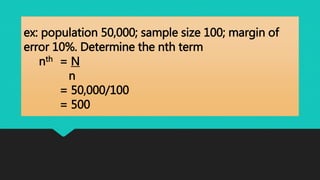
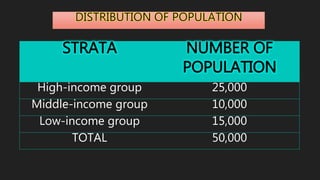
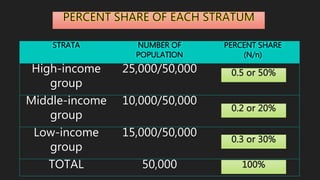
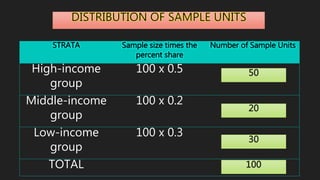
This document discusses data collection methods. It defines data collection as gathering numerical measurements or information on variables of interest in an established systematic way. There are two main sources of data: documentary sources like published reports and field sources like individuals with knowledge of the study topic. Common data collection methods include direct interviews, indirect questionnaires, registration of existing data, observation, and experiments. The document also outlines how to plan a study, including determining sample size, selecting sampling techniques, and creating structured versus open-ended questions. It discusses probability and non-probability sampling methods.