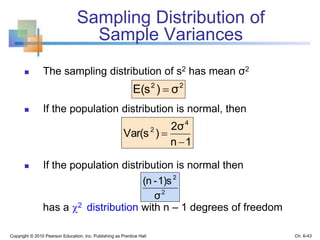
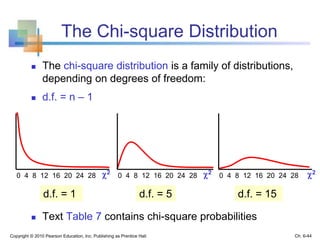
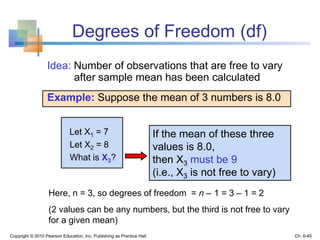
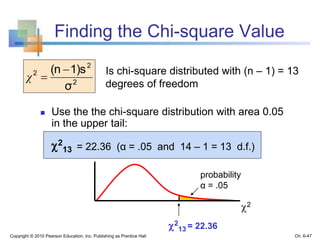
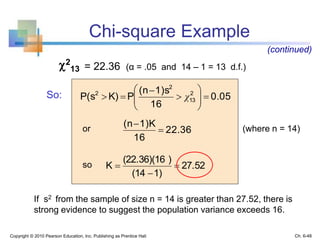
This chapter discusses sampling and sampling distributions. The key points are:
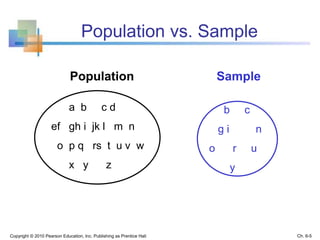
1) A sample is a subset of a population that is used to make inferences about the population. Sampling is important because it is less time consuming and costly than a census.
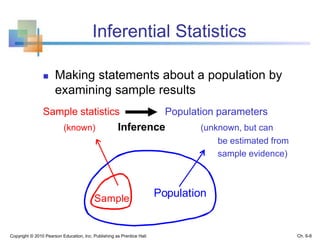
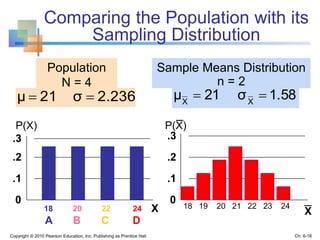
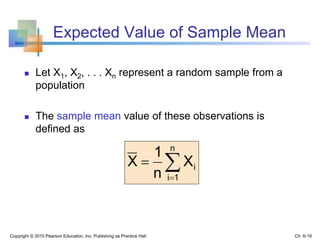
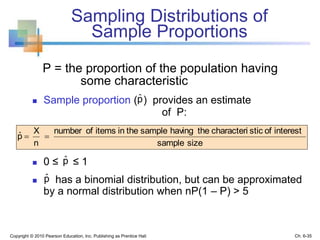
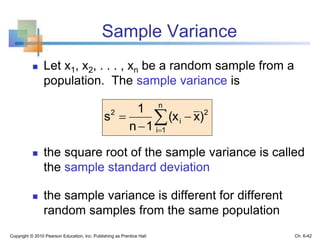
2) Descriptive statistics describe samples, while inferential statistics make conclusions about populations based on sample data. Sampling distributions show the distribution of all possible values of a statistic from samples of the same size.
