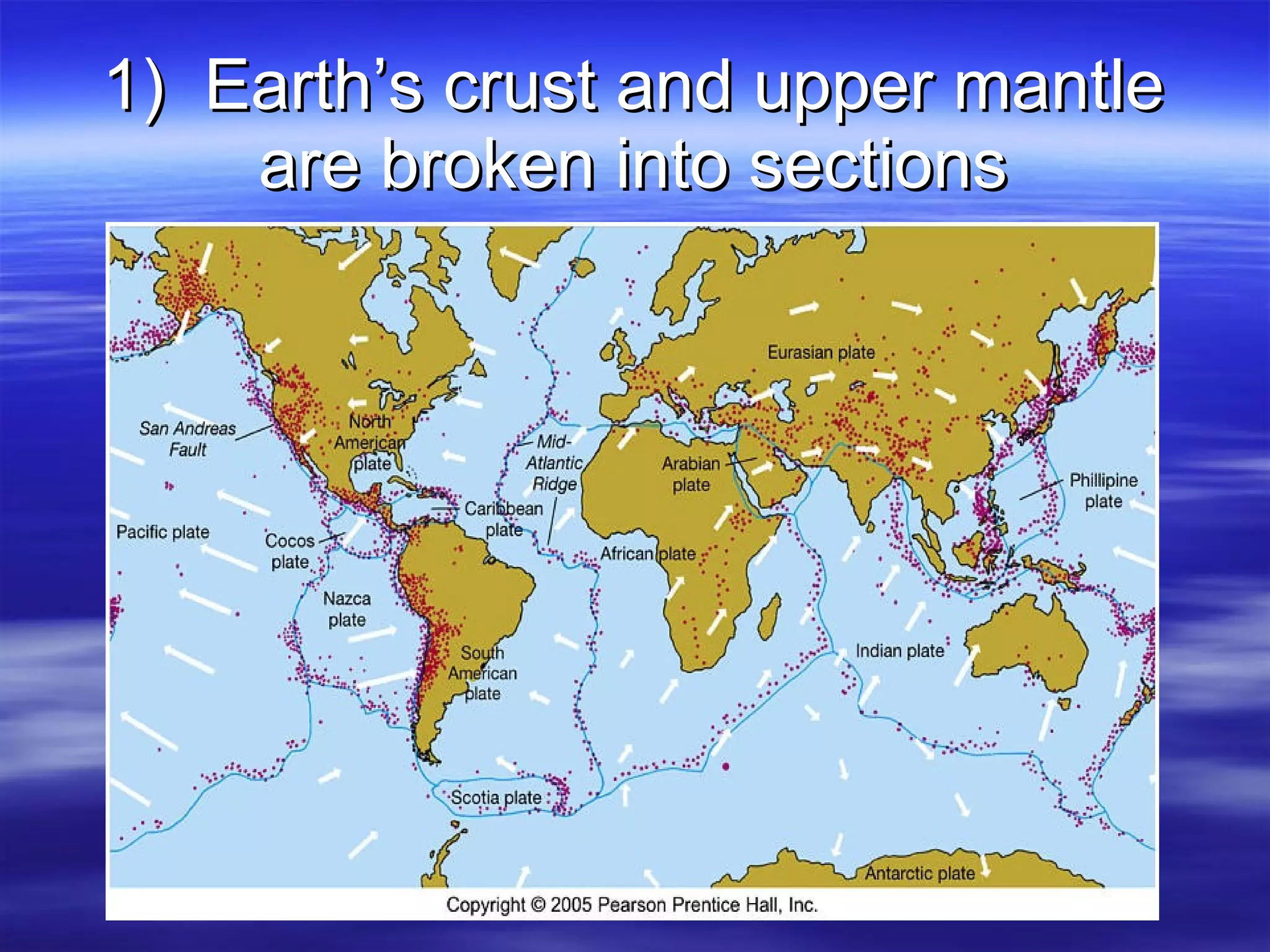
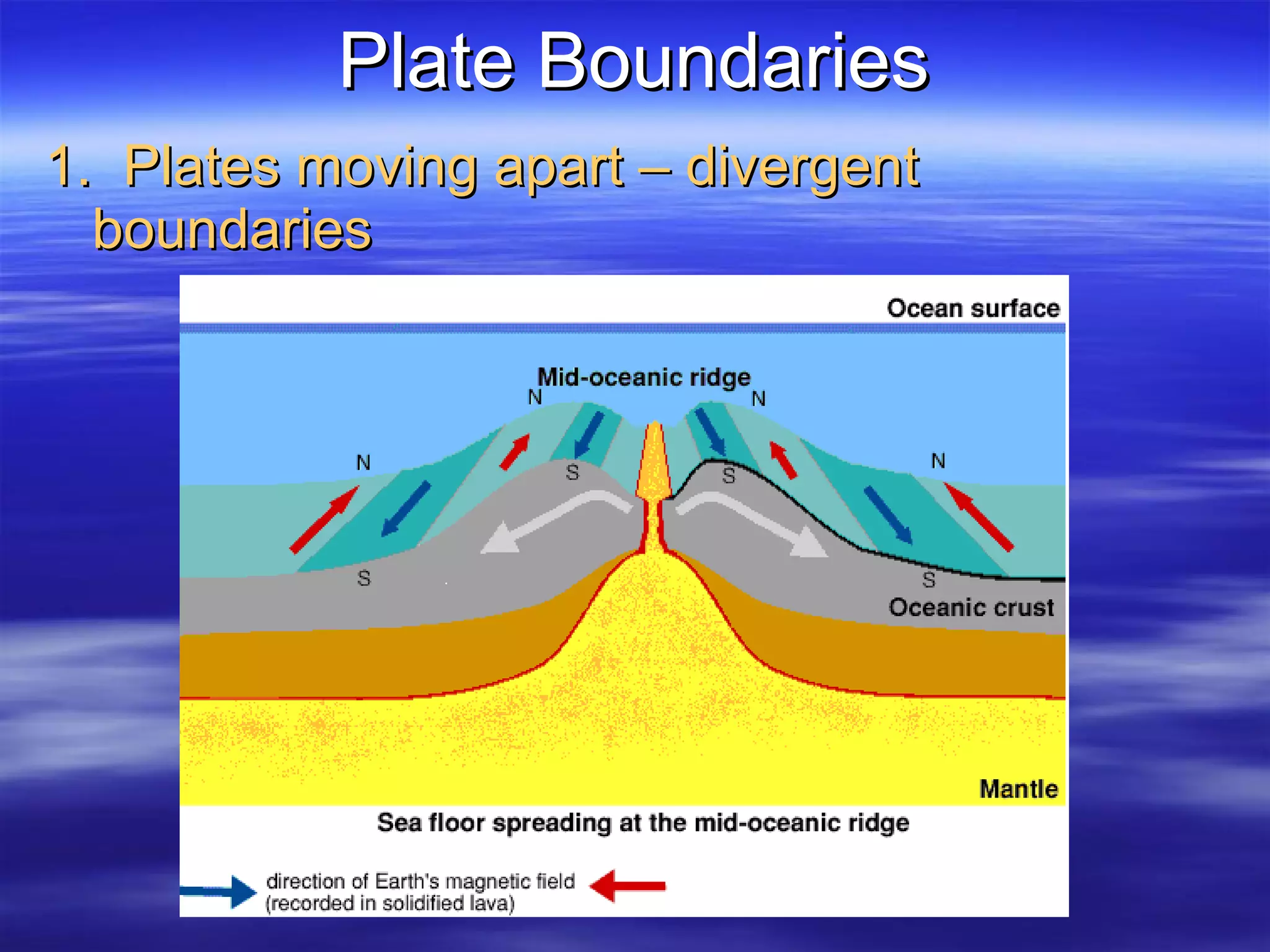
