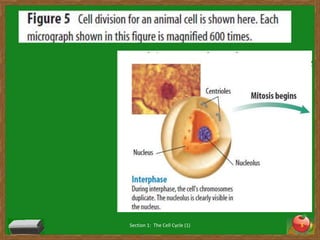
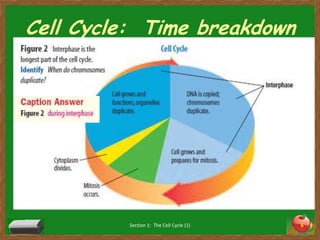
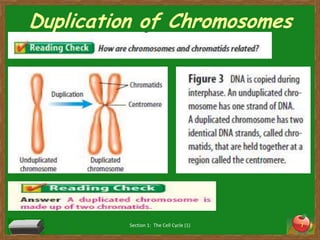
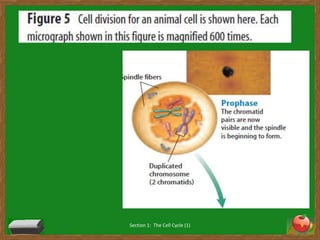
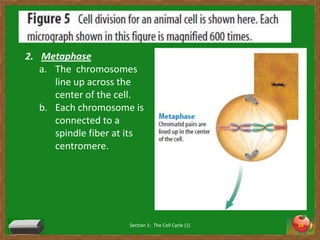
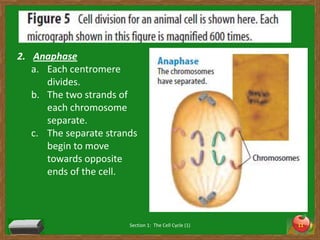
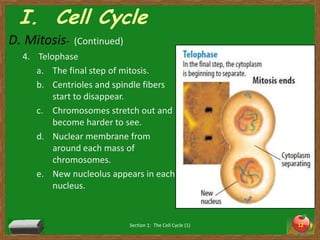
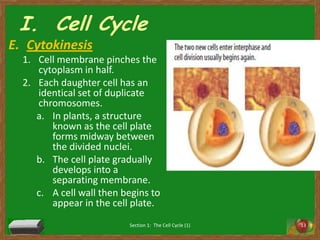
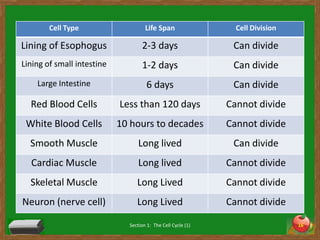
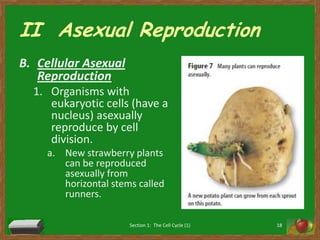
Cells undergo a life cycle of growth, division, and replication. The cell cycle consists of interphase, where the cell grows and duplicates its DNA, and mitosis, where the cell divides into two identical daughter cells. During interphase, cells progress through G1, S, and G2 phases before entering mitosis. Mitosis is further divided into prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase where the duplicated chromosomes separate and new nuclei form. Cytokinesis then partitions the cytoplasm, organelles and membranes, resulting in two daughter cells each with identical genetic material to the original parent cell. Asexual reproduction relies on this process of cell division to produce offspring that are genetically identical to the parent.