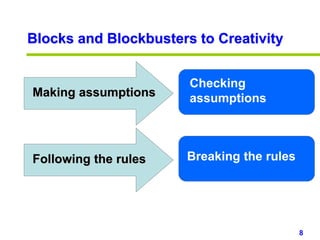
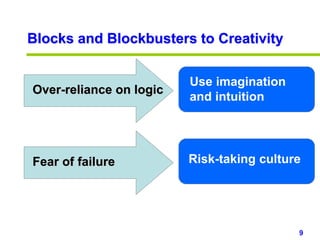
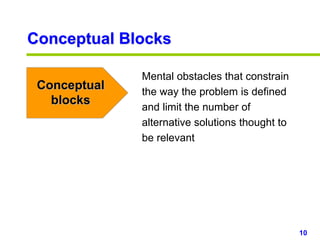
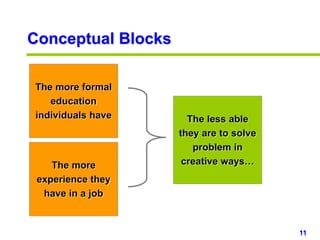
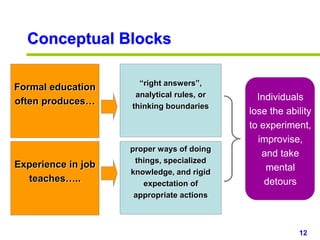
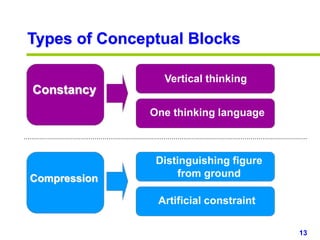
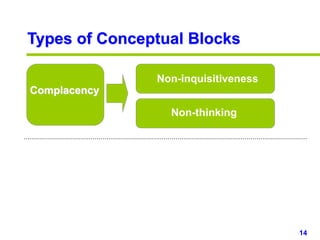
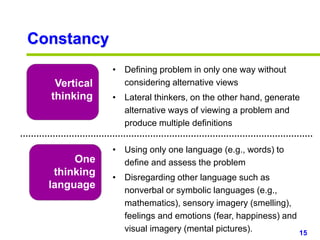
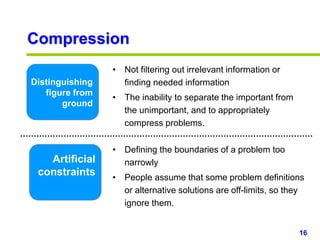
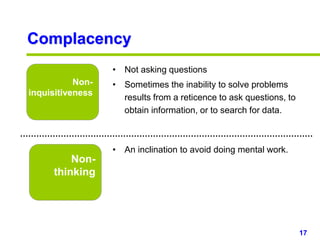
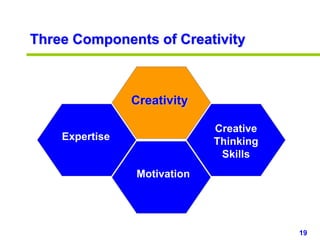
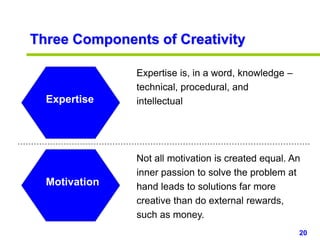
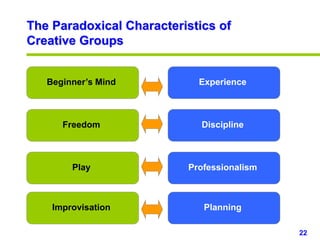
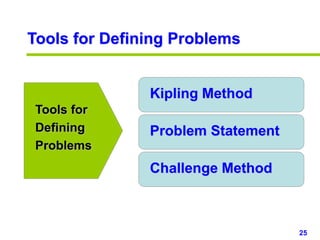
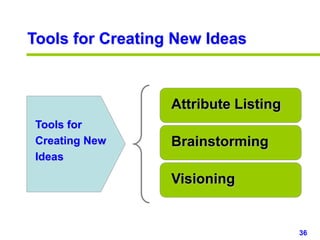
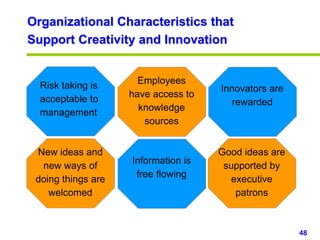
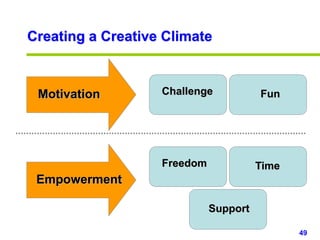
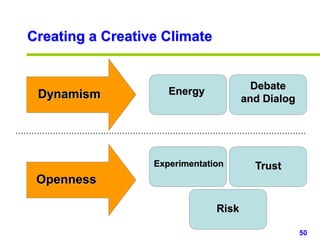
This document provides an overview of creativity skills for HR managers. It discusses conceptual blocks to creativity such as constancy, compression, and complacency. The three components of creativity are expertise, motivation, and creative thinking skills. Tools for defining problems creatively include the Kipling method, problem statements, and challenge methods. Brainstorming, attribute listing, and visioning are presented as tools for generating new ideas. Finally, the document outlines characteristics that support an organizational climate conducive to creativity, such as risk-taking, open information sharing, and rewarding innovators.