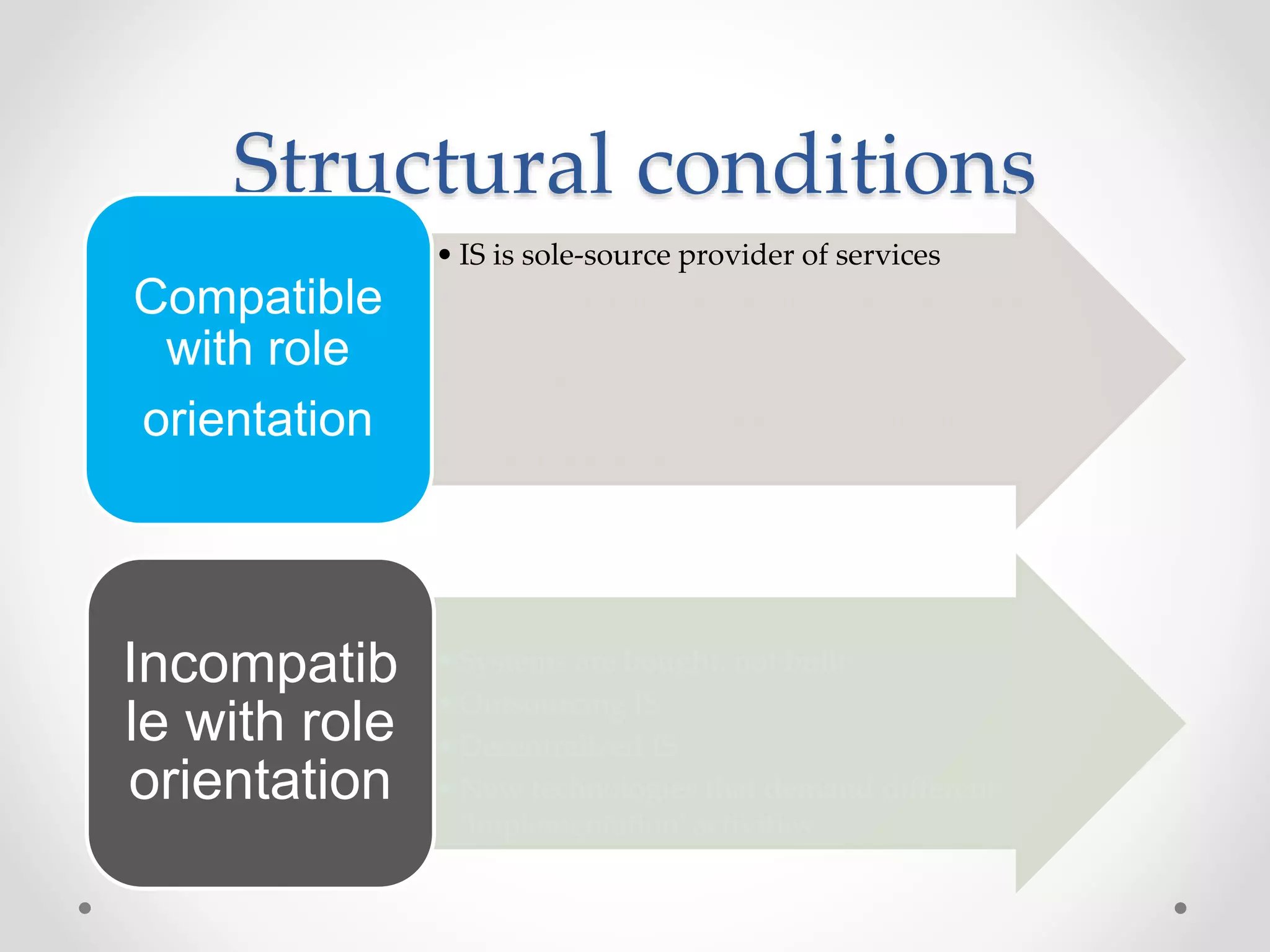
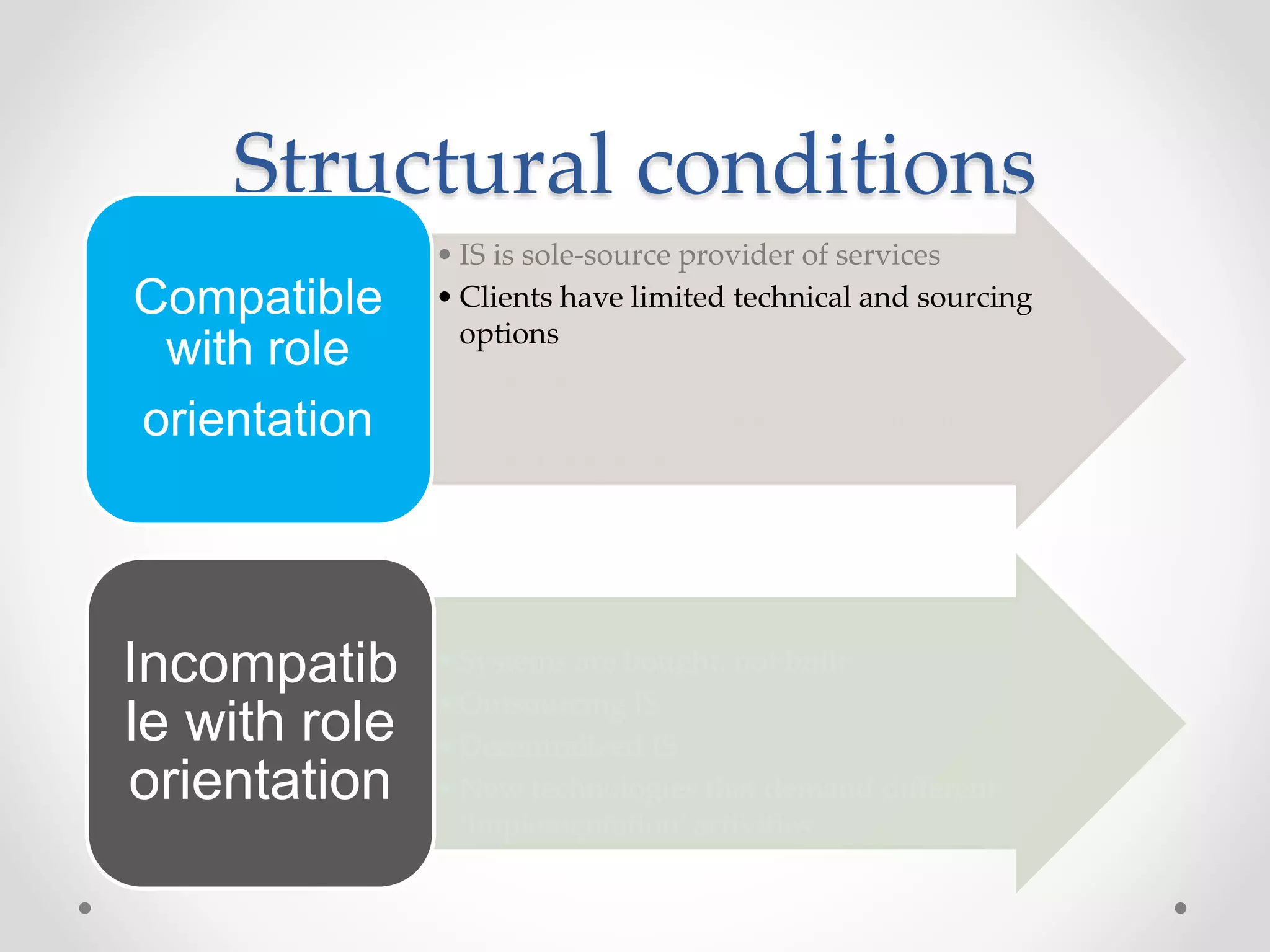
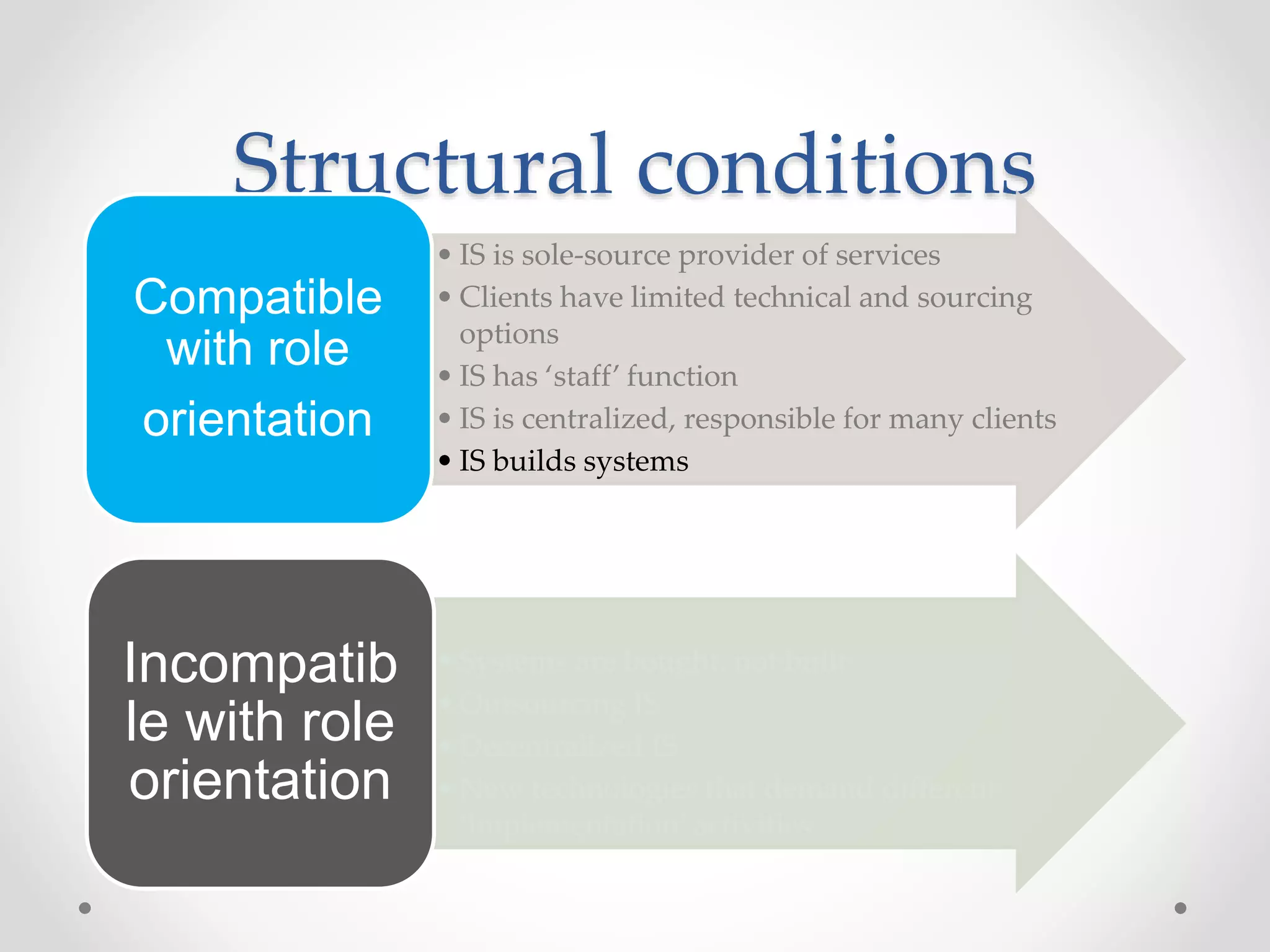
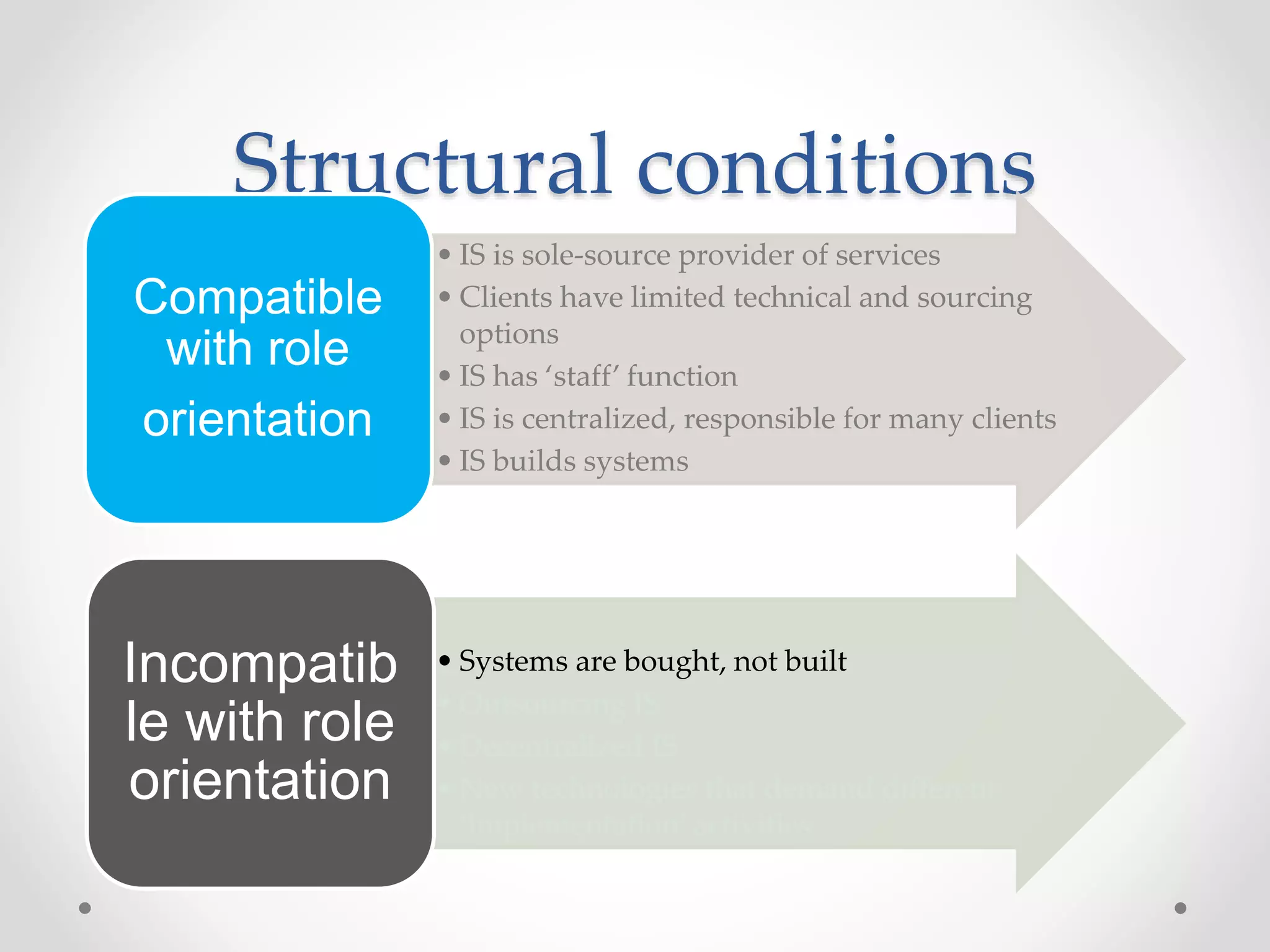
