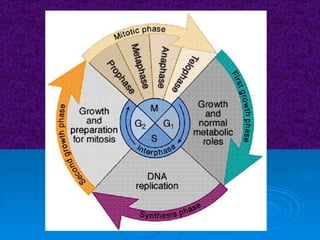
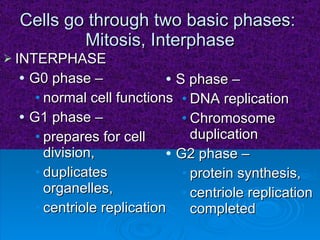
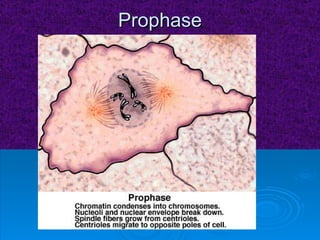
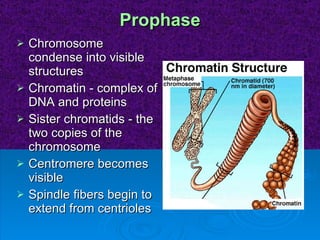
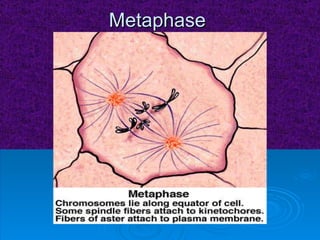
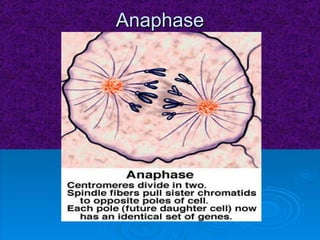
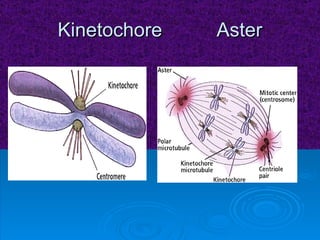
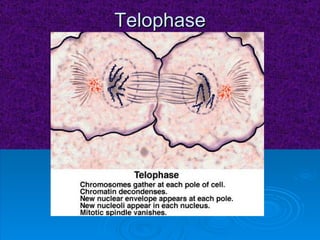
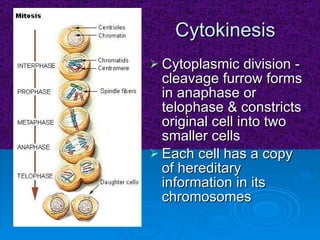
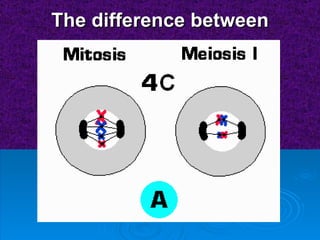
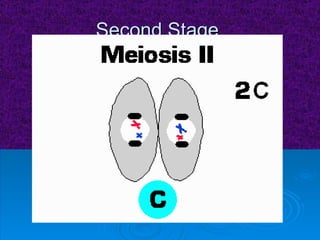
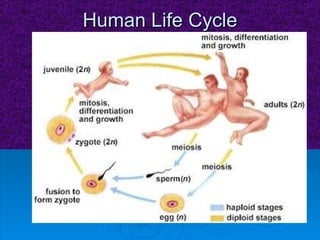
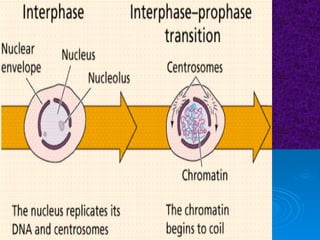
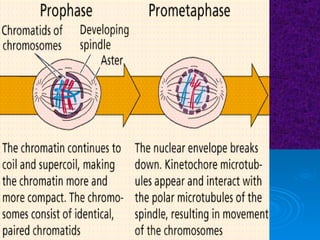
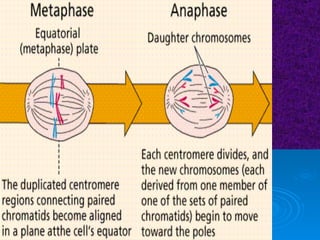
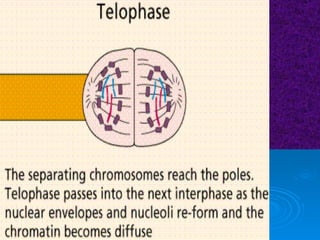
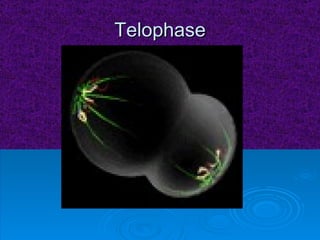
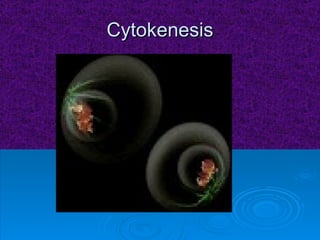
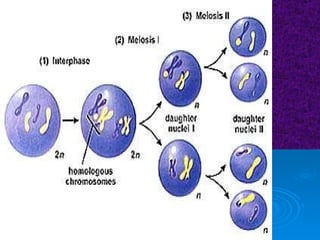
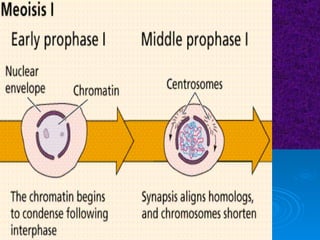
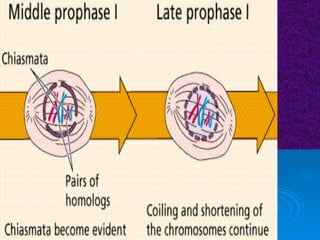
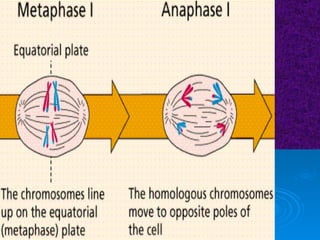
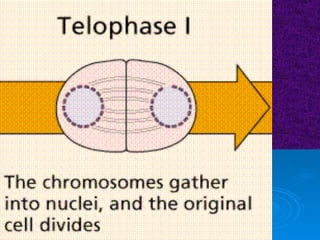
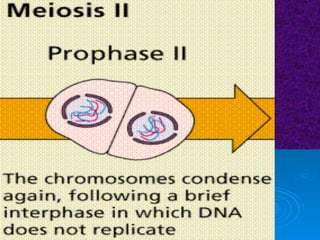
