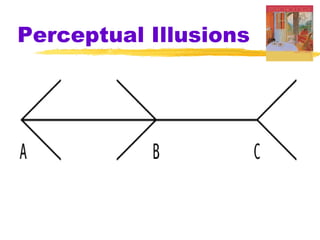
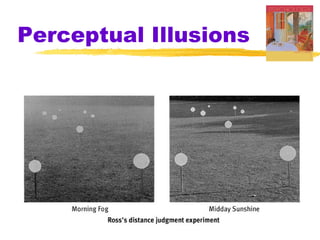
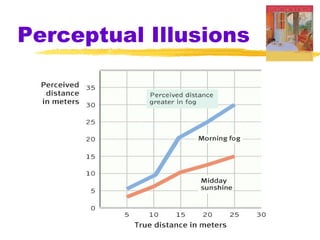
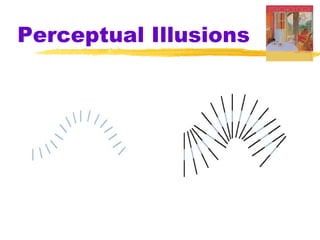
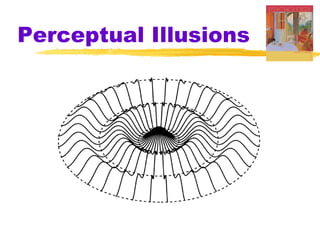
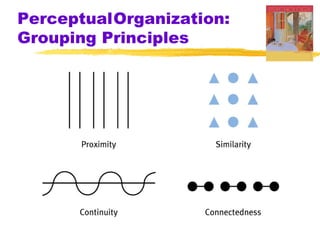
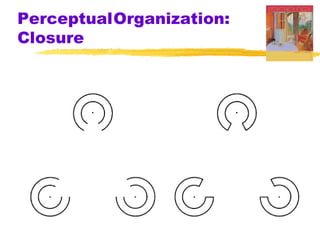
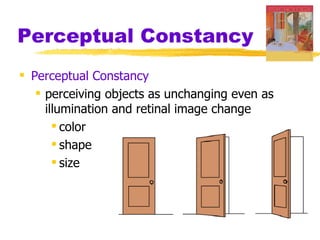
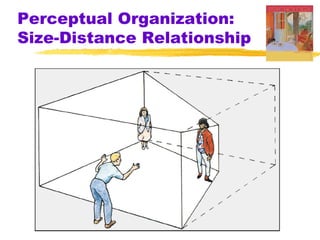
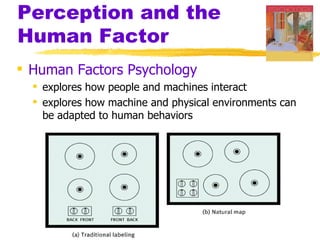
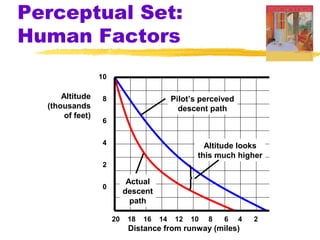
This chapter of the Psychology textbook discusses perception. It covers topics like selective attention, change blindness, perceptual illusions, gestalt grouping principles, figure-ground perception, depth perception through binocular and monocular cues, perceptual constancy, and schemas. It also discusses sensory restriction experiments, perceptual adaptation, perceptual set, human factors psychology, and debates around extrasensory perception.