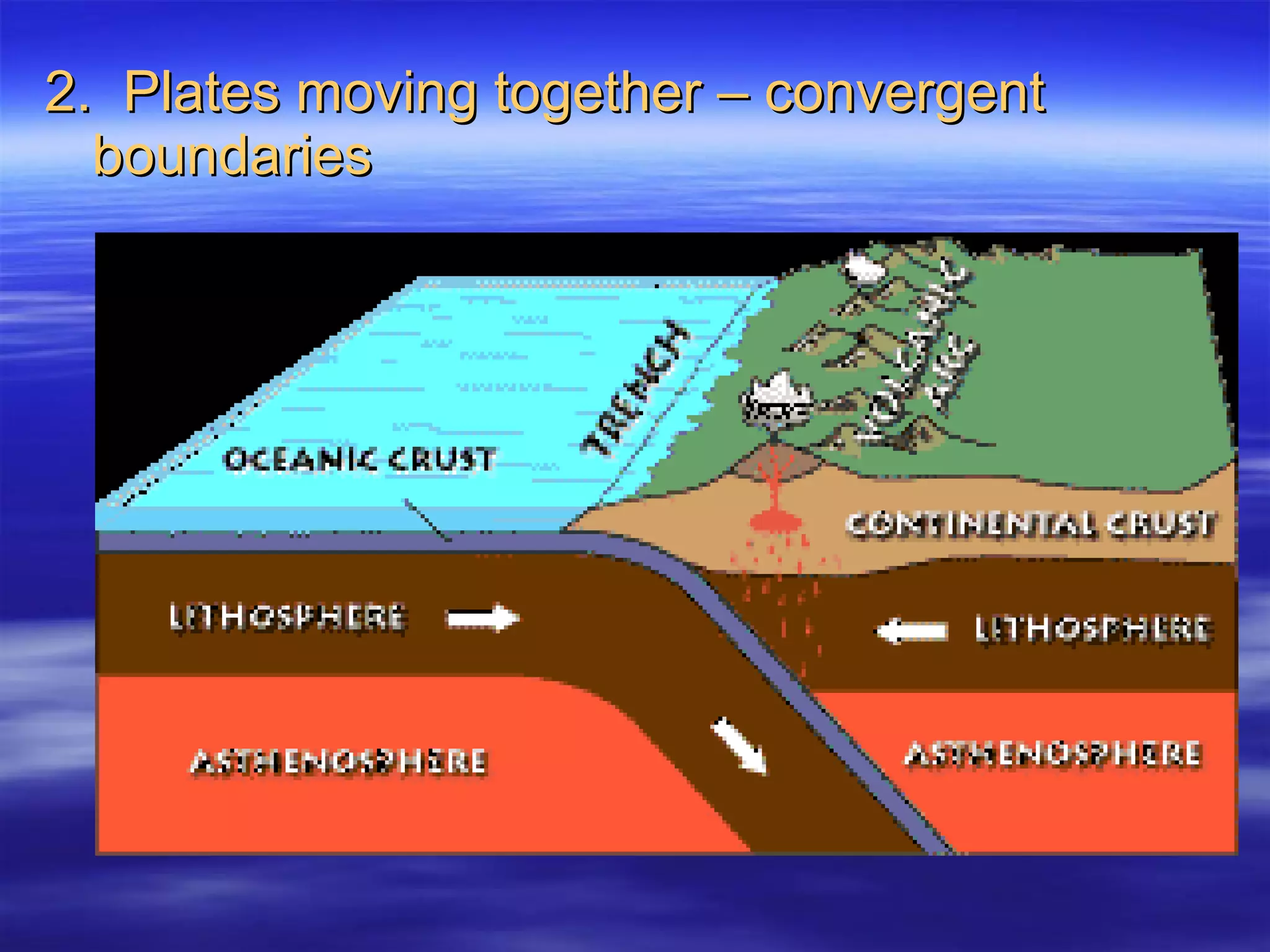
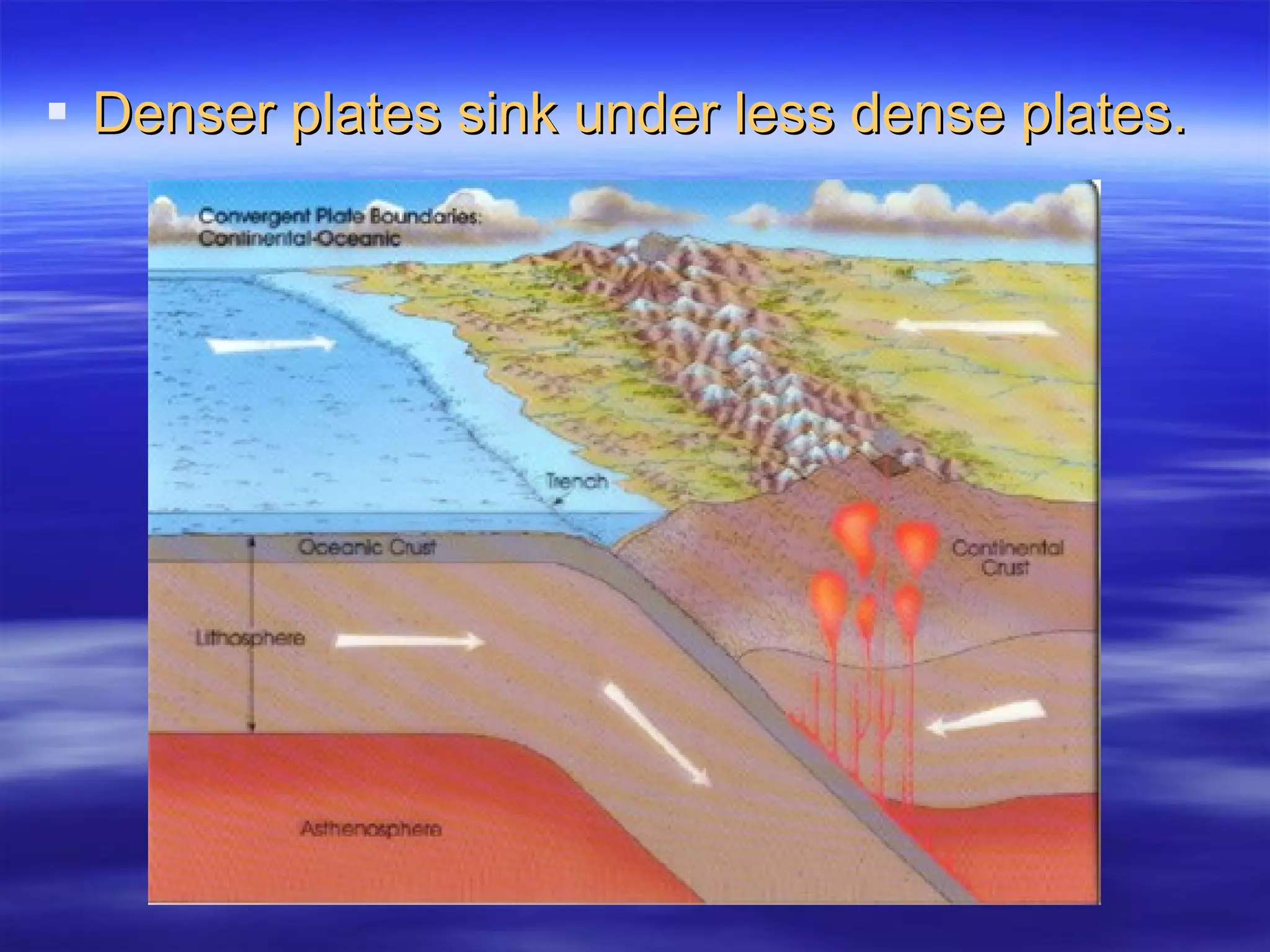
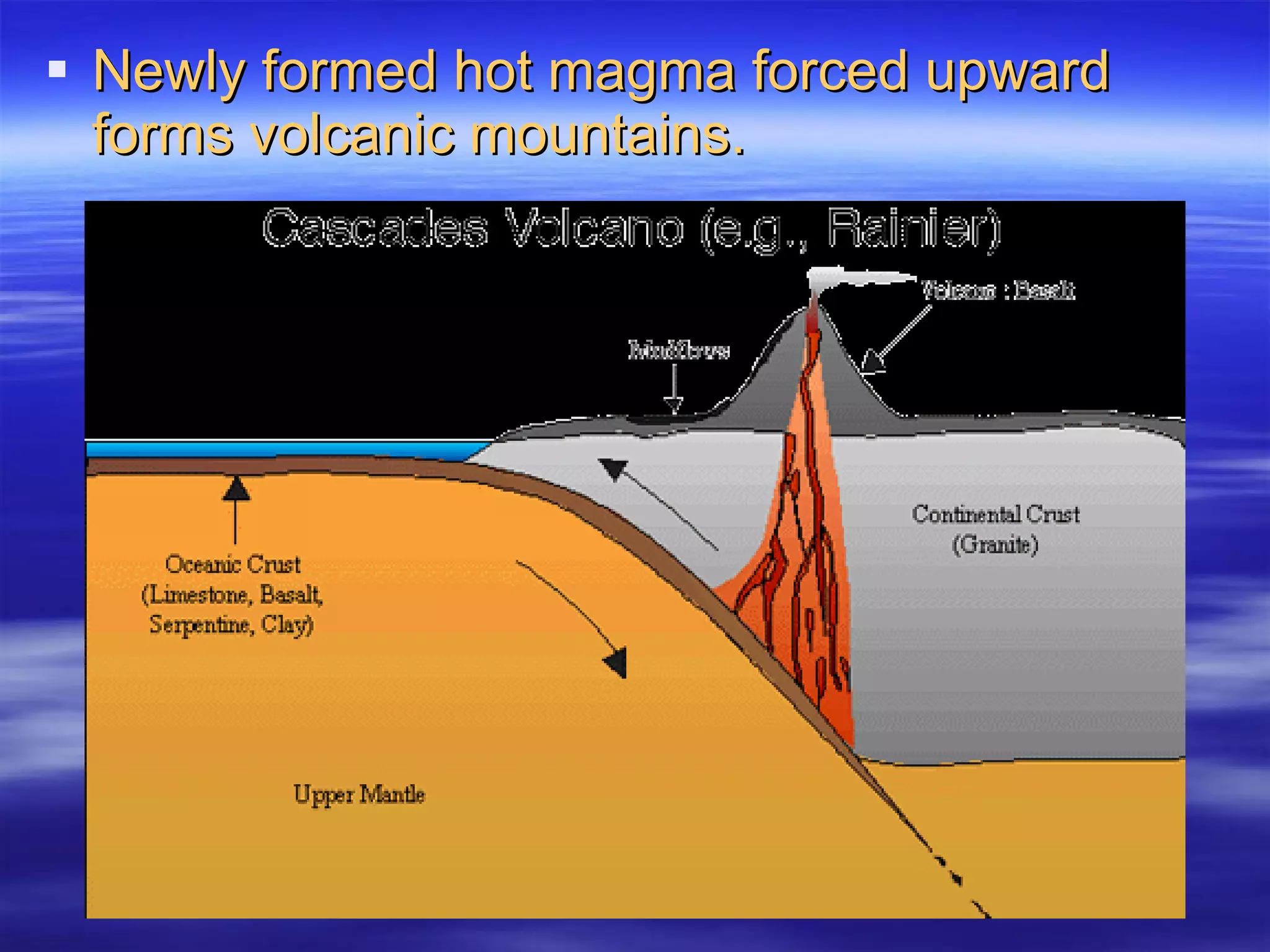
