The document discusses various aspects of organizational change including:
1. The nature of change being vital to avoid stagnation and being a constant process rather than a single event.
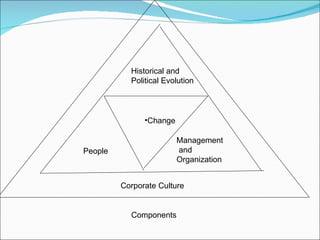
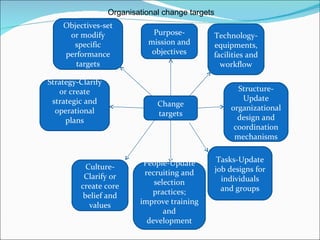
2. Historical, political, management, organizational, people, and cultural components influencing change.
3. External forces like globalization and internal forces like organizational silence driving change.
4. The relationship between stability and change in organizations.
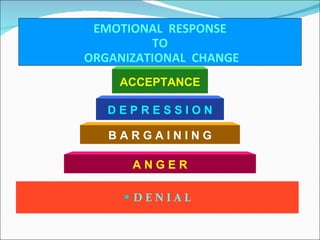
5. Reasons for resistance to change like insecurity, fear, and uncertainty.
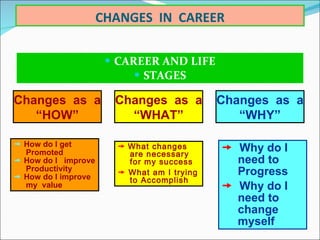
6. Reactive versus proactive responses to change opportunities and threats.