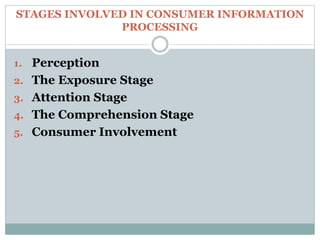
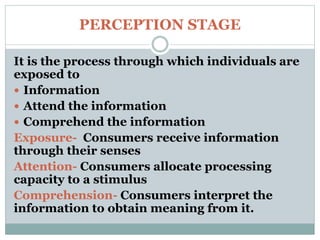
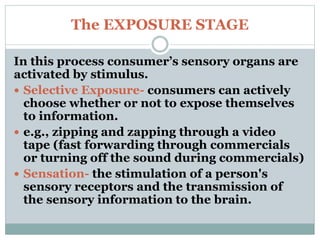
Consumer information processing involves several stages: exposure, where consumers are exposed to information through their senses; attention, where consumers allocate cognitive capacity to stimuli; and comprehension, where consumers interpret information to derive meaning. Higher consumer involvement leads to deeper information processing, greater arousal, and more extensive decision making, as involvement reflects personal importance and interest in a purchase. Consumer information processing examines how individuals perceive, pay attention to, make sense of, and are influenced by information during purchasing decisions.