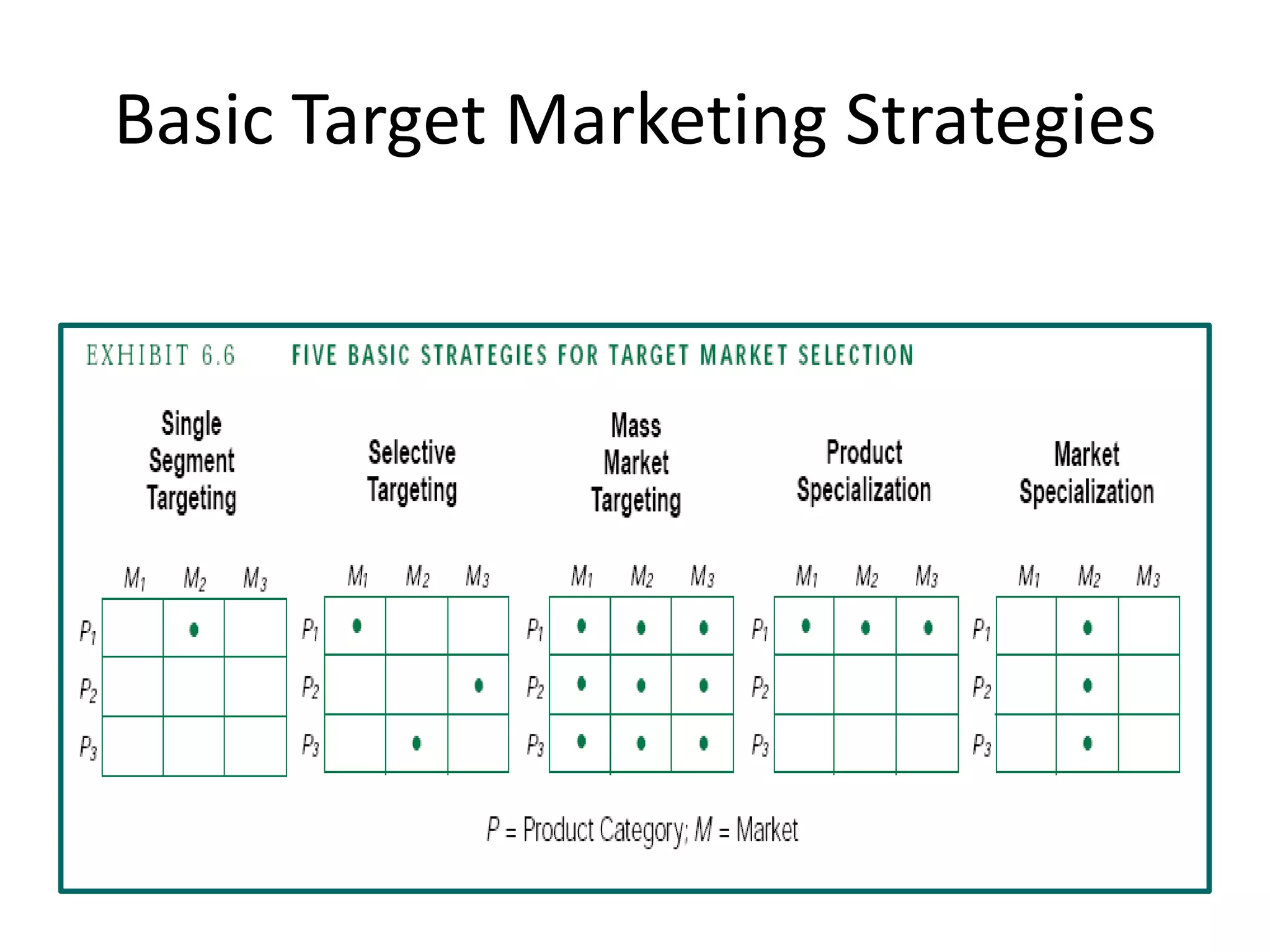
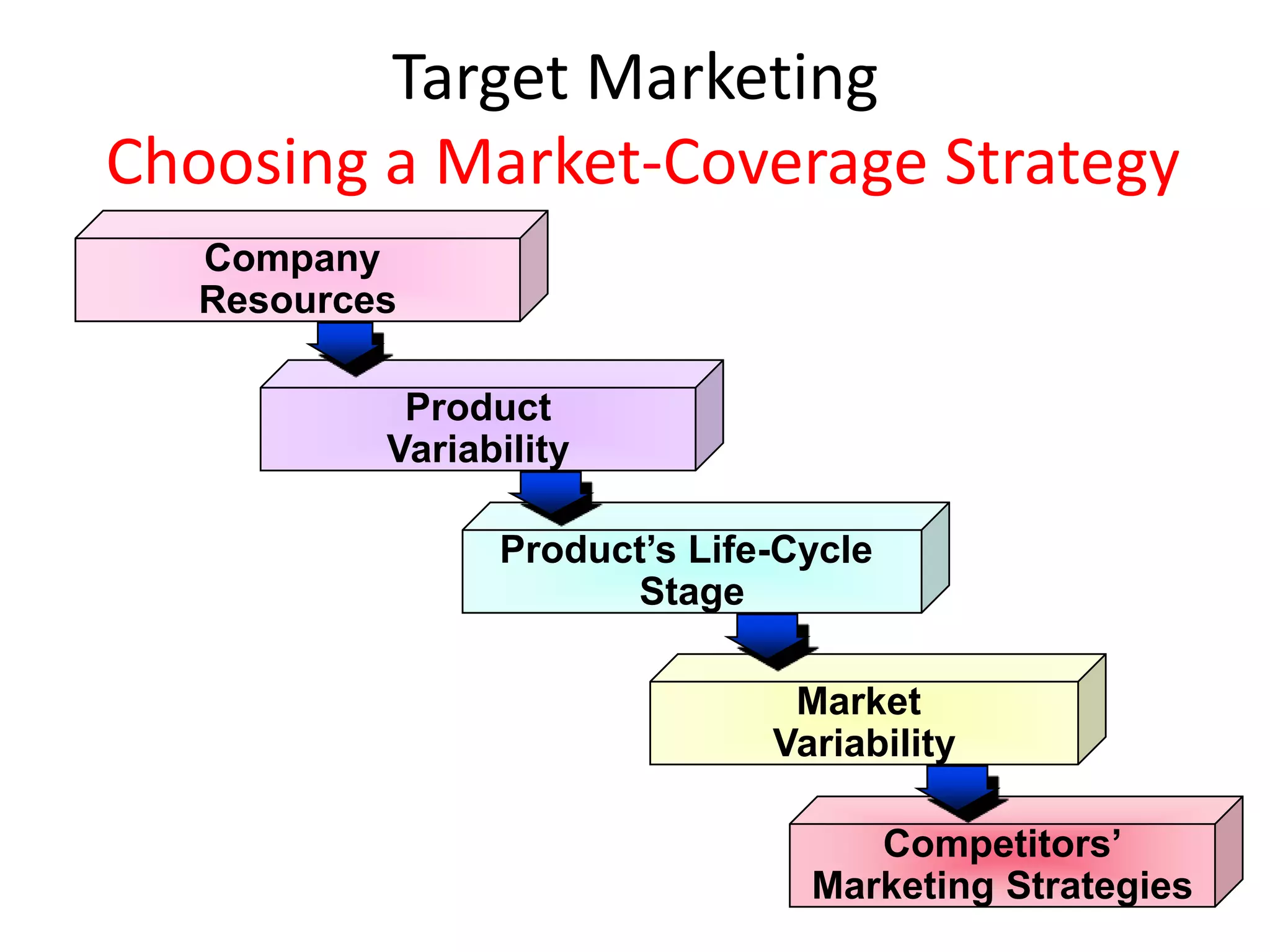
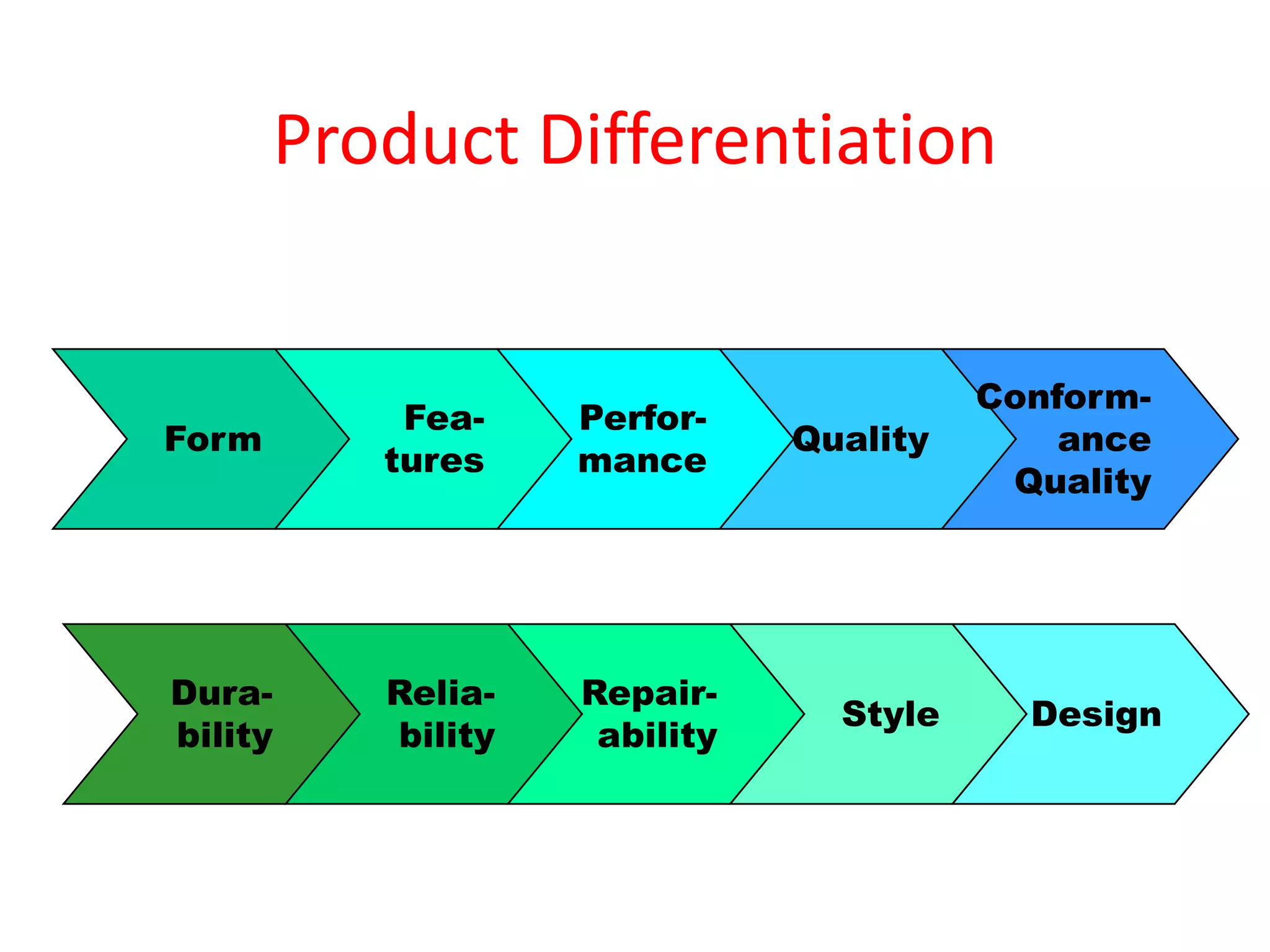
