingkan jisim atom tersebut dengan atom yang lain yang dipanggil jisim atom relatif.
Rajah menunjukkan perbandingan jisim antara atom X dengan atom karbon-12.
The mass of an atom is very small. Therefore, a chemist determines the mass of an atom by
comparing the mass of the atom with another atom which is called relative atomic mass. Diagram
shows the comparison of mass between atom X with atom carbon-12.
(a) Kenal pasti atom X.
Identify the atom X.
………………………………………………………………………………………………...
(b) Apakah jisim atom relatif bagi atom X?
What is the relative atomic mass of atom X?
………………………………………………………………………………………………...
(c) Beri alasan anda di 4(b).
Give your reason in 4(b).
………………………………………………………………………………………………...
Exercise 2 : Jisim Molekul Relatif, JMR
Relative Molecular Mass, RMM
Example : Tentukan jisim molekul relatif bagi heksane, C6H14.
Determine the relative molecular mass of Hexane, C6H14.
[JAR / RAM : H = 1, C = 12]
= 6(12) + 14(1)
= 86
1 Nyatakan maksud bagi jisim molekul relatif.
State the meaning of relative molecular mass.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….
C-12
C-12
Atom X
C-12 C-12](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-54-2048.jpg)
![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
55
2 Lengkapkan jadual di bawah dengan menghitung jisim molekul relatif bagi setiap bahan berikut.
Complete the table below with calculate the relative molecular mass of each of the following
substances.
[JAR / RAM : H = 1, C =12, O = 16, S = 32, Cl = 35.5, Ca = 40, Zn = 65, Br = 80]
(a) Glukosa, C6H12O6
Glucose
(b) Gas oksigen, O2
Oxygen gas
(c) Air, H2O
Water
(d) Etanol, C2H5OH
Ethanol
(e) Gas klorin, Cl2
Chlorine gas
(f) Karbon dioksida, CO2
Carbon dioxide
(g) Sulfur dioksida, SO2
Sulphue dioxide
(h) Metana, CH4
Methane
(i) Air bromin, Br2
Bromine water
(j) Kalium karbonat, CaCO3
Calcium carbonate](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-55-2048.jpg)
![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
56
3 Tentukan jisim atom relatif bagi unsur atom X yang berikut.
Determine the relative atomic mass of the following atom element X.
[JAR / RAM : H = 1, C =12, O = 16, N = 14, Na = 23, Cl = 35.5, Ca = 40]
(a) Jisim molekul relatif bagi C3H7XH ialah
60.
The relative molecular mass of C2H5XH
is 60.
(b) Jisim molekul relatif bagi
Na2XO3.10H2O ialah 286.
The relative molecular mass of
Na2XO3.10H2O is 286.
(c) Jisim molekul relatif bagi XCl2.2H2O
ialah 244.
The relative molecular mass of
XCl2.2H2O is 244.
(d) Jisim molekul relatif bagi XO2 ialah 46.
The relative molecular mass of XO2 is
46.
(e) Jisim molekul relatif bagi CaX2.6H2O
ialah 219.
The relative molecular mass of
CaX2.6H2O is 219.
(f) Jisim molekul relatif bagi X10H8 ialah
128.
The relative molecular mass of X10H8 is
128.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-56-2048.jpg)
![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
57
Exercise 3 : Jisim Formula Relatif, JFR.
Relative Formula Mass, RFM
Example : Tentukan jisim formula relatif bagi natrium klorida, NaCl.
Determine the relative formula mass of sodium chloride, NaCl.
[JAR / RAM : Na = 23, Cl = 35.5]
= 23 + 35.5
= 58.5
1 Nyatakan maksud bagi jisim formula relatif.
State the meaning of relative formula mass.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….
2 Lengkapkan jadual di bawah dengan menghitung jisim formula relatif bagi setiap bahan berikut.
Complete the table below with calculate the relative formula mass of each of the following
substances.
[JAR / RAM : H = 1, C =12, N = 14, O = 16, Mg = 24, S = 32, Cl = 35.5, K = 39, Fe = 56, Cu =
64, Zn = 65]
(a) Magnesium sulfat, MgSO4
Magnesium sulphate
(b) Magnesium nitrat, Mg(NO3)2
Magnesium nitrate
(c) Zink klorida, ZnCl2
Zinc chloride
(d) Zink sulfat, ZnSO4
Zinc sulphate
(e) Ammonium karbonat, (NH4)2CO3
Ammonium carbonate
(f) Kalium karbonat, K2CO3
Potassium carbonate
(g) Ferum(II) sulfat, FeSO4
Iron(II) sulphate
(h) Kuprum(II) nitrat, Cu(NO3)2
Copper(II) nitrate](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-57-2048.jpg)
![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
58
3 Tentukan jisim atom relatif bagi unsur atom X yang berikut.
Determine the relative atomic mass of the following atom element X.
[JAR / RAM : C =12, O = 16, N = 14, Al = 27, S = 32, Cl = 35.5, Zn = 65]
(a) Jisim formula relatif bagi X2(SO4)3 ialah
342.
The relative formula mass of X2(SO4)3
is 342.
(b) Jisim formula relatif bagi ZnX2 ialah
136.
The relative formula mass of ZnX2 is
136.
(c) Jisim formula relatif bagi X(NO3)2 ialah
188.
The relative formula mass of X(NO3)2
is 188.
(d) Jisim formula relatif bagi Al(XO3)3
ialah 213.
The relative formula mass of Al(XO3)3
is 213.
(e) Jisim formula relatif bagi X2SO4 ialah
98.
The relative formula mass of X2SO4 is
98.
(f) Jisim formula relatif bagi X2CO3 ialah
106.
The relative formula mass of X2CO3 is
106.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-58-2048.jpg)
![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
60
1 Nyatakan unit SI untuk kuantiti sesuatu bahan.
State the SI unit of amount of substance.
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….
2 Lengkapkan jadual di bawah dengan menghitung bilangan molekul dan bilangan atom bagi setiap
bahan berikut.
Complete the table below with calculate number of molecules and number of atoms of each of the
following substances.
[Pemalar Avogadro / Avogadro constant, NA = 6.02 x 1023
mol-1
]
(a) Sebuah balang gas berisi 2 mol gas
nitrogen, N2.
A gas jar is filled with 2 mol of nitrogen
gas, N2.
(b) Sebuah belon berisi 1.5 mol gas
ammonia, NH3.
A balloon is filled with 1.5 mol
ammonia gas, NH3.
(c) Satu sampel mengandungi 0.2 mol gas
etena, C2H4.
A sample contains 0.2 mol of ethene
gas, C2H4.
(d) Sebuah belon berisi 1.2 mol gas
hidrogen, H2.
A balloon is filled with 1.2 mol
hydrogen gas, H2.
(e) Sebuah balang gas berisi 0.8 mol gas
oksigen, O2.