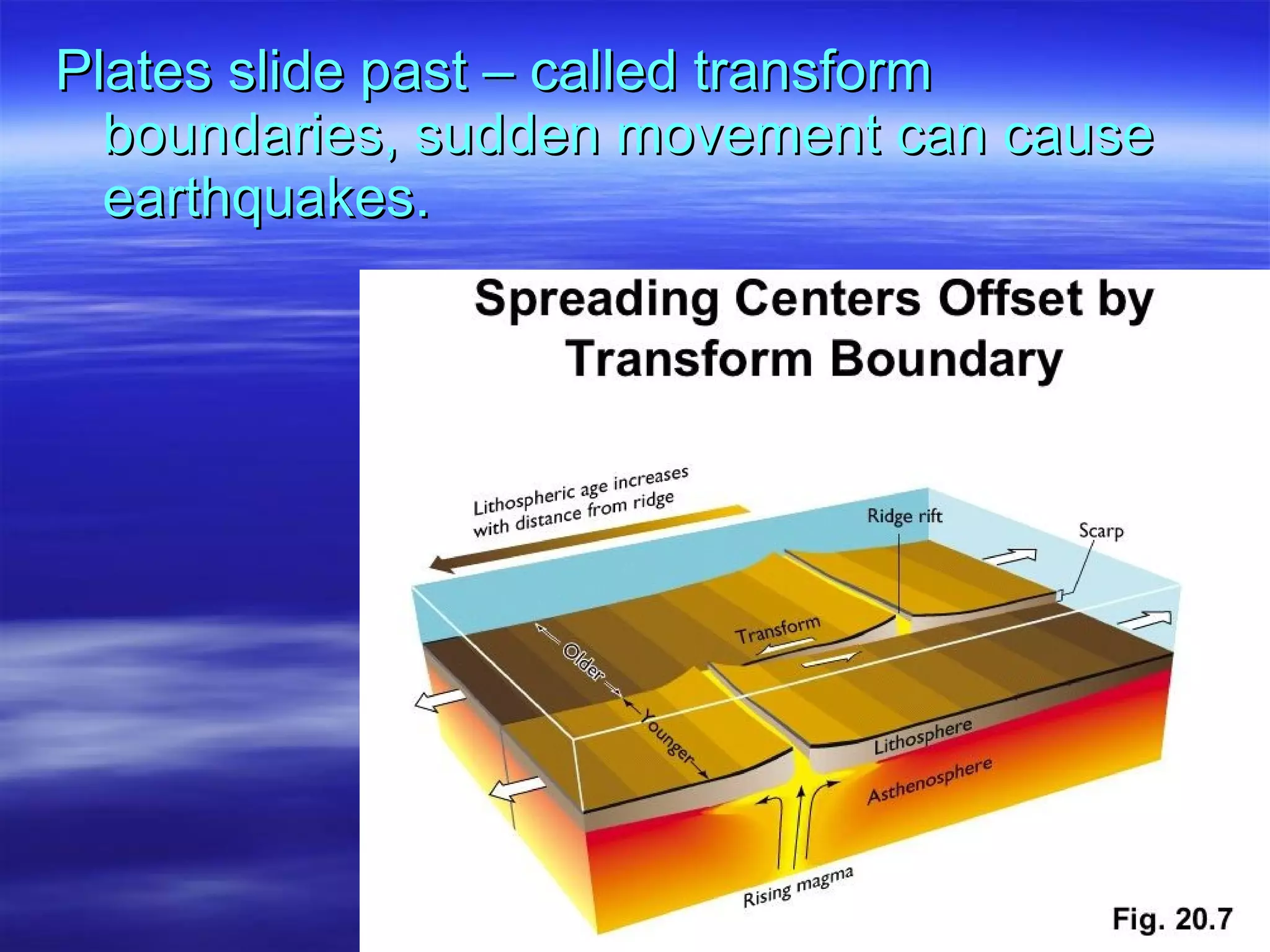
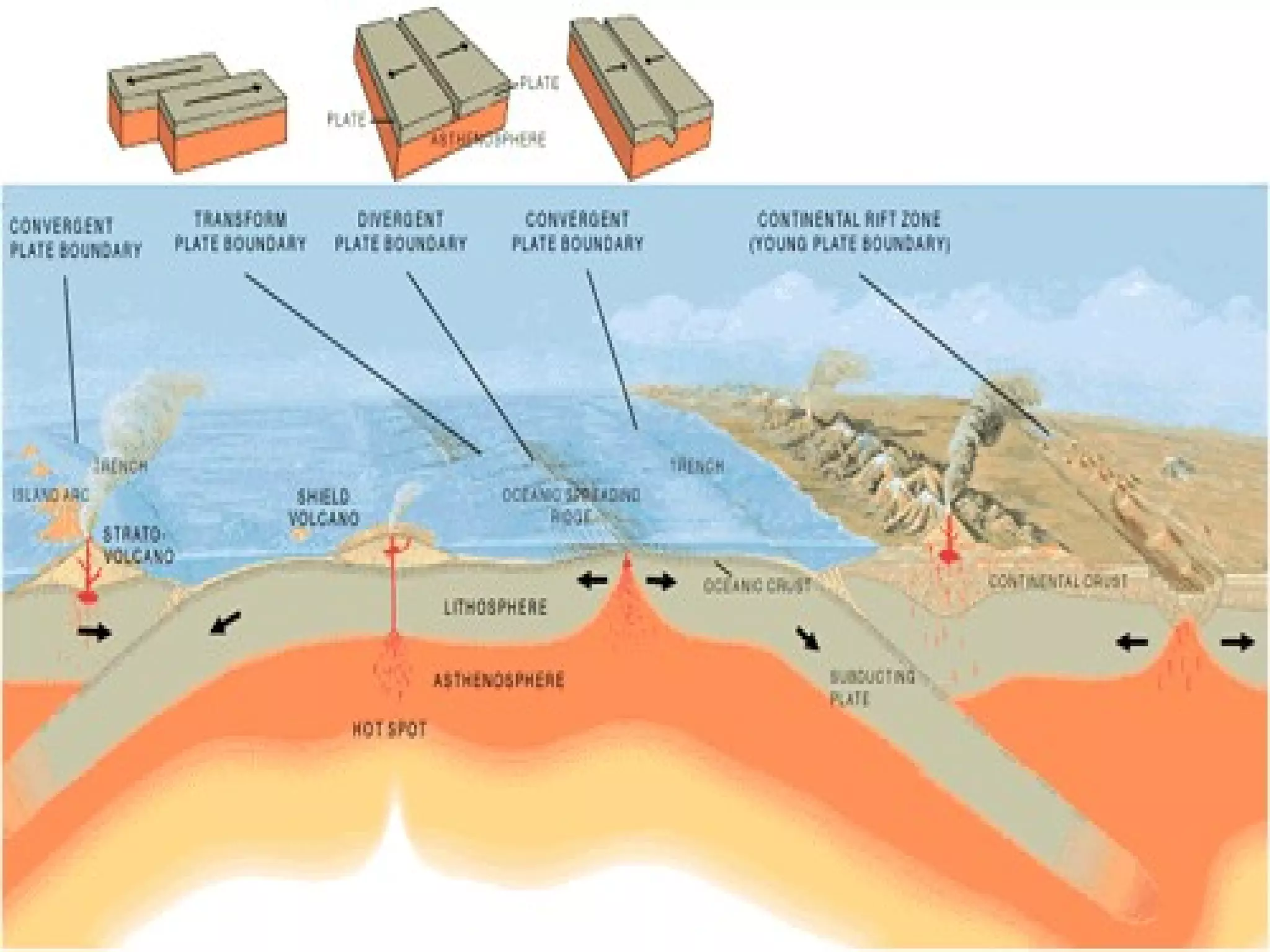