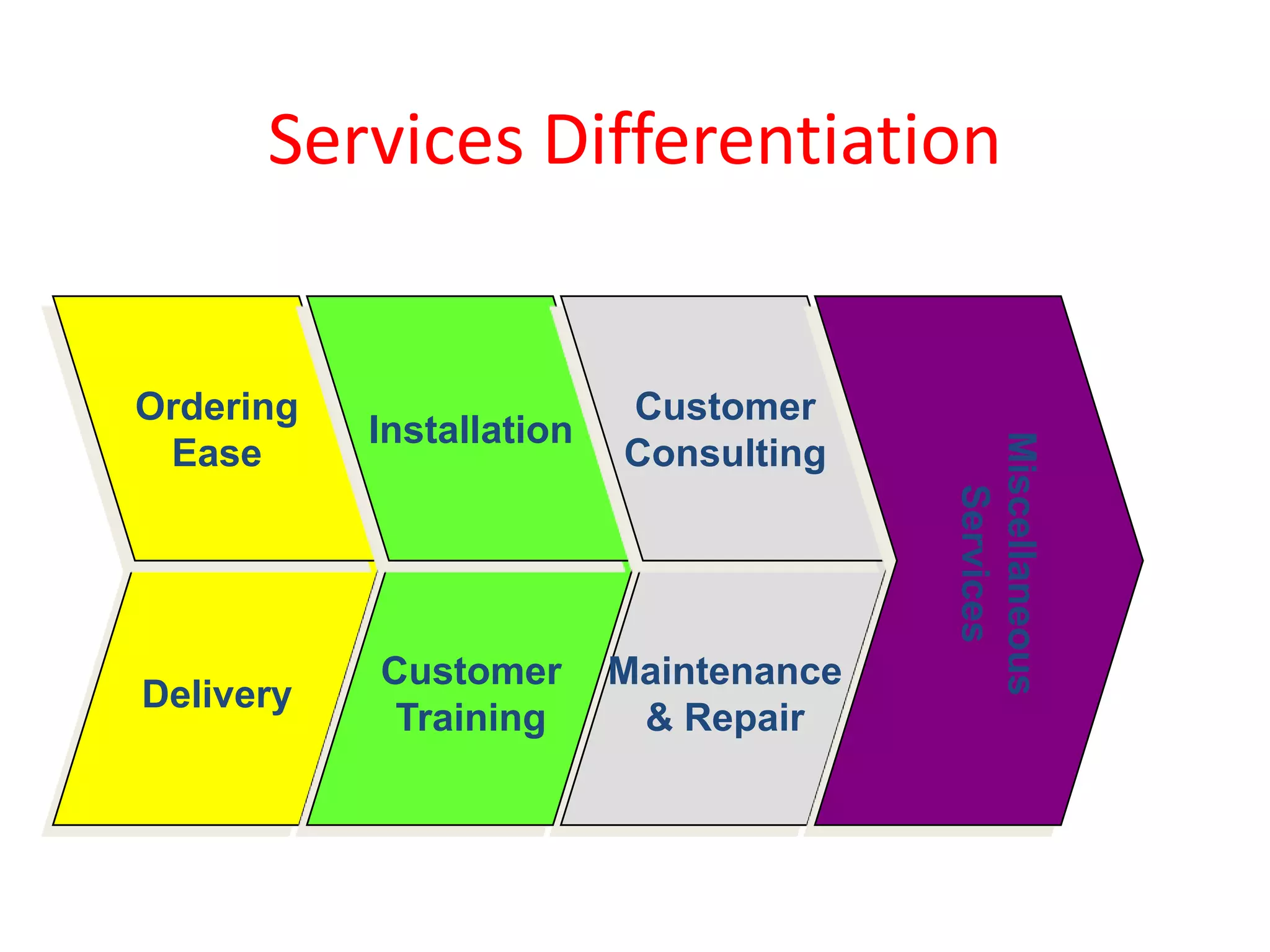
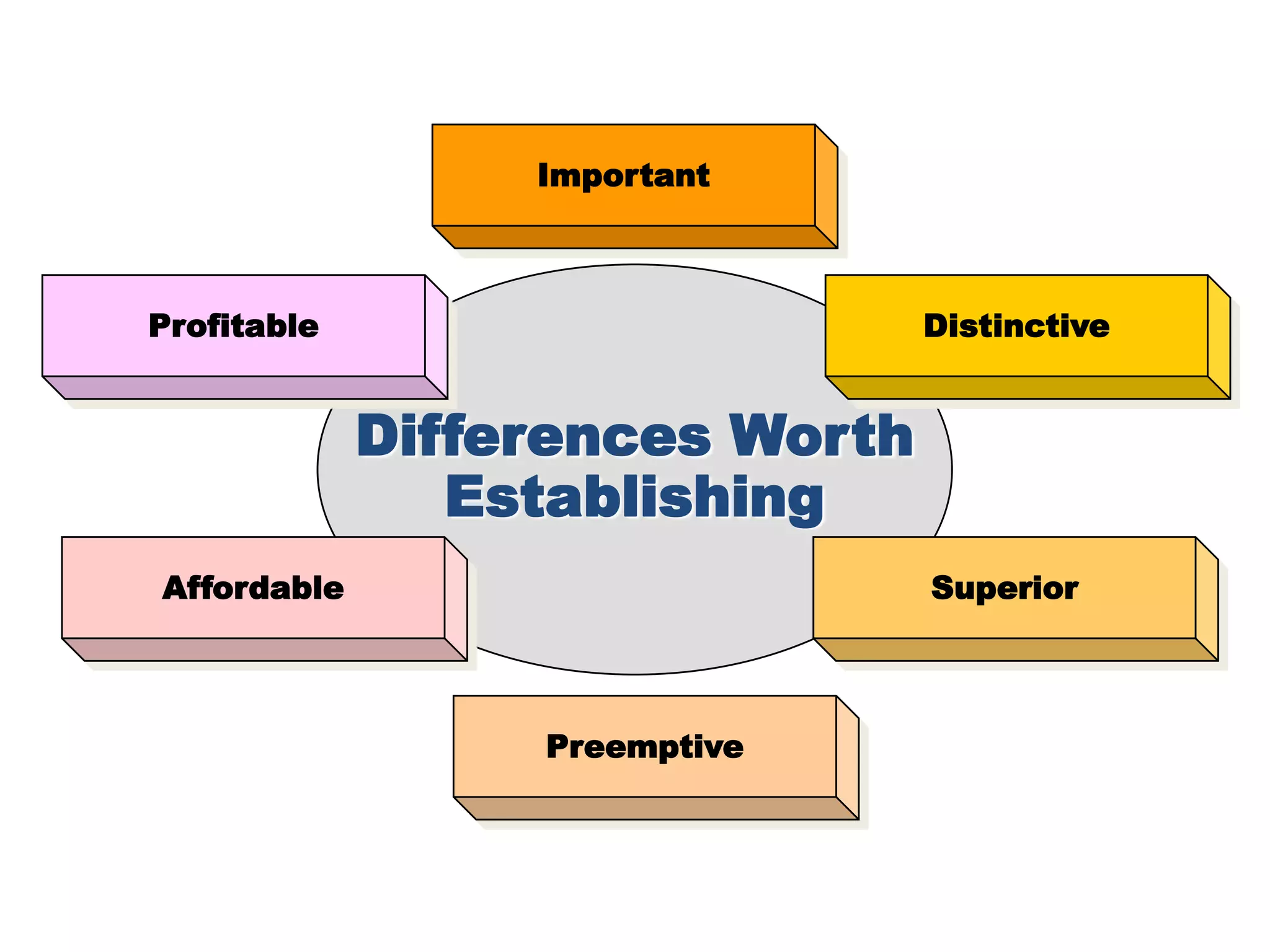
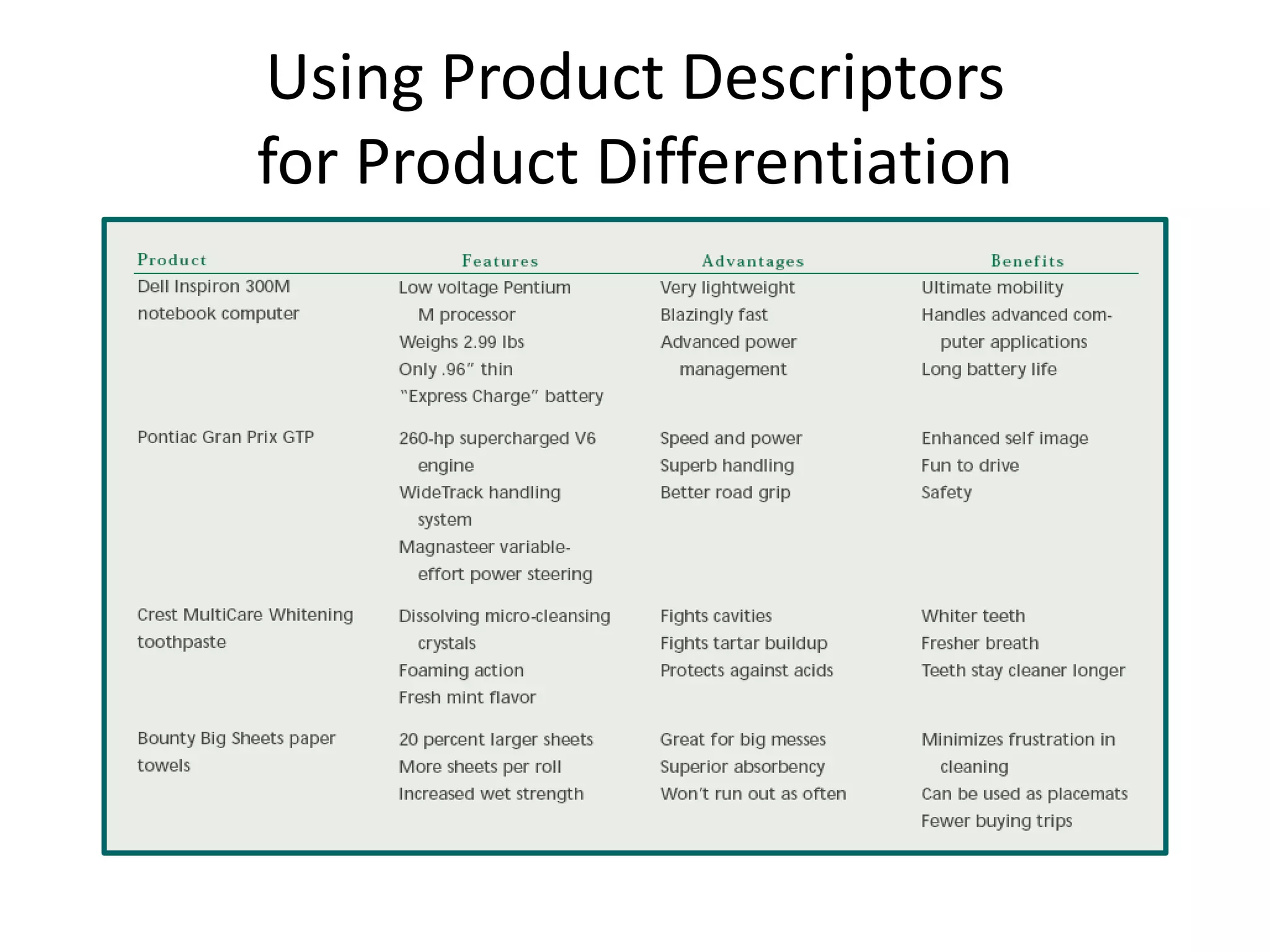