A gas jar is filled with 0.8 mol of oxygen
gas, O2.
(f) Satu sampel mengandungi 0.5 mol gas
helium, He.
A sample contains 0.5 mol of helium
gas, He.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-60-2048.jpg)
![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
61
3 Lengkapkan jadual di bawah dengan menghitung bilangan mol dan bilangan unit formula bagi
setiap bahan berikut.
Complete the table below with calculate number of mol and number of formula units of each of
the following substances.
[Pemalar Avogadro / Avogadro constant, NA = 6.02 x 1023
mol-1
]
(a) Satu sampel natrium klorida, NaCl
mengandungi 3.612 x 1023
atom.
A sample of sodium chloride, NaCl
contains 3.612 x 1023
atoms.
(b) Sebuah belon berisi gas oksigen, O2
mengandungi 2.408 x 1024
atom.
A balloon is filled with oxygen gas, O2
contains 2.408 x 1024
atoms.
(c) Satu sampel karbon dioksida, CO2
mengandungi 1.0836 x 1025
atom CO2.
A sample of carbon dioxide, CO2
contains 1.0836 x 1025
CO2 atoms.
(d) Sebuah belon berisi gas nitrogen, N2
mengandungi 6.02 x 1025
atom.
A balloon is filled with nitrogen gas, N2
contains 6.02 x 1025
atoms.
(e) Satu sampel magnesium oksida, MgO
mengandungi 8.428 x 1023
atom.
A sample of magnesium oxide, MgO
contains 8.428 x 1023
atoms.
(f) Satu sampel kuprum, Cu mengandungi
6.02 x 1024
atom.
A sample of copper, Cu contains 6.02 x
1024
atoms.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-61-2048.jpg)
![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
62
Exercise 5 : Bilangan Mol dan Jisim Bahan
Number of Moles and Mass of Substances
Example 1 : Berapakah jisim bagi 1.5 mol magnesium, Mg?
What is the mass of 1.5 mol of magnesium, Mg?
[JAR / RAM : Mg = 24]
= 1.5 mol x 24 g mol-1
= 36 g
Example 2 : Berapakah bilangan mol molekul yang terdapat di dalam 44.8 g sulfur dioksida, SO2?
How many moles of molecules are found in 44.8 g of sulphur dioxide gas, SO2?
[JAR / RAM : O = 16, S = 32]
JMR/RMM = 32 + (16)
= 64 g mol-1
=
44 8 g
64 g
= 0.7 mol
1 Apakah jisim molar?
What is molar mass?
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….
2 Lengkapkan jadual di bawah dengan menghitung jisim bagi setiap bahan berikut.
Complete the table below with calculate the mass of each of the following substances.
[JAR / RAM : H = 1, C = 12, N = 14, O = 16, S = 32, Fe = 56]
(a) 0.4 mol serbuk besi, Fe.
0.4 mol of iron fillings, Fe.
(b) 2.2 mol karbon monoksida, CO.
2.2 mol of carbon monoxide, CO.
Bilangan mol, n =
Jisi (g)
Jisi ar (g )
Number of moles, n =
𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠 (𝑔)
𝑀𝑜𝑙𝑎𝑟 𝑚𝑎𝑠𝑠 (𝑔 𝑚𝑜𝑙 )
Bilangan mol
Number of moles
Jisim (g)
Mass (g)
x Jisim molar
Molar mass
÷ Jisim molar
Molar mass
Hubung kait antara bilangan mol dan jisim
bahan:
The relationship between the number of mole
and the number of substances mass:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-62-2048.jpg)
![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
63
(c) Satu eksperimen memerlukan 0.05 mol
hablur ammonium sulfat, (NH4)2SO4.
An experiment requires 0.05 mol of
ammonium sulphate crystals,
(NH4)2SO4.
(d) Satu eksperimen memerlukan 0.08 mol
hablur ammonium nitrat, NH4NO3.
An experiment requires 0.08 mol of
ammonium nitrate crystals, NH4NO3.
3 Lengkapkan jadual di bawah dengan menghitung bilangan mol bagi setiap bahan berikut.
Complete the table below with calculate the number of each of the following substances.
[JAR / RAM : H = 1, O = 16, Na = 23, P = 31, S = 32, I = 127, Pb = 207]
(a) 29.4 g asid sulfurik, H2SO4.
29.4 g of sulphuric acid, H2SO4.
(b) 4.61 g plumbum(II) iodida, PbI2.
4.61 g of lead(II) iodide, PbI2.
(c) 7.84 g asid fosfat, H3PO4.
7.84 g of phosphoric acid, H3PO4.
(d) 28.6 g natrium karbonat terhidrat,
Na2CO3.10H2O.
28.6 g of sodium carbonate
decahydrate, Na2CO3.10H2O.
4 Lengkapkan jadual di bawah dengan menghitung jisim molekul relatif bagi setiap bahan berikut.
Complete the table below with calculate the relative molecular mass of the following substances.
(a) 0.9 mol gas X berjisim 3.6 g.
0.9 mol of gas X has the mass of 3.6 g.
(b) 0.3 mol bahan X berjisim 18.9 g.
0.3 mol of substance X has the mass of
18.9 g.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-63-2048.jpg)
![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
64
Exercise 6 : Bilangan Mol dan Isi Padu Gas
Number of Moles and Volume of Gases
Example 1 : Hitungkan isi padu 1.2 mol gas neon, Ne dalam dm3
pada STP?
Calculate the volume of 1.2 mol of neon gas, Ne in dm3
at STP?
[Isi padu molar / Molar volume = 22.4 dm3
mol-1
pada/at STP]
= 1.2 mol x 22.4 dm3
mol-1
= 26.88 dm3
Example 2 : Berapakah isi padu 0.03 mol gas hidrogen, H2 dalam cm3
pada keadaan bilik?
What is the volume of 0.03 mol of hydrogen gas, H2 in cm3
at room conditions?
[Isi padu molar = 24 dm3
mol-1
pada keadaan bilik]
[Molar volume = 24 dm3
mol-1
at room conditions]
= 0.03 mol x 24 dm3
mol-1
= 0.72 dm3
= 0.72 x 1000 cm3
= 720 cm3
1 Apakah isi padu molar?
What is molar volume?
……………………………………………………………………………………………………….
2 Lengkapkan jadual di bawah dengan menghitung isi padu gas dalam cm3
pada STP bagi setiap
gas berikut.
Complete the table below with calculate the volume of gases in cm3
at STP of each of the
following gases.
[Isi padu molar = 22.4 dm3
mol-1
pada STP]
[Molar volume = 22.4 dm3
mol-1
at STP]
(a) 0.5 mol gas klorin, Cl2.
0.5 mol of chlorine gas, Cl2.
(b) 1 mol karbon dioksida, CO2.
1 mol of carbon dioxide, CO2.
