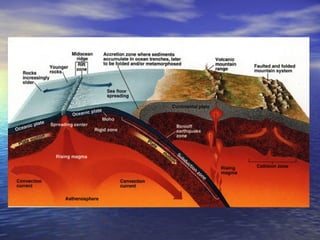
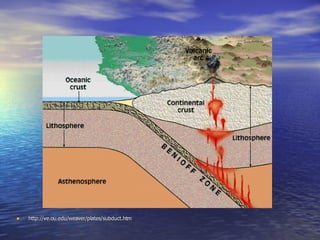
New evidence supported the theory of sea floor spreading and plate tectonics. Mapping of the seafloor using sonar revealed a mid-ocean ridge running through the Atlantic Ocean. Rocks near the ridge are younger, becoming progressively older further from the ridge, showing new crust is generated at the ridge through sea floor spreading. While new crust is created at ridges, older oceanic crust is recycled back into the Earth through subduction at plate boundaries, keeping the size of the Earth stable over time. This evidence of sea floor spreading supported Wegener's theory of continental drift.