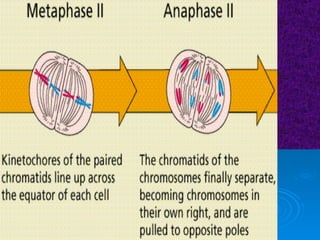
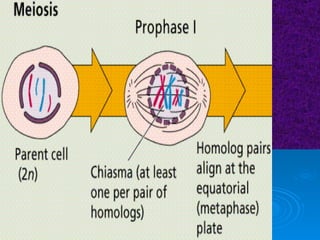
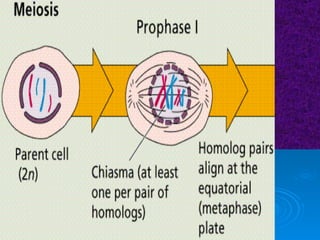
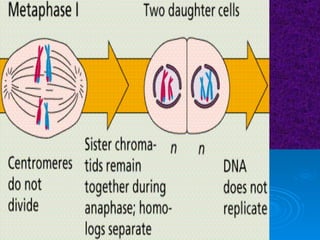
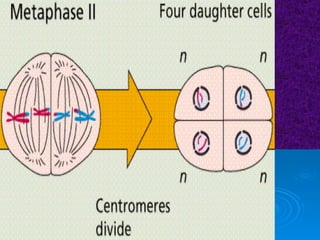
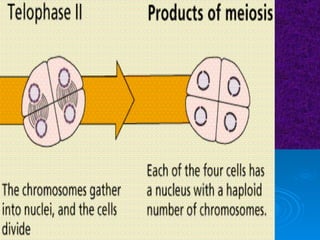
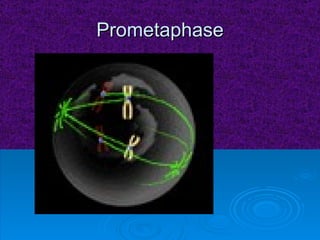
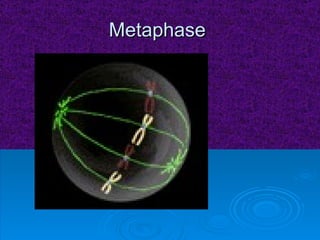
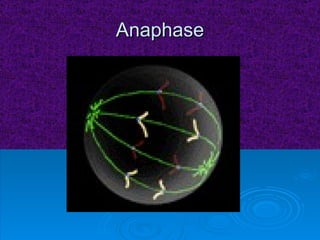
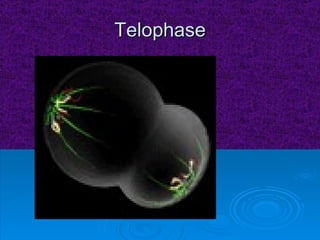
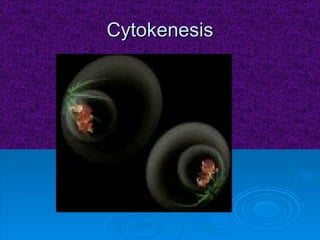
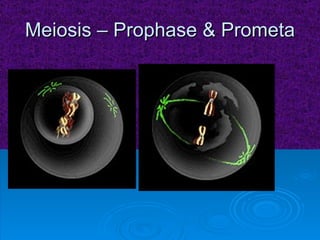
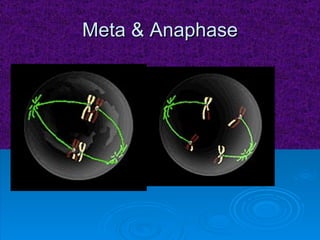
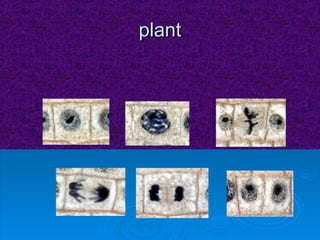
The document summarizes cell division and the two main types: mitosis and meiosis. Mitosis produces two identical daughter cells and is used for growth, repair, and replacement of somatic cells. It involves the phases of interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis. Meiosis produces four non-identical gamete cells through two rounds of division and is involved in sexual reproduction.