Bilangan mol, n =
Isi padu gas
Isi padu ar
Number of moles, n =
𝑉𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑚𝑒 𝑜𝑓 𝑔𝑎𝑠
𝑀𝑜𝑙𝑎𝑟 𝑣𝑜𝑙𝑢𝑚𝑒
Bilangan mol
Number of moles
Isi padu gas
Volume of gas
x Isi padu molar
Molar volume
÷ Isi padu molar
Molar volume
Hubung kait antara bilangan mol dan isi
padu gas:
The relationship between the number of mole
and the volume of gas:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-64-2048.jpg)
![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
65
(c) 3 mol gas ammonia, NH3.
3 mol of ammonia gas, NH3.
(d) 0.3 mol gas oksigen, O2.
0.3 mol of oxygen gas, O2.
.
3 Lengkapkan jadual di bawah dengan menghitung isi padu gas dalam cm3
pada keadaan bilik bagi
setiap gas berikut.
Complete the table below with calculate the volume of gases in cm3
at room conditions of each of
the following gases.
[Isi padu molar = 24 dm3
mol-1
pada keadaan bilik]
[Molar volume = 24 dm3
mol-1
at room conditions]
(a) 1 mol gas klorin, Cl2.
1 mol of chlorine gas, Cl2.
(b) 0.01 mol karbon dioksida, CO2.
0.01 mol of carbon dioxide, CO2.
(c) 0.08 mol gas ammonia, NH3.
0.08 mol of ammonia gas, NH3.
(d) 0.5 mol gas oksigen, O2.
0.5 mol of oxygen gas, O2.
.
(e) 0.7 mol gas hidrogen, H2.
0.7 mol of hydrogen gas, H2.
(f) 2 mol gas karbon monoksida, CO.
2 mol of carbon monoxide gas, CO.
.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-65-2048.jpg)
![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
67
(b) Hitungkan,
Calculate,
[Pemalar Avogadro / Avogadro constant, NA = 6.02 x 1023
mol-1
]
(i) Bilangan mol
Number of mole
(ii) Bilangan atom
Number of atom
(iii) Isi padu gas X dalam cm3
Gas volume X in cm3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-67-2048.jpg)
![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
69
3 Lengkapkan jadual di bawah dengan formula molekul dan formula empirik beberapa bahan.
Complete the table below with molecular formula and empirical formula of several substances.
Bahan
Substance
Formula molekul
Molecular formula
Formula empirik
Empirical formula
Air
Water
Ammonia
Ammonia
Hidrazin
Hydrazine
Propena
Propene
Benzena
Benzene
Asid sulfurik
Sulphuric acid
Heksena
Hexene
Exercise 9 : Penentuan Formula Empirik
Determination of an Empirical Formula
Example 1 : 1.35 g aluminium berpadu dengan 1.2 g oksigen untuk menghasilkan aluminium
oksida.
Apakah formula empirik aluminium oksida?
1.35 g of aluminium combines with 1.2 g of oxygen to form aluminium oxide.
What is the empirical formula of aluminium oxide?
Unsur
Element
Al O
Jisim
Mass (g)
1.35 1.2
Bilangan mol atom
Number of moles of atoms
1 35
27
= 0.05
1 2
16
= 0.075
Nisbah mol atom
Mole ratio
5
5
= 1
75
5
= 1.5
Nisbah mol atom paling
ringkas
Simplest mole ratio of
atom
2 3
[JAR / RAM : O = 16, Al = 27]
2 mol atom aluminium berpadu dengan 3 mol atom oksigen.
Jadi, formula empirik aluminium oksida ialah Al2O3.
2 mol of aluminium atoms combine with 3 mol of oxygen atoms.
Thus, the empirical formula of aluminium oxide is Al2O3.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-69-2048.jpg)
![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
70
1 Satu sampel kalium bromida mengandungi 6.24 g kalium dan 12.8 g bromin.
Apakah formula empirik kalium bromida?
A sample of potassium bromine contains 6.24 g of potassium and 12.8 g of bromine.
What is the empirical formula of potassium bromine?
[JAR / RAM : K = 39, Br = 80]
2 Satu sampel 26.1 g stanum klorida didapati mengandungi 11.9 g stanum.
Nyatakan formula empirical stanum klorida itu.
A sample of 26.1 g of tin chloride contains 11.9 g of tin.
State the empirical formula if the tin chloride.
[JAR / RAM : Cl = 35.5, Sn = 119]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-70-2048.jpg)
![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
71
3 0.03 mol unsur Y berpadu dengan 7.62 g iodin untuk menghasilkan garam iodida.
Nyatakan formula empirik bagi garam iodida itu.
0.03 mol of element Y combines with 7.62 g of iodine to produce an iodide salt.
State the empirical formula of the iodide salt.
[JAR / RAM : I = 127]
4 Seorang ahli kimia menganalisis sebatian yang memberikan bau kepada buah pisang yang
masak ranum. Dia mendapati sebatian ini mengandungi 64.62 % karbon, 10.77 % hidrogen dan
24.61 % oksigen. Apakah formula empirik sebatian tersebut?
A chemist analysed the compound that gives smell to fully ripe bananas. He found that the
compound contains 64.62 % carbon, 10.77 % hydrogen and 24.61 % oxygen. What is the
empirical formula of that compound?
[JAR / RAM : H = 1, C = 12, O = 16]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-71-2048.jpg)
![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
72
Exercise 10 : Penentuan Formula Molekul
Determination of a Molecular Formula
Example 1 : Satu sebatian mempunyai formula empirik CH2. Jisim molekul relatifnya ialah 56.
Apakah formula molekul sebatian itu?
A compound has the empirical formula CH2. Its relative molecular mass is 56.
What is the molecular formula of the compound?
[JAR / RAM : H = 1, C = 12]
JRM sebatian
RMM of compound = n[12 + 2(1)]
Diberikan JRM sebatian 14n = 56
Given the RMM of compound
n =
56
14
= 4
Maka, formula molekul sebatian ialah C4H8.
Hence, the molecular formula of the compound is C4H8.
1 Asid etanoik mempunyai jisim molar 60 g mol-1
. Jika formula empiriknya ialah CH2O, tentukan
formula molekul asid etanoik.
Etahnoic acid has a molar mass of 60 g mol-1
. If its empirical formula is CH2O, determine the
molecular formula of ethanoic acid.
[JAR / RAM : H = 1, C = 12, O = 16]
2 Hidrokarbon terdiri daripada karbon dan hidrogen. 5.7 g satu hidrokarbon mengandungi 4.8 g
karbon. Jika jisim molekul relatif hidrokarbon itu ialah 114, tentukan formula molekulnya.
Hydrocarbons consist of carbon and hydrogen. 5.7 g of hydrocarbon contains 4.8 g of carbon. If
the relative molecular mass of the hydrocarbon is 114, determine its molecular formula.