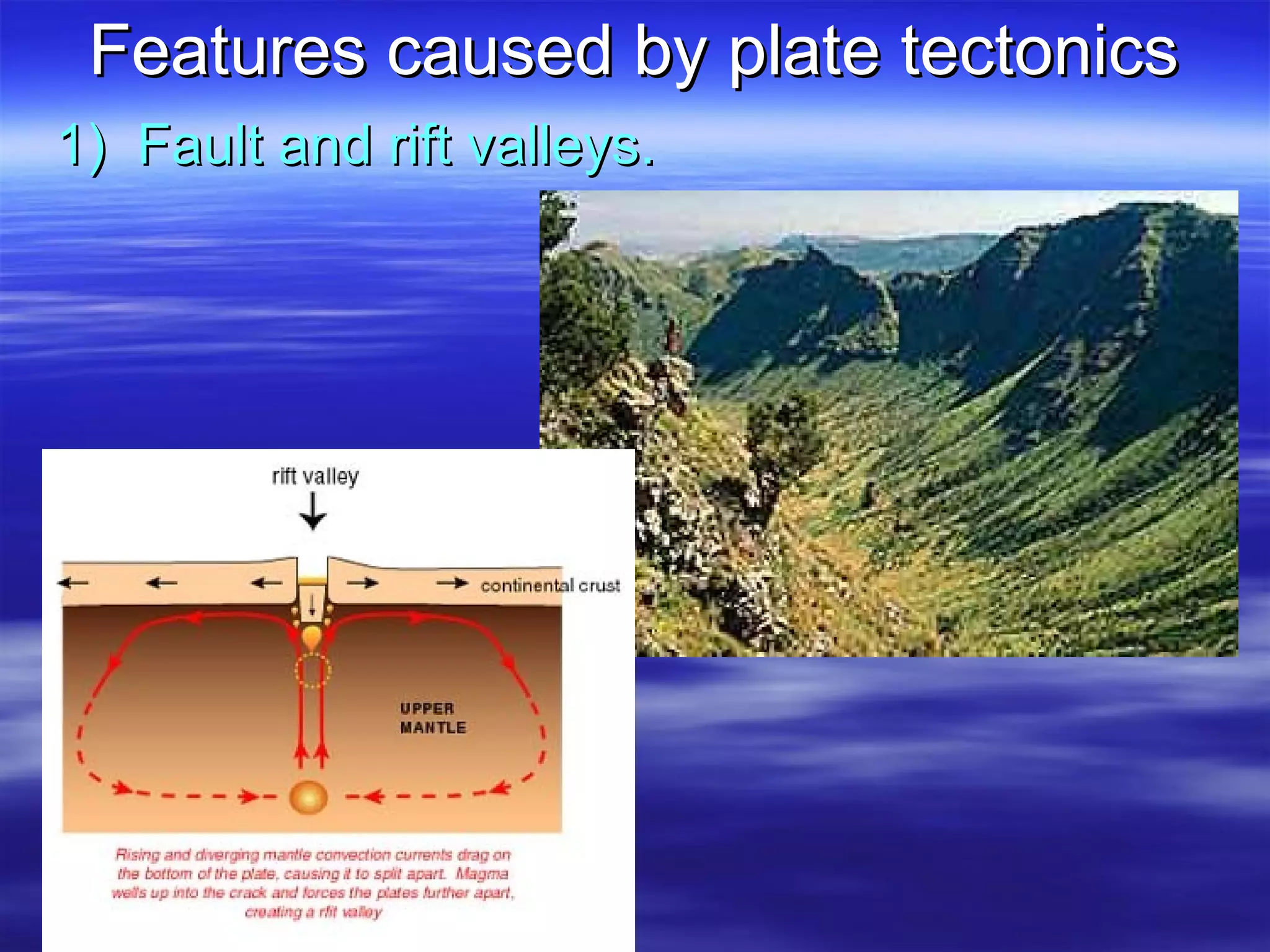
1) Scientists discovered underwater mountain ranges called mid-ocean ridges using sound waves, and Harry Hess proposed the theory of seafloor spreading to explain them.
2) Seafloor spreading involves hot material rising at ridges and flowing sideways, carrying the seafloor away as new material cools and forms at the cracks.
3) Evidence for seafloor spreading includes younger rocks at ridges and magnetic reversals recorded in strips of rock parallel to ridges.