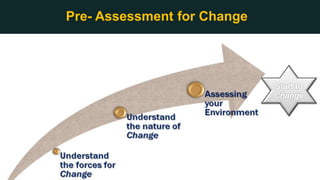
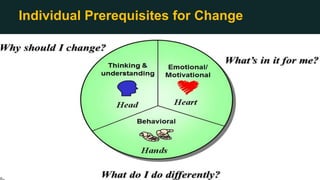
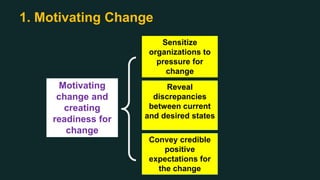
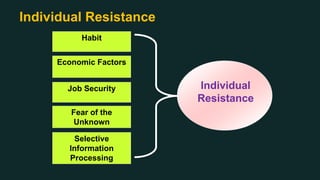
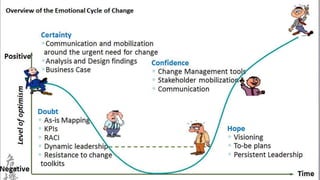
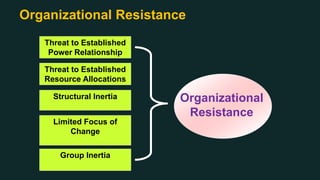
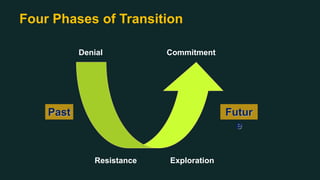
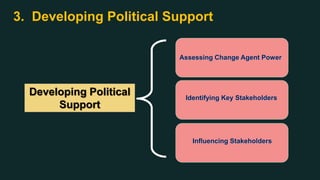
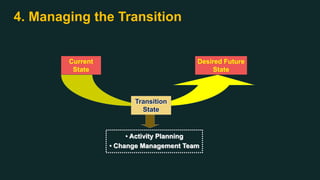
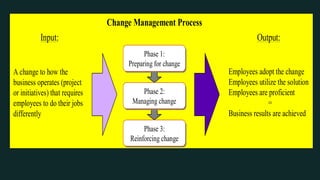
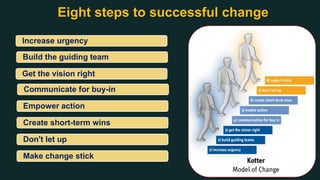
This document discusses change management and provides an overview of key concepts. It defines change management as managing the people side of change to achieve organizational results. It discusses individual and organizational change management and who is involved. It also summarizes several theories of change management and models for managing change, including Lewin's three-phase model, Kotter's eight steps, and different types of change. The document emphasizes the importance of leadership, communication, learning, and reinforcement in effective change management.