[JAR / RAM : H = 1, C = 12]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-72-2048.jpg)
![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
73
3 Berapakah jisim zink yang diperlukan untuk berpadu dengan 0.5 mol klorin bagi menghasilkan
zink klorida, ZnCl2?
What is the mass of zinc required to combine with 0.5 mol of chloride to produce zinc chloride,
ZnCl2?
[JAR / RAM : Zn = 65]
4 Andaikan anda ialah seorang peladang. Anda ingin memilih baja dengan kandungan nitrogen
yang tinggi untuk tanaman anda. Berikut ialah tiga jenis baja yang lazim digunakan.
Assume you are a farmer. You want to choose a fertiliser with a high nitrogen content for your
plants. Three types of commonly used fertilisers are as follows.
Baja
Fertiliser
Formula kimia
Chemical formula
Ammonium nitrat
Ammonium nitrate
NH4NO3
Urea
Urea
CO(NH2)2
Nitrosol
Nitrosol
Ca(NO3)2
Baja yang manakah anda akan pilih? Berikan alasan bagi pilihan anda. Tunjukkan jalan kerja
penghitungan yang dibuat.
Which fertiliser would you choose? Give reasons for your choice. Show the steps used in the
calculation.
[JAR / RAM : H = 1, C = 12, O = 16, N = 14]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-73-2048.jpg)
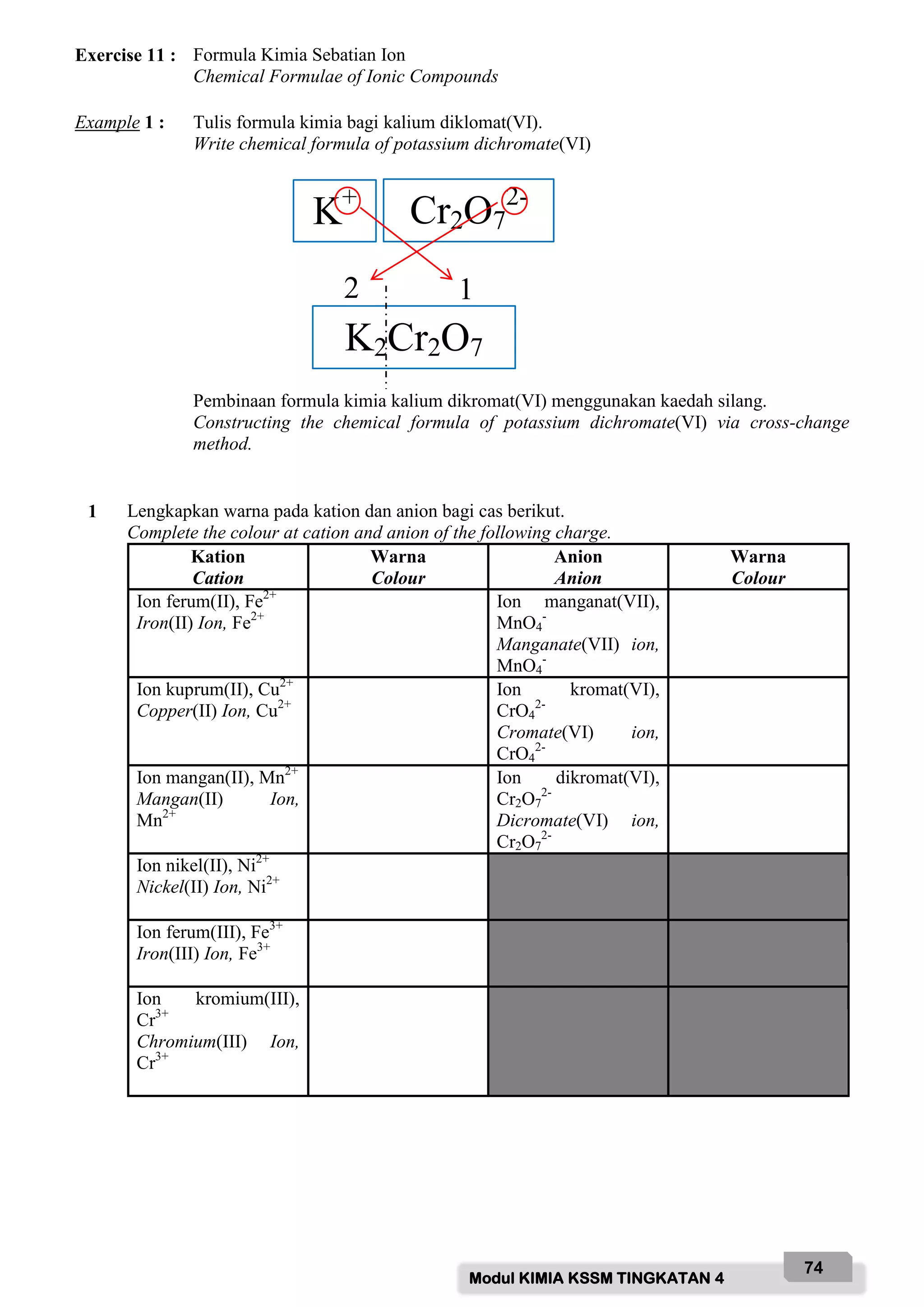
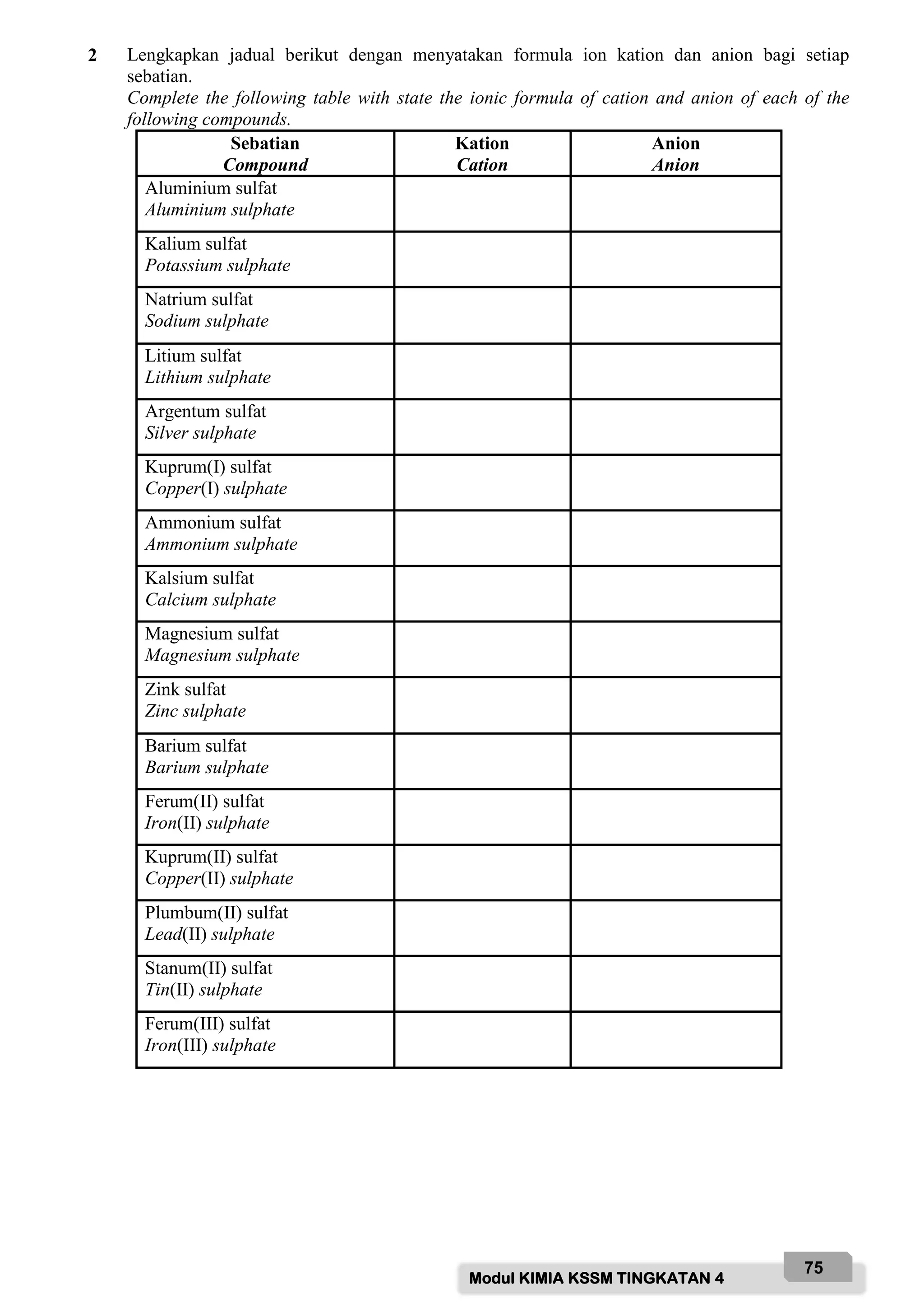
![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
78
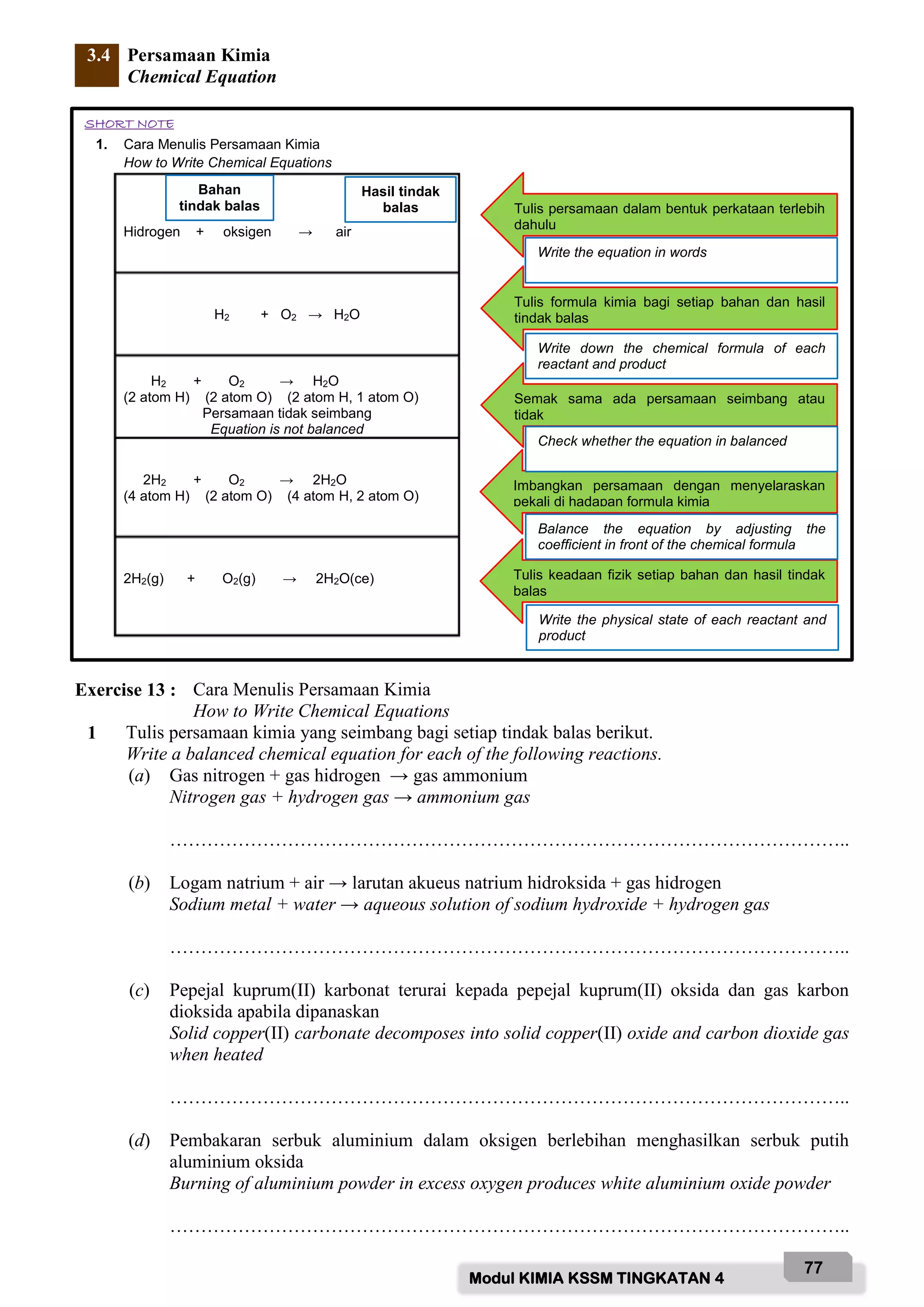
2 Imbangkan persamaan kimia berikut.
Balance the following chemical equations.
(a) KI(ak) + Br2(ak) → I2(p) + KBr(ak)
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(b) Zn(p) + AgNO3(ak) → Zn(NO3)2(ak) + Ag(p)
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(c) C3H8(g) + O2(g) → CO2(g) + H2O(ce)
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
(d) AgNO3(p) → Ag(p) + NO2(g) + O2(g)
………………………………………………………………………………………………..
Exercise 14 : Menggunakan Persamaan Kimia
Using Chemical Equations
Example 1 : Etanol terbakar dalam udara yang berlebihan seperti berikut.
Ethanol burnt in excess oxygen as follows.