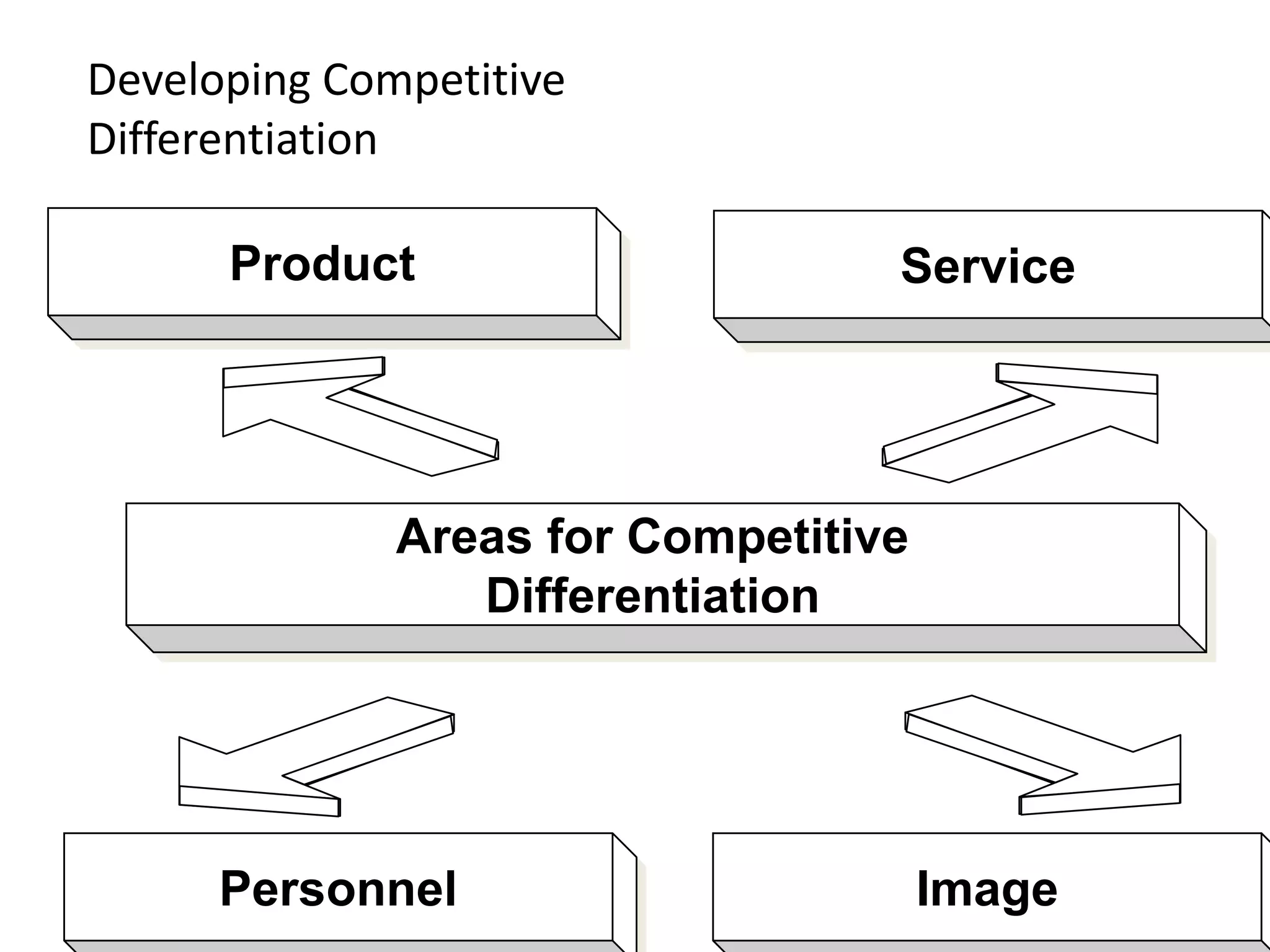
The document discusses target marketing and positioning. It defines target marketing as evaluating market segments to focus on those with the most potential. There are various target marketing strategies such as single segment, selective, mass market, product/market specialization. Positioning is designing the company's offering and image to occupy a distinctive place in customers' minds relative to competitors. The document outlines steps to choose and implement a positioning strategy including identifying competitive advantages, selecting the right advantage, and communicating the chosen position.