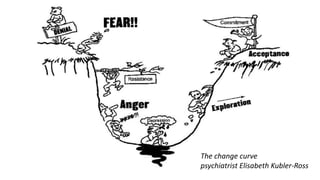
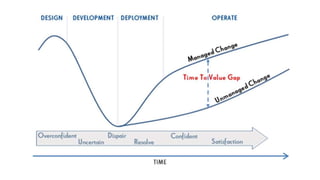
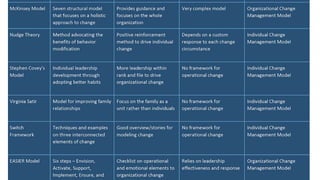
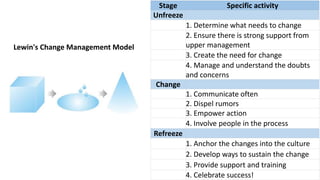
The document discusses the challenges of change management in organizations, highlighting resistance to change as a common human condition linked to fear and discomfort. It outlines the importance of structured change management approaches, including communication, support, and training, to facilitate successful transitions. Additionally, it presents models and methodologies for managing change effectively, emphasizing the need for executive support and stakeholder involvement.