C2H5OH + 3O2 → 2CO2 + 3H2O
Berapakah isi padu gas pada keadaan bilik yang dibebaskan jika 4.6 g etanol dibakar
lengkap dalam udara?
What is the volume of gas released at room conditions if 4.6 g of ethanol burnt
completely un air?
[JMR / RAM : H = 1, C = 12, O = 16]
[Isi padu molar = 24 dm3
mol-1
pada keadaan bilik]
[Molar volume = 24 dm3
mol-1
at room conditions]
Bilangan mol di dalam etanol 4.6 g etanol
Number of moles in 4.6 g of ethanol
=
ass (g)
ar ass (g )
=
4 6 g
46 g
= 0.1 mol
1 mol C2H5OH : 2 mole CO2
0.1 mol C2H5OH : 0.2 mole CO2
Isi padu gas karbon dioksida, CO2
= Bilangan mol X Isi padu molar
= 0.2 mol x 24 dm3
= 2.4 dm3
1 mole of C2H5OH : 2 moles of CO2
0.1 mole of C2H5OH : 0.2 moles of CO2
The volume of karbon dioxide, CO2
= Number of moles X Molar volume
= 0.2 mol x 24 dm3
= 2.4 dm3
∆](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-78-2048.jpg)
![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
79
1 Selesaikan masalah numerikal stoikiometri berikut.
Solve numerical the following stroichiometry problems.
(a) Penguraian kalsium karbonat oleh haba menghasilkan kalsium oksida dan karbon
dioksida. Berapakah jisim kalsium karbonat yang diperlukan untuk menghasilkan 1.2
dm3
gas karbon dioksida pada keadaan bilik?
Decomposition of calcium carbonate by heating to produce calcium oxide and carbon
dioxide. What is the mass of calcium carbonate required to produce 1.2 dm3
of carbon
dioxide gas at room conditions?
[JMR / RAM : C = 12, O = 16, Ca = 40]
[Isi padu molar = 24 dm3
mol-1
pada keadaan bilik]
[Molar volume = 24 dm3
mol-1
at room conditions]
(b) Satu sampel ferum(III) oksida dipanaskan dalam aliran gas hidrogen berlebihan untuk
menghasilkan 5.6 g logam besi.
Hitungkan jisim sampel ferum(II) oksida itu.
A sample of iron(III) oxide is heated in stream of excess hydrogen gas to produce 5.6 g
of iron metal.
Calculate the mass of the iron(III) oxide sample.
[JMR / RAM : O = 16, Fe = 56]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-79-2048.jpg)
![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
81
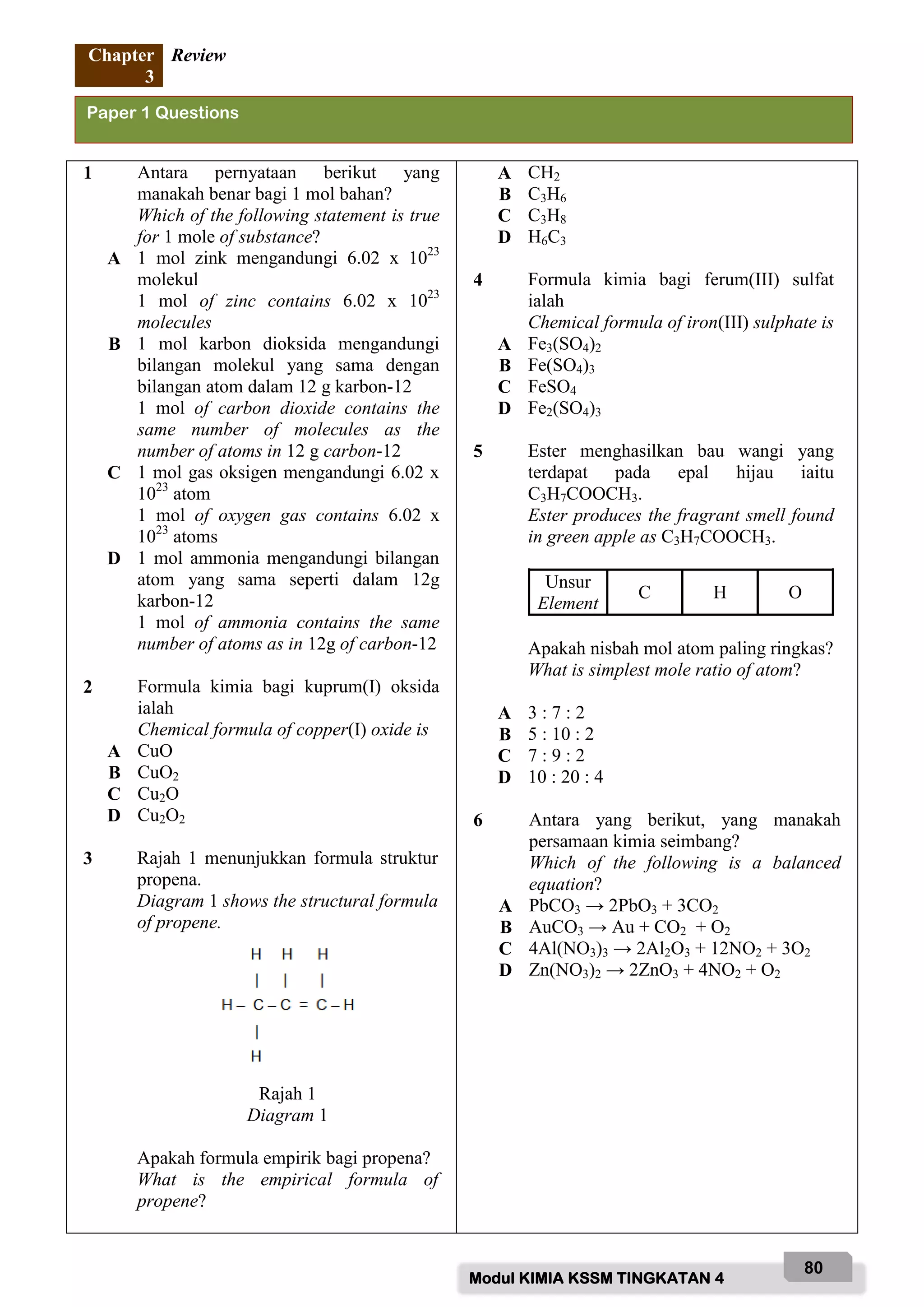
Soalan 7 hingga 10 berdasarkan Rajah 2.
Questions 7 to 10 are based on Diagram 2.
Rajah 2 menunjukkan peratusan mengikut jisim bagi unsur dalam alisin iaitu sebatian yang
menyebabkan bau pada bawang putih.
Diagram 2 shows the percentage by mass of elements in the allicin, which is a compound that
causes the smell in garlic.
Rajah 2
Diagram 2
7 Apakah maksud dengan formula
empirik?
