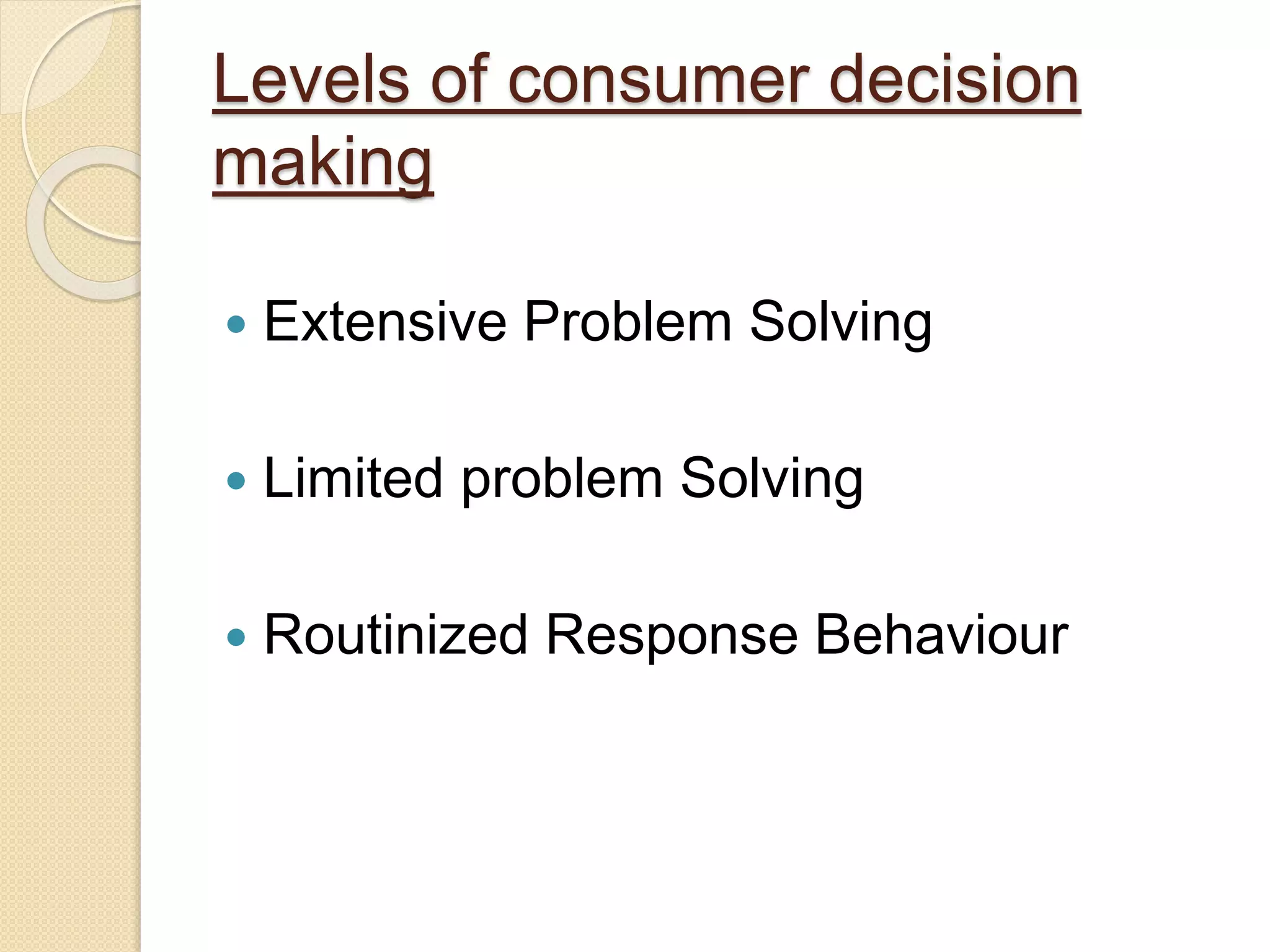
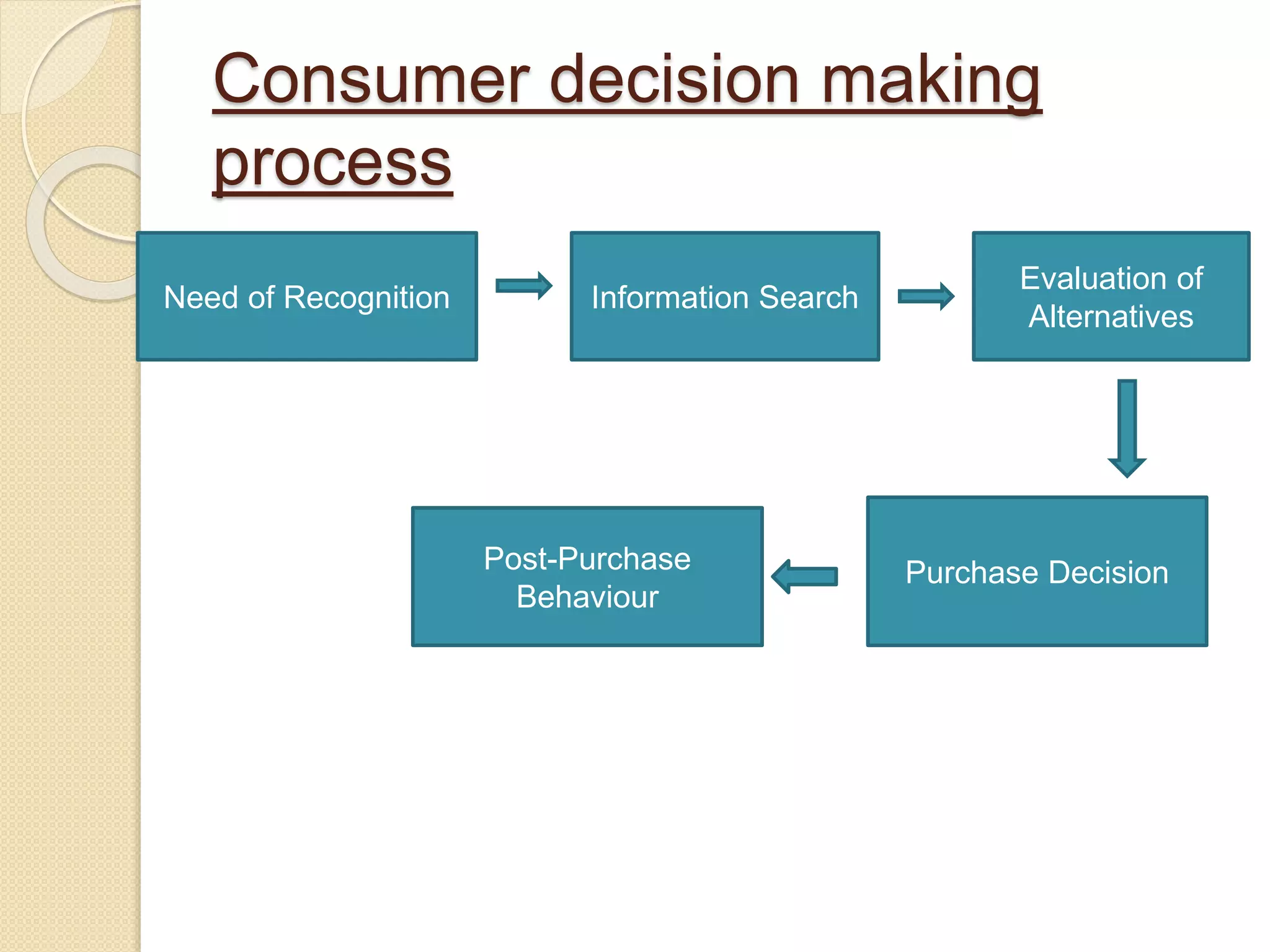
The document discusses consumer decision making, including three levels of involvement (routine response behavior, limited decision making, and extensive decision making), and presents a five-stage model of consumer decision making. The model includes need recognition, information search, evaluation of alternatives, purchase decision, and post-purchase behavior. Routine decisions involve little consideration, while extensive decisions involve high costs and extensive research between many alternatives.