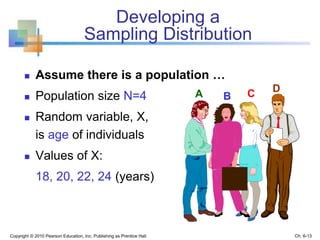
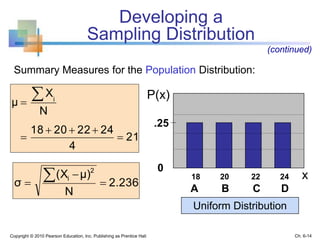
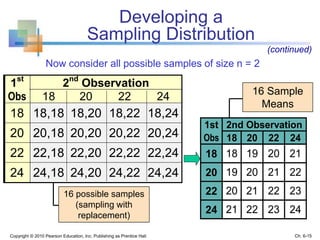
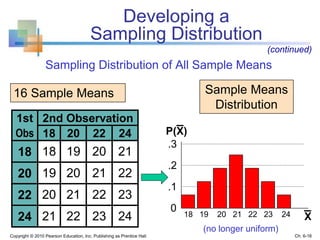
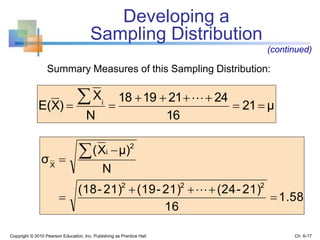
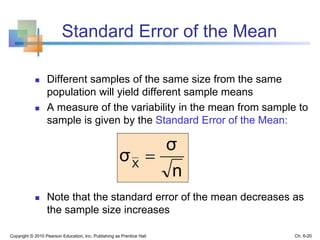
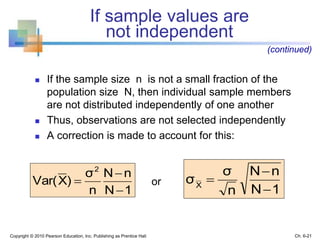
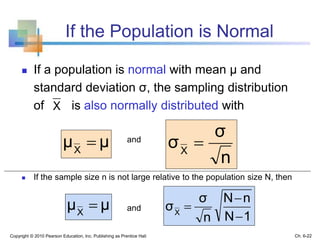
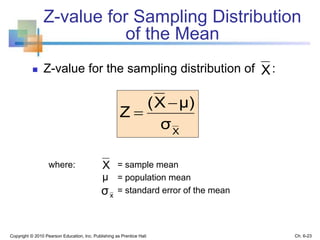
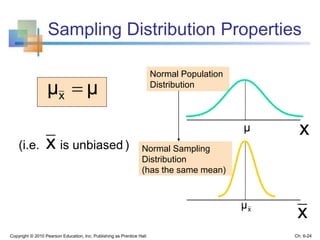
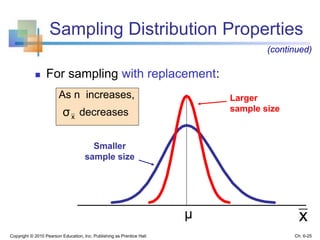
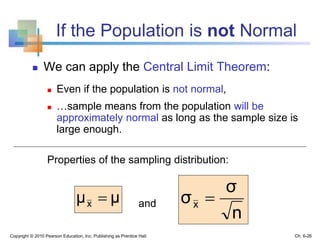
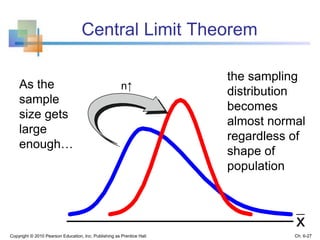
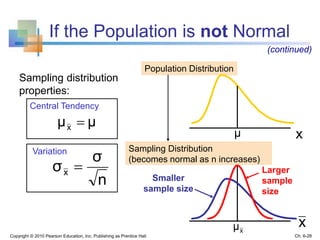
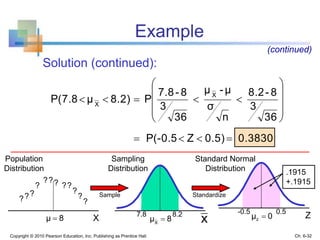
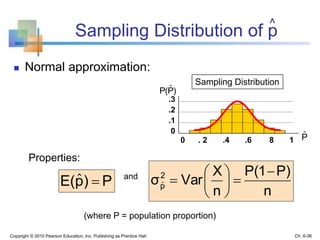
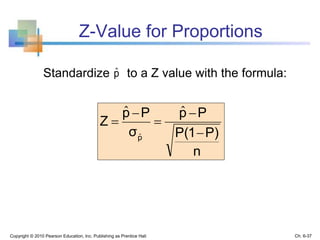
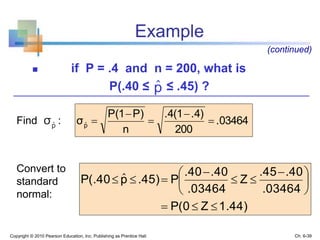
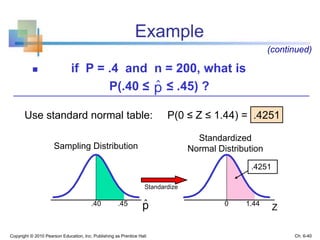
3) The sampling distribution of the sample mean is normally distributed for large sample sizes due to the central limit theorem. Its mean is the population mean and its standard deviation decreases with increasing sample size. Acceptance intervals can be used to determine the range a