What is meant by an empirical
formula?
A Perwakilan sesuatu bahan kimia dengan
menggunakan huruf bagi mewakili
atom dan nombor subskrip untuk
menunjukkan bilangan setiap jenis
yang terdapat di dalam entiti asas bahan
itu
A representation of a chemical
substance using alphabets to represent
the atoms and subscript numbers to
show the number of each type of atoms
founds in the elementary entities of the
substance
B Perwakilan sesuatu bahan kimia dengan
menggunakan huruf bagi mewakili
atom dan nombor subskrip untuk
menunjukkan bilangan ringkas setiap
jenis yang terdapat di dalam entiti asas
bahan itu
A representation of a chemical
substance using alphabets to represent
the atoms and subscript numbers to
show the simplest number of each type
of atoms founds in the elementary
entities of the substance
C Formula kimia yang menunjukkan
bilangan sebenar atom setiap jenis
unsur yang terdapat di dalam satu
molekul sesuatu sebatian
The chemical formula that shows the
actual number of atoms of each element
found in a molecule of a compound
D Formula kimia yang menunjukkan
nisbah paling ringkas bagi bilangan
atom setiap jenis unsur dalam sesuatu
sebatian
The chemical formula that shows the
simplest ratio of the number of atoms of
each element in a compound
9 Apakah formula empirik bagi alisin?
What is the empirical formula of
allicin?
[JMR / RAM : H = 1, O = 16, S = 32]
A C6H10S2O
B C6H12S4O
C C12H5S2O
D C12H10S4O
8 Apakah jisim atom relatif bagi X jika
3.7 mol dalam unsur X?
What is the relative atomic mass of X if
3.7 moles in element of X?
A 9
B 12
C 24
D 32
10 Apakah yang mungkin bagi unsur X?
What is the possible of element of X?
A Karbon
Carbon
B Nitrogen
Nitrogen
C Magnesium
Magnesium
D Litium
Lithium
Alisin
Allicin
X = 44.4%
H = 6.21%
S = 39.5%
O = 9.86%
Bawang putih
Garlic](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-81-2048.jpg)
![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
82
Bahagian A
Section A
1 Tumbuhan hijau menjalankan fotosintesis untuk menghasilkan glukosa. Formula molekul bagi
glukosa adalah C6H12O6.
Green plant undergoes photosynthesis to produce glucose. The molecular formula of glucose is
C6H12O6.
(a)(i) Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan formula molekul?
What is the meaning of molecular formula?
……………………………………………………………………………………………...
[1 markah]
[1 mark]
(ii) Tulis formula empirik bagi glukosa, C6H12O6.
Write the empirical formula for glucose, C6H12O6.
……………………………………………………………………………………………...
[1 markah]
[1 mark]
(iii) Persamaan kimia bagi fotosintesis adalah seperti di bawah.
The chemical equation for photosynthesis is as below.
6CO2 + 6H2O C6H12O6 + 6O2
Berikan tiga maklumat yang dapat ditaksir daripada persamaan kimia itu.
Give three information that can be interpreted from the chemical equation.
……………………………………………………………………………………………...
……………………………………………………………………………………………...
……………………………………………………………………………………………...
[2 markah]
[2 marks]
Paper 2 Questions
SPM 16’](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-82-2048.jpg)
![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
83
(b) Paku besi yang terdedah kepada udara dan air menghasilkan karat, ferum(III) oksida
terhidrat, Fe2O3.H2O. persamaan kimia untuk tindak balas itu adalah seperti berikut :
An iron nail that is exposed to air and water to form rust, hydrated iron(II) oxide,
Fe2O3.H2O. Chemical equation for the reaction is as follow:
xFe + yO2 + zH2O 2Fe2O3.H2O
(i) Seimbangkan persamaan kimia untuk tindak balas itu dengan menentukan nilai x, y dan
z.
Balanced the chemical equation for the reaction by determine the value of x, y and z.
x : …………….. y : …………….. z : ……………..
[3 markah]
[3 marks]
(ii) Nyatakan bilangan mol ferum yang diperlukan untuk menghasilkan 1 mol ferum(III)
oksida terhidrat.
State the number of moles of iron that is required to produced 1 mole of hydrated
iron(III) oxide.
……………………………………………………………………………………………...
[1 markah]
[1 mark]
(iii) Hitung jisim formula relatif bagi ferum(III) oksida terhidrat.
Calculate the relative formula mass of hydrates iron(III) oxide.
[Jisim atom relatif / Relative atomic mass : H = 1, O = 16, Fe = 56]
[1 markah]
[1 mark]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-83-2048.jpg)
![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
84
2 Jadual 1 menunjukkan empat bahan dengan formula kimia dan jisim molarnya.
Table 1 shows four substances with their chemical formula and molar mass.
Bahan
Substances
Formula Kimia
Chemical formula
Gas Nitrogen
Oxygen gas
N2
Kalsium klorida terhidrat
Hydrated calsium chloride
CaCl2.6H2O
Kuprum(II) karbonat
Copper(II) carbonate
CuCO3
Asid sulfurik
Sulphuric acid
H2SO4
Jadual 1
Table 1
(a)(i) Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan jisim atom relatif?
What meant by relative atomic mass?
……………………………………………………………………………………………...
[1 markah]
[1 mark]
(ii) Apakah yang dimaksudkan dengan jisim molekul relatif?
What meant by relative molecular mass?
……………………………………………………………………………………………...
[1 markah]
[1 mark]
(b) Apakah jenis zarah yang terdapat dalam
What type of particle is found in
gas nitrogen : ……………………………………
nitrogen gas
asid sulfurik : ……………………………………
sulphuric acid
[2 markah]
[2 marks]
(c) Hitung,
Calculate,
[Jisim atom relatif : Cu = 64, O =16, C = 12, Ca = 40, Cl = 35.5]
[Relative atomic mass : Cu = 64, O = 16 , C = 12, Ca = 40, Cl = 35.5]
(i) jisim molar kalsium klorida terhidrat.
the molar mass for hydrated calsium chloride.
[1 markah]
[1 mark]
(ii) jisim molar kuprum(II) karbonat.
the molar mass for copper(II) carbonate.
[1 markah]
[1 mark]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-84-2048.jpg)
![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
85
3 Satu eksperimen untuk menentukan formula empirik bagi magnesium oksida telah dijalankan
dengan jayanya oleh sekumpulan murid.
An experiment to determine the empirical formula of magnesium oxide was successfully done by
a group of students.
(a) Lukis dan labelkan susunan radas yang telah digunakan oleh murid tersebut untuk
menjalankan eksperimen di atas.
Draw and label the set-up of apparatus used by the students to carry out this experiment.
[2 markah]
[2 marks]
(b) Jadual 2 menunjukkan keputusan eksperimen ini.
Table 2 shows the results of this experiment.
