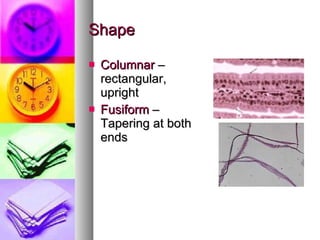
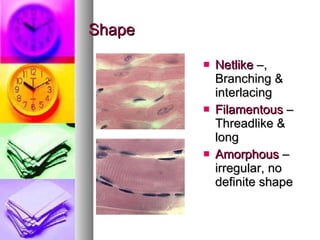
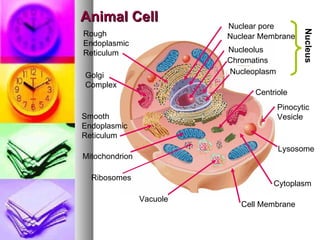
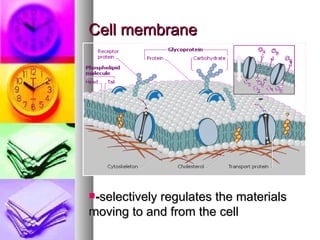
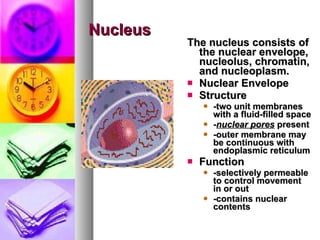
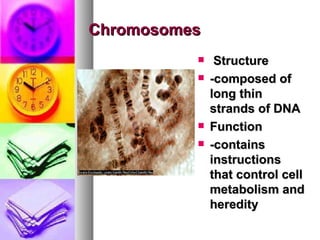
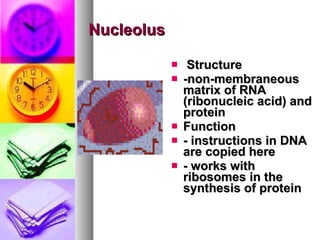
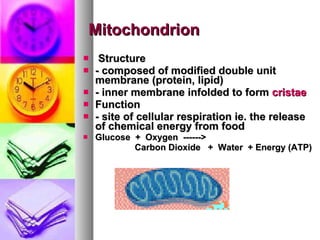
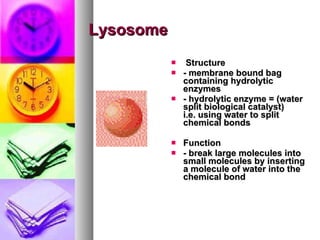
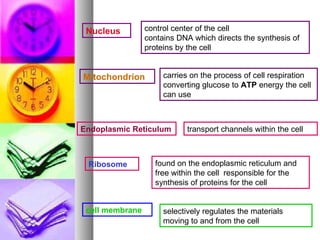
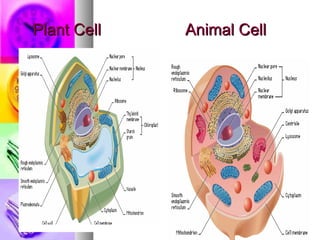
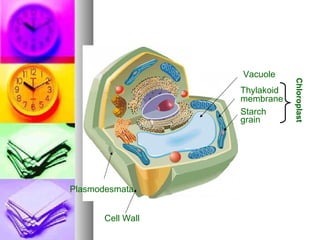
The document summarizes the history and components of cells. It describes how early scientists like Van Leeuwenhoek, Hooke and Brown discovered cells and cell structures using microscopes. It then outlines the cell theory developed by Rudolf Virchow stating that cells are the basic unit of structure and function and that new cells are produced from existing cells. The summary then provides details on the generalized functions of cells and describes the structures and functions of key animal and plant cell organelles such as the nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts and cell membrane.