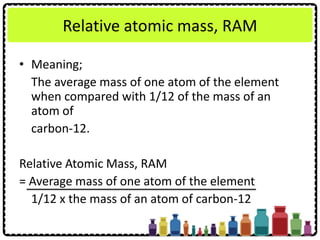
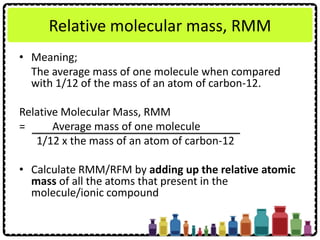
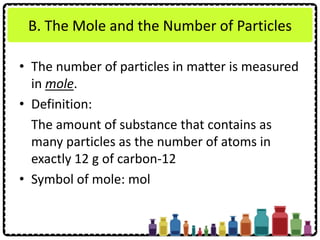
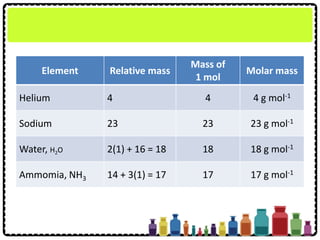
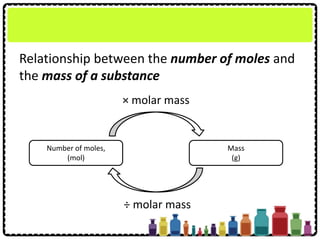
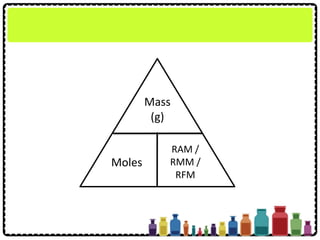
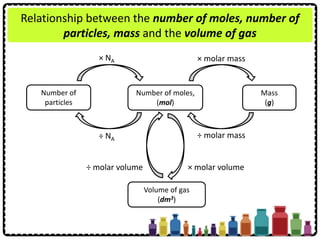
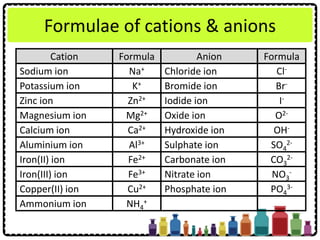
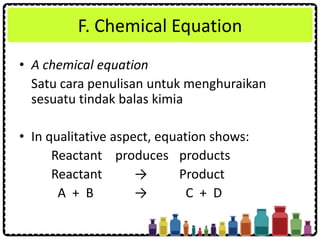
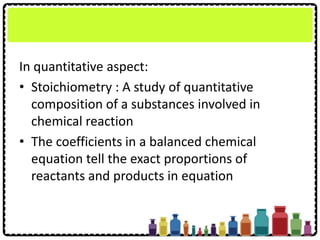
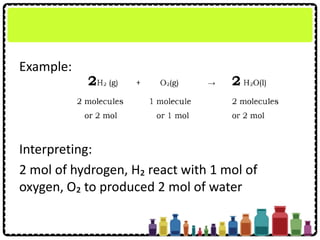
This document discusses chemical formulae and equations. It defines relative atomic mass and relative molecular mass, which are used to calculate the mass of elements and compounds from their chemical formulae. The mole concept is introduced, relating the Avogadro constant to the number of particles in a given number of moles. Relationships are shown between moles, mass, particles and volume. Empirical and molecular formulae are distinguished. Ionic compounds have formulae showing cation and anion combinations. Examples of writing and balancing chemical equations are provided.