Penerangan
Description
Jisim (g)
Mass (g)
Jisim mangkuk pijar + tudung
Mass of the crucible + lid
23.00
Jisim mangkuk pijar + tudung + pita magnesium
Mass of the crucible + lid + magnesium ribbon
23.30
Jisim mangkuk pijar + tudung + magnesium
oksida
Mass of the crucible + lid + magnesium oxide
23.50
Jadual 2
Table 2
(i) Pita magnesium dibersihkan dengan kertas sebelum dipanaskan. Terangkan mengapa.
The magnesium ribbon is cleaned with sandpaper before heating. Explain why.
……………………………………………………………………………………………...
[1 markah]
[1 mark]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-85-2048.jpg)
![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
86
(ii) Berdasarkan jadual di atas,
Based on the table above,
Hitung jisim bagi:
Calculate the mass of:
Magnesium
Magnesium : ……………………..
Oksigen
Oxygen : ……………………..
[2 markah]
[2 marks]
(iii) Hitungkan nisbah mol bagi atom magnesium kepada atom oksigen.
[Jisim atom relatif : O = 16, Mg = 24]
Calculate the ratio of moles of magnesium atoms to oxygen atoms.
[Relative atomic mass : O = 16, Mg = 24]
[2 markah]
[2 marks]
(iv) Tentukan formula empirik bagi magnesium oksida.
Determine the empirical formula of magnesium oxide.
……………………………………………………………………………………………...
[1 markah]
[1 mark]
(v) Tuliskan persamaan kimia bagi tindak balas tersebut.
Write the chemical equation of the reaction.
……………………………………………………………………………………………...
[1 markah]
[1 mark]
(vi) Ramalkan sama ada boleh atau tidak formula empirik bagi plumbum(II) oksida
ditentukan dengan kaedah yang sama dalam eksperimen ini? Terangkan mengapa.
Predict whether the empirical formula of lead(II) oxide can be determined by this
experiment? Explain why.
……………………………………………………………………………………………...
……………………………………………………………………………………………...
[2 markah]
[2 marks]
(c) Logam W adalah kurang reaktif berbanding hidrogen terhadap oksigen. Bagaimana
hendak memastikan bahawa tindak balas telah selesai.
Metal W is less reactive than hydrogen towards oxygen.
How to determine that the reaction is completed.
……………………………………………………………………………………………...
[1 markah]
[1 mark]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-86-2048.jpg)
![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
87
Bahagian B
Section B
1(a) Rajah 1.1 menunjukkan formula struktur nikotin.
Diagram 1.1 shows the structural formula of nicotine.
Rajah 1.1
Diagram 1.1
Nyatakan formula empirik dan formula molekul bagi nikotin.
Bandingkan dan bezakan formula empirik dan formula molekul bagi nikotin.
State the empirical formula and molecular formula of nicotine.
Compare and contrast the empirical formula and molecular formula of nicotine.
[6 markah]
[6 marks]
(b) Rajah 1.2 menunjukkan susunan radas untuk menentukan formula empirik bagi satu oksida
logam Y. Y kurang reaktif berbanding hidrogen.
Diagram 1.2 shows the apparatus set-up to determine the empirical formula for an oxide of
metal Y. Y is less reactive than hydrogen.
Rajah 1.2
Diagram 1.2
Gas hidrogen
Hydrogen gas
Oksida logam Y
Oxide of metal Y
Perahu porselin
Porcelain boat
Panaskan
Heat](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-87-2048.jpg)
![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
88
Maklumat di bawah menunjukkan keputusan bagi eksperimen tersebut.
Information below show the results of the experiment.
Penerangan
Description
Jisim (g)
Mass (g)
Tiub pembakaran + perahu porselin
Combustion tube + porcelain boat
52.34
Tiub pembakaran + perahu porselin + oksida Y
Combustion tube + porcelain boat + oxide of Y
105.86
Tiub pembakaran + perahu porselin + Y
Combustion tube + porcelain boat + Y
102.02
Tentukan formula empirik oksida Y.
Determine the empirical formula of the oxide of Y.
[Jisim atom relatif : O = 16, Y = 107]
[Relative atomic mass : O = 16, Y = 107]
[4 markah]
[4 marks]
(c) Hidrogen ialah sebatian organik yang mengandungi hanya karbon dan hidrogen. Maklumat
berikut ialah tentang satu daripada hidrokarbon.
Hydrocarbon is an organic compound that contain only carbon and hydrogen. The information
below is regarding one hydrocarbon.
(i) Berdasarkan maklumat di atas, hitung formula molekul bagi hidrokarbon tersebut.
Based on the information above, calculate the molecular formula of the hydrocarbon.
[5 markah]
[5 marks]
(ii) 4.6 g logam natrium dibakar dalam gas oksigen berlebihan menghasilkan natrium klorida.
Tulis persamaan kimia bagi tindak balas ini.
Hitungkan jisim natrium oksida yang dihasilkan.
[Jisim atom relatif : O = 16, Na = 23]
4.6 g of sodium metal is burnt excess oxygen gas to produce sodium oxide. Write the
chemical equation of this reaction.
Calculate the mass of sodium oxide produced.
[Relative atomic mass : O = 16, Na = 23]
[5 markah]
[5 marks]
Karbon 85.7 %
carbon 85.7 %
hidrogen 14.3 %
hydrogen 14.3 %
jisim molekul relatif = 42
molecular mass = 42
[Jisim atom relatif : H = 1, C = 12]
[Relative atomic mass : H = 1, C = 12]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-88-2048.jpg)

![Modul KIMIA KSSM TINGKATAN 4
90
(a)(i) Berdasarkan perbuatan di atas, tentukan formula empirik bagi oksida X.
Based on conversation above, determine the empirical formula of oxide of X.
[Jisim atom relatif : O = 16, X = 24]
[Relative atomic mass : O = 16, X = 24]
[3 markah]
[3 marks]
(ii) Tulis persamaan kimia yang terlibat. Kemudian, berikan tiga maklumat yang dapat
ditaksir daripada persamaan kimia itu.
Write the chemical equation involved. Give three information that can be interpreted
from the chemical equation.
[5 markah]
[5 marks]
(b) Terangkan kaedah yang digunakan. Kemudian, cadangkan serbuk X.
Explain the method used in this experiment. Then, suggest the powder X.
[2 markah]
[2 marks]
(c) Dengan menggunakan contoh serbuk X, huraikan satu eksperimen untuk membuktikan
pernyataan di atas.
Jawapan anda haruslah mengandungi prosedur, keputusan dan kesimpulan.
By using one example of powder X, describe an experiment to prove the statement
above.
Your answer should include procedure, result and conclusion.
[10 markah]
[10 marks]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/modulkimiapro-xkssm2022f4-220315212933/75/Modul-kimia-pro-x-kssm-2022-FORM-4-90-2048.jpg)
