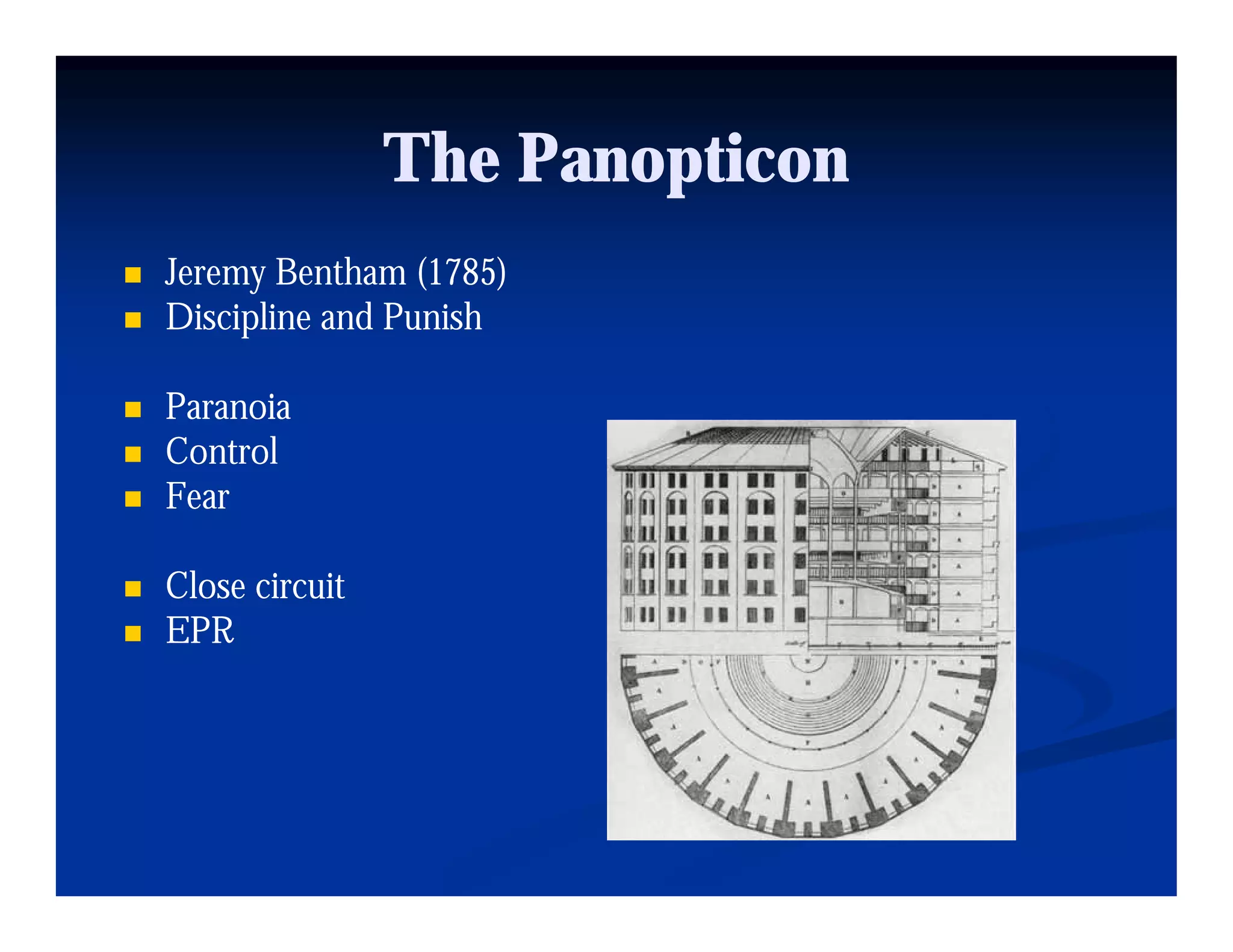
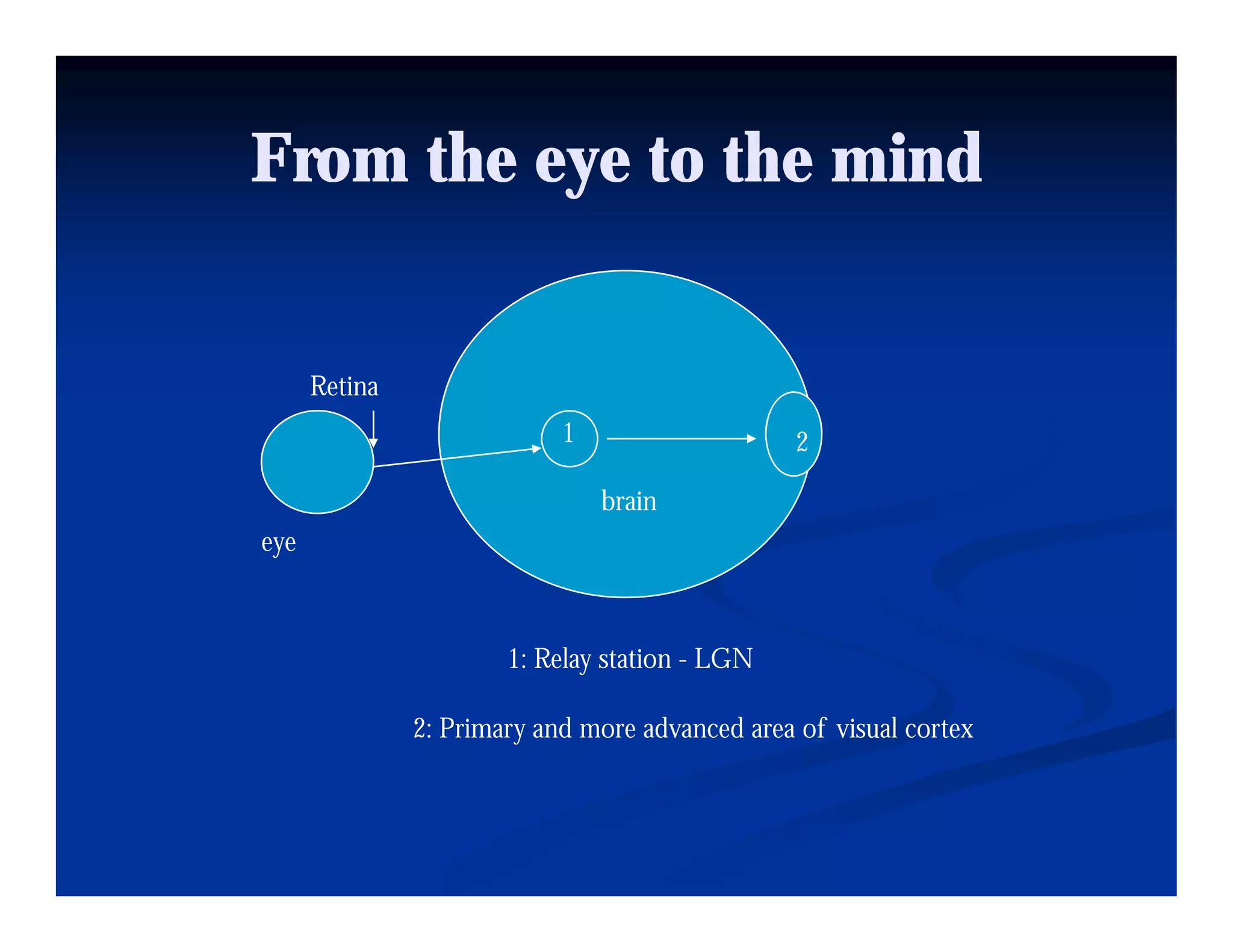