![Example 1:
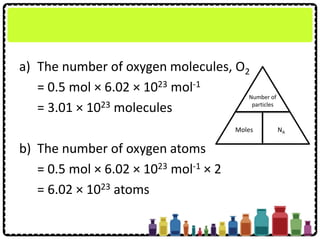
A closed glass bottle contains 0.5 mol of oxygen
gas, O2
(a) How many oxygen molecules, O2 are there in
the bottle?
(b)How many oxygen atoms are there in the
bottle?
[Avogadro constant: 6.02 × 1023 mol-1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter3chemicalformulaeandequations-150319100642-conversion-gate01/85/Chapter-3-Chemical-Formulae-and-Equations-12-320.jpg)
![Example 2:
Find the number of moles of 9.03 × 1023 molecules
in a sample containing molecules of carbon dioxide,
CO2
[Avogadro constant: 6.02 × 1023 mol-1]
The number of moles carbon dioxide
= 9.03 × 1023
6.02 × 1023 mol-1
= 1.5 mol
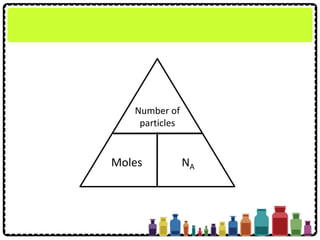
Number of
particles
Moles NA](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter3chemicalformulaeandequations-150319100642-conversion-gate01/85/Chapter-3-Chemical-Formulae-and-Equations-14-320.jpg)

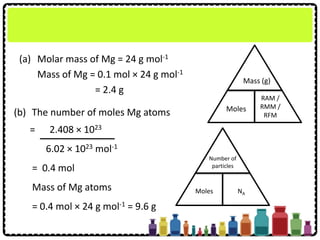
![Example 1:
What is the mass of
(a) 0.1 mol of magnesium?
(b)2.408 × 1023 atoms of magnesium?
[Relative atomic mass: Mg=24; Avogadro
constant: 6.02 × 1023 mol-1]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter3chemicalformulaeandequations-150319100642-conversion-gate01/85/Chapter-3-Chemical-Formulae-and-Equations-19-320.jpg)
![Example 2:
RMM of SO2
= 32 + 2(16) = 64
Molar mass of SO2 = 64 g mol-1
The number of moles
= 16 g
64 g mol-1
= 0.25 mol
Mass (g)
Moles
RAM /
RMM /
RFM
How many moles of molecules are there in 16 g of sulphur
dioxide gas, SO2?
[Relative atomic mass: O=16, S=32]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter3chemicalformulaeandequations-150319100642-conversion-gate01/85/Chapter-3-Chemical-Formulae-and-Equations-21-320.jpg)

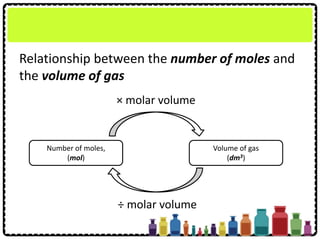
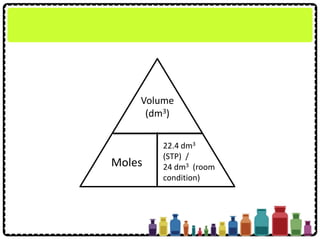
![What is the volume of 1.2 mol of ammonia gas,
NH3 at STP?
[Molar volume: 22.4 dm3 mol-1 at STP]
Example 1:
Volume
(dm3)
Moles
22.4 dm3
(STP) /
24 dm3 (RC)
The volume of ammonia gas, NH3
= 1.2 mol × 22.4 dm3 mol-1
= 26.88 dm3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter3chemicalformulaeandequations-150319100642-conversion-gate01/85/Chapter-3-Chemical-Formulae-and-Equations-25-320.jpg)
![How many moles of ammonia gas, NH3 are present
in 600 cm3 of the gas measured at room conditions?
[Molar volume: 24 dm3 mol-1 at room condition]
Example 2:
Volume
(dm3)
Moles
22.4 dm3
(STP) /
24 dm3 (RC)
The number of moles of ammonia gas, NH3
= 600 cm3
1000
= 0.6 dm3
= 0.6 dm3
24 dm3 mol-1
= 0.025 mol](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter3chemicalformulaeandequations-150319100642-conversion-gate01/85/Chapter-3-Chemical-Formulae-and-Equations-26-320.jpg)
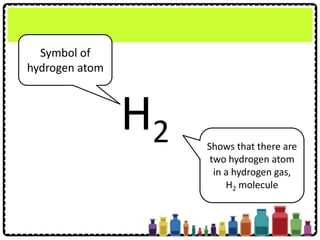
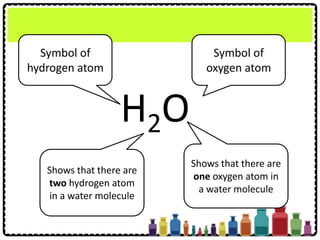
![Example
A sample of aluminium oxide contains 1.08 g of
aluminium and 0.96 g of oxygen. What is the
empirical formula of this compound?
[Relative atomic mass: O = 16; Al = 27]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter3chemicalformulaeandequations-150319100642-conversion-gate01/85/Chapter-3-Chemical-Formulae-and-Equations-33-320.jpg)
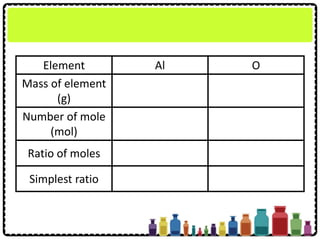

