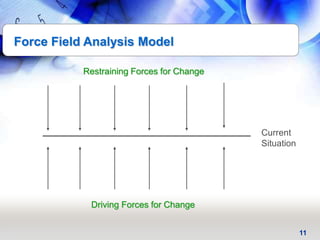
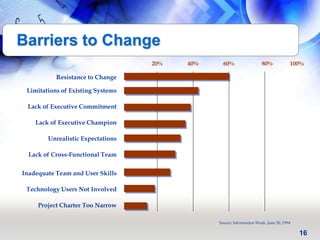
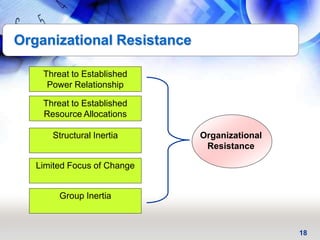
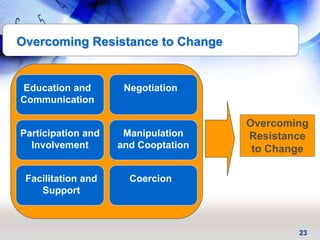
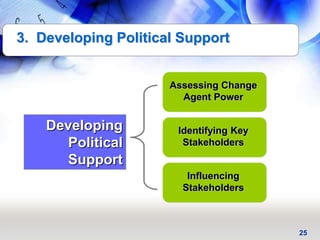
This document provides an overview of key principles and activities for effective change management in corporate transformations. It discusses (1) principles of change including that change is a process enabled not managed and behavioral change occurs at the emotional level, (2) five key activities for change management - motivating change, creating a vision, developing political support, managing the transition, and sustaining momentum, and (3) additional concepts like overcoming resistance to change, roles in organizational change, and skills needed by change agents.