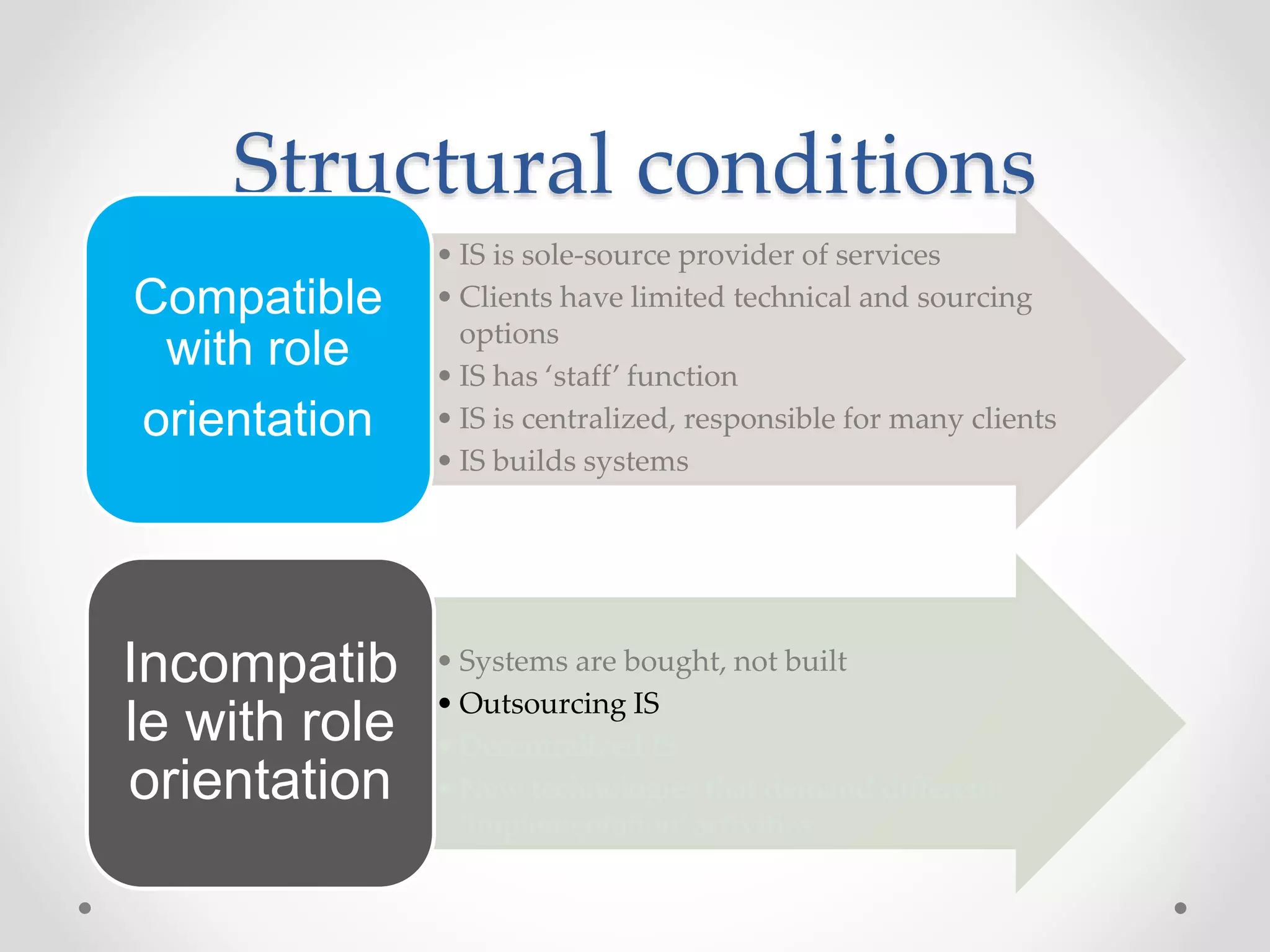
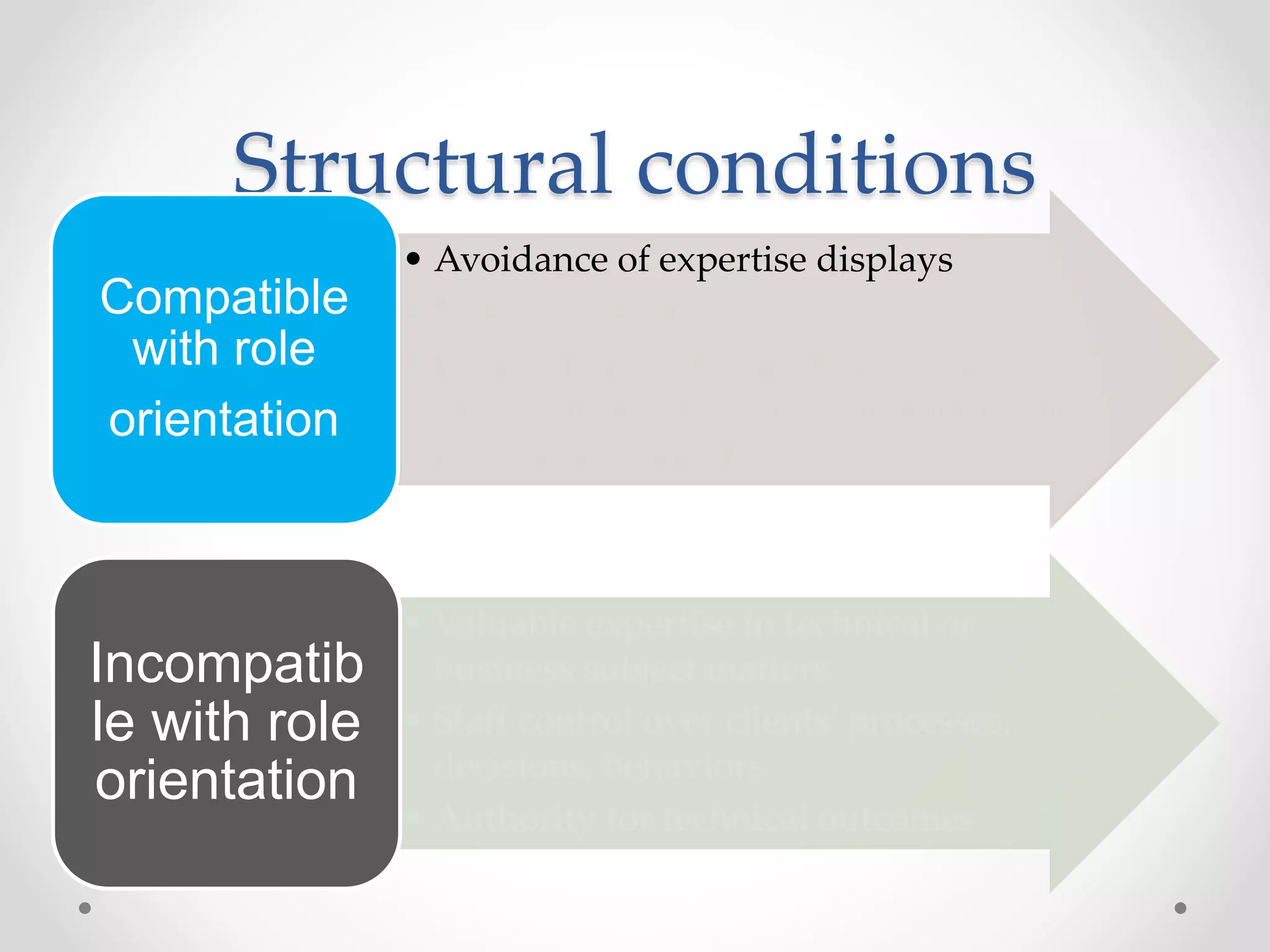
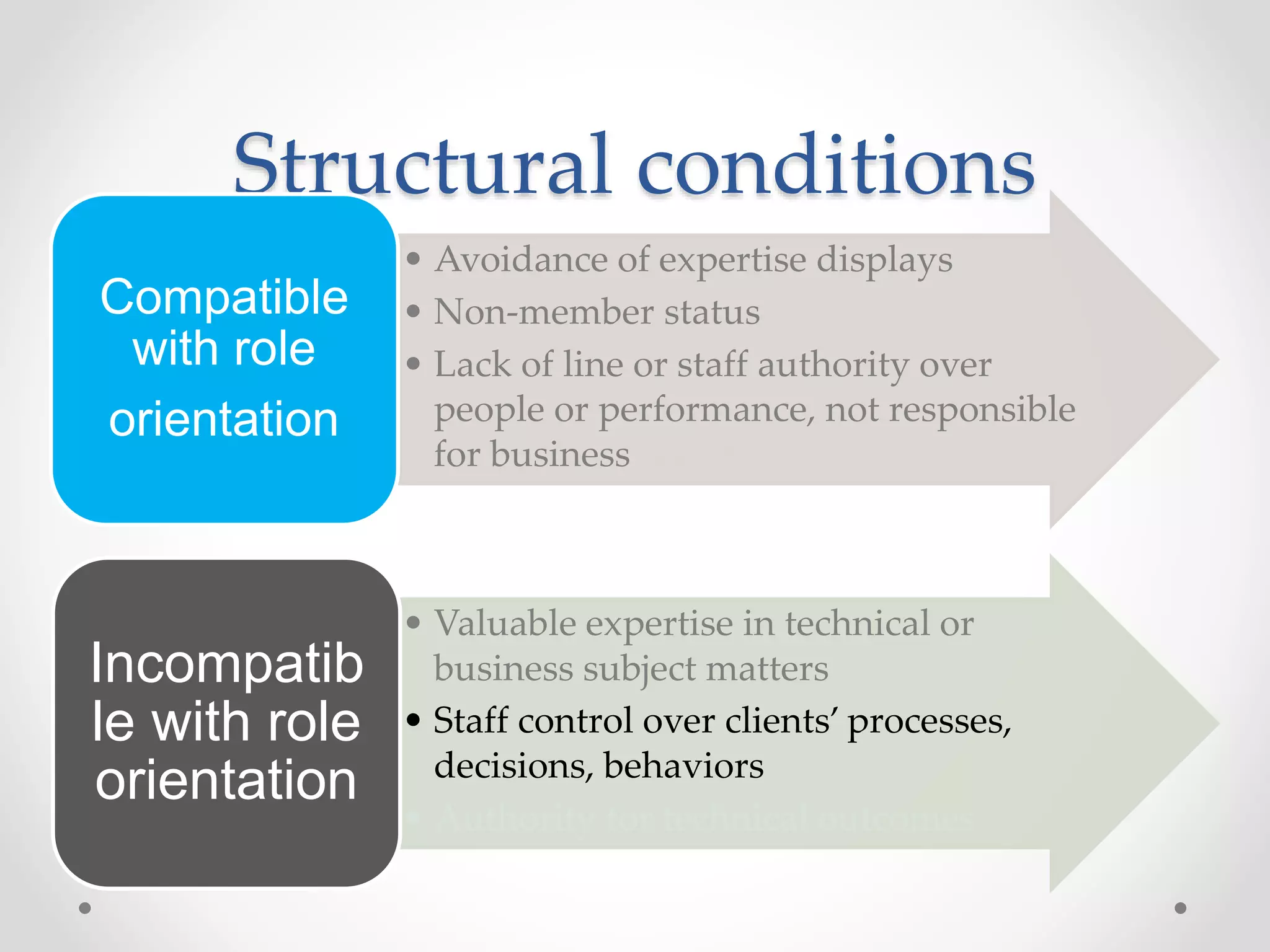
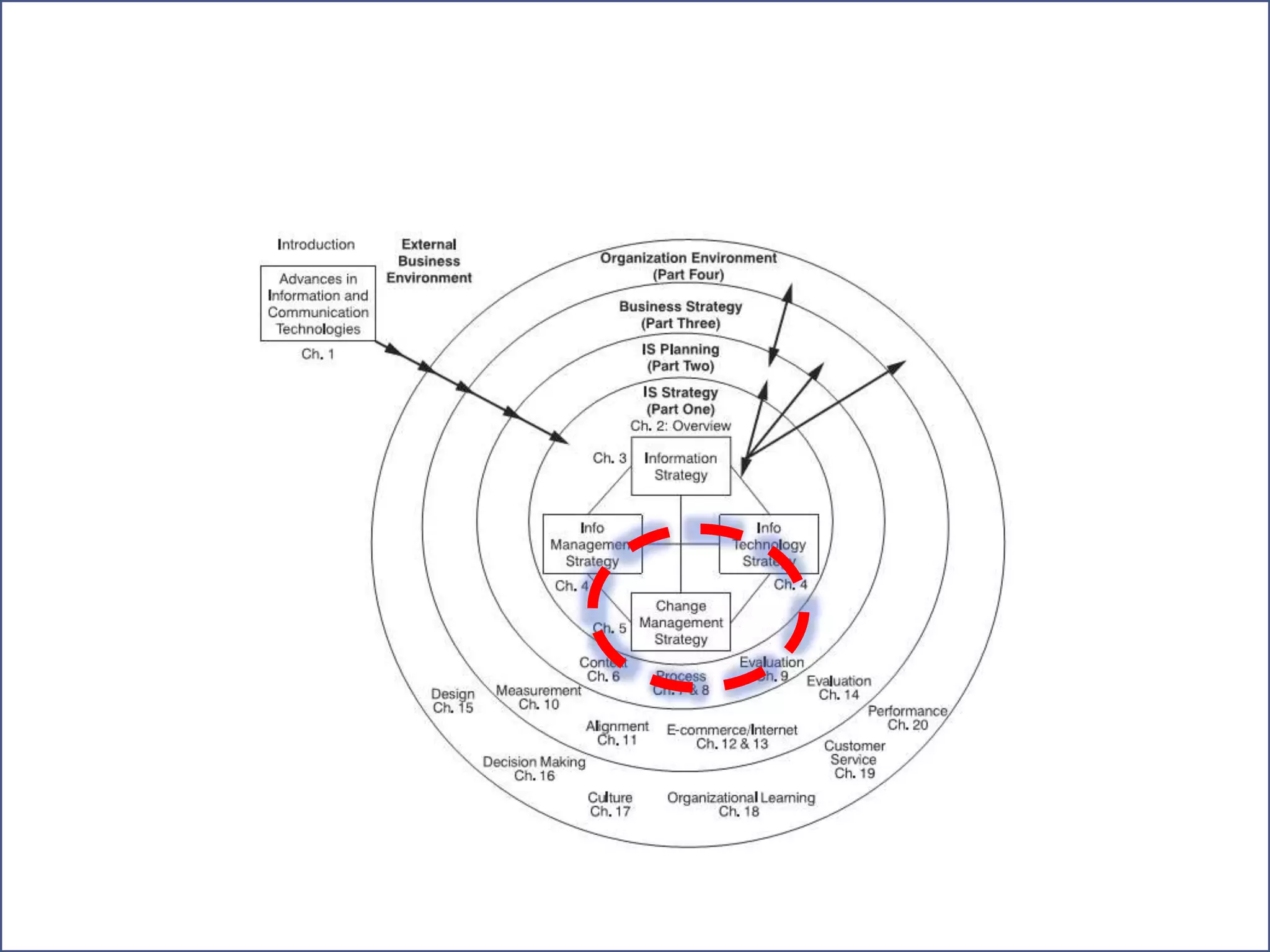
This document discusses three models of change management strategy for information systems (IS) specialists: the traditional IS model, the facilitator model, and the advocate model. The traditional model views technology as the driver of change and the IS specialist as an expert responsible only for technical matters. This can lead to reduced credibility and inhibit organizational change. The facilitator model sees people, not technology, as the drivers of change and positions the IS specialist as a facilitator of group processes to build user capacity. The advocate model positions the IS specialist as responsible for achieving organizational change through technology.





















![Many IT failures
We’re [the IS group is] a common carrier – we make
no guarantees about data quality. As for the problem
of obsolescence, if they [the users] don’t know it by
now it is not my job to tell them. (Orlikowski and Gash,
1994)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/changemanagementstrategyteamxyz-141109024527-conversion-gate01/75/Change-management-strategy_team_xyz-23-2048.jpg)