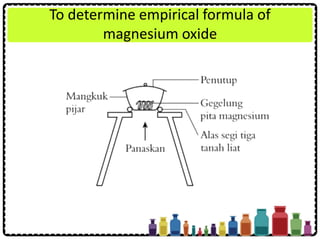
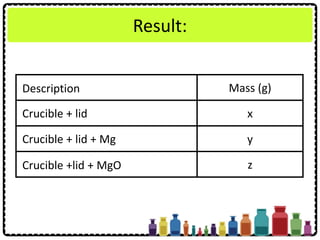
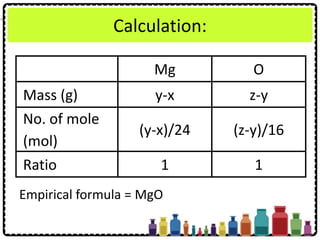
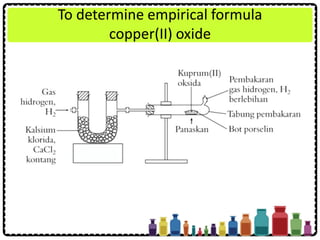
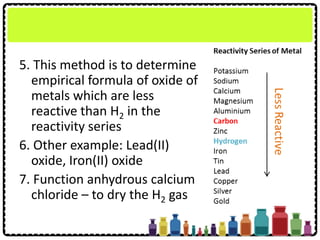
![Experiment question:
Describe how you can carry out an experiment
to determine the empirical formula of
magnesium oxide. Your description should
include
• Procedure of experiment
• Tabulation of result
• Calculation of the results obtained
[Relative atomic mass: O = 16; Mg = 24]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter3chemicalformulaeandequations-150319100642-conversion-gate01/85/Chapter-3-Chemical-Formulae-and-Equations-37-320.jpg)


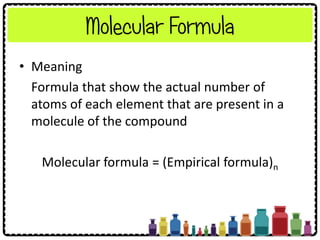
![Example:
(CH3)n = 30
n [12 + 3(1) ] = 30
15n = 30
n = 30/15
= 2
Molecular formula = (CH3)2
= C2H6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter3chemicalformulaeandequations-150319100642-conversion-gate01/85/Chapter-3-Chemical-Formulae-and-Equations-45-320.jpg)

![Numerical Problems Involving
Chemical Equations
Copper(II) oxide, CuO reacts with aluminium
according to the following equations.
3CuO + 2Al → Al2O3 + 3Cu
Calculate the mass of aluminium required to react
completely with 12 g of copper(II) oxide, CuO
[Relative atomic mass: O, 16; Al, 27; Cu, 64]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/chapter3chemicalformulaeandequations-150319100642-conversion-gate01/85/Chapter-3-Chemical-Formulae-and-Equations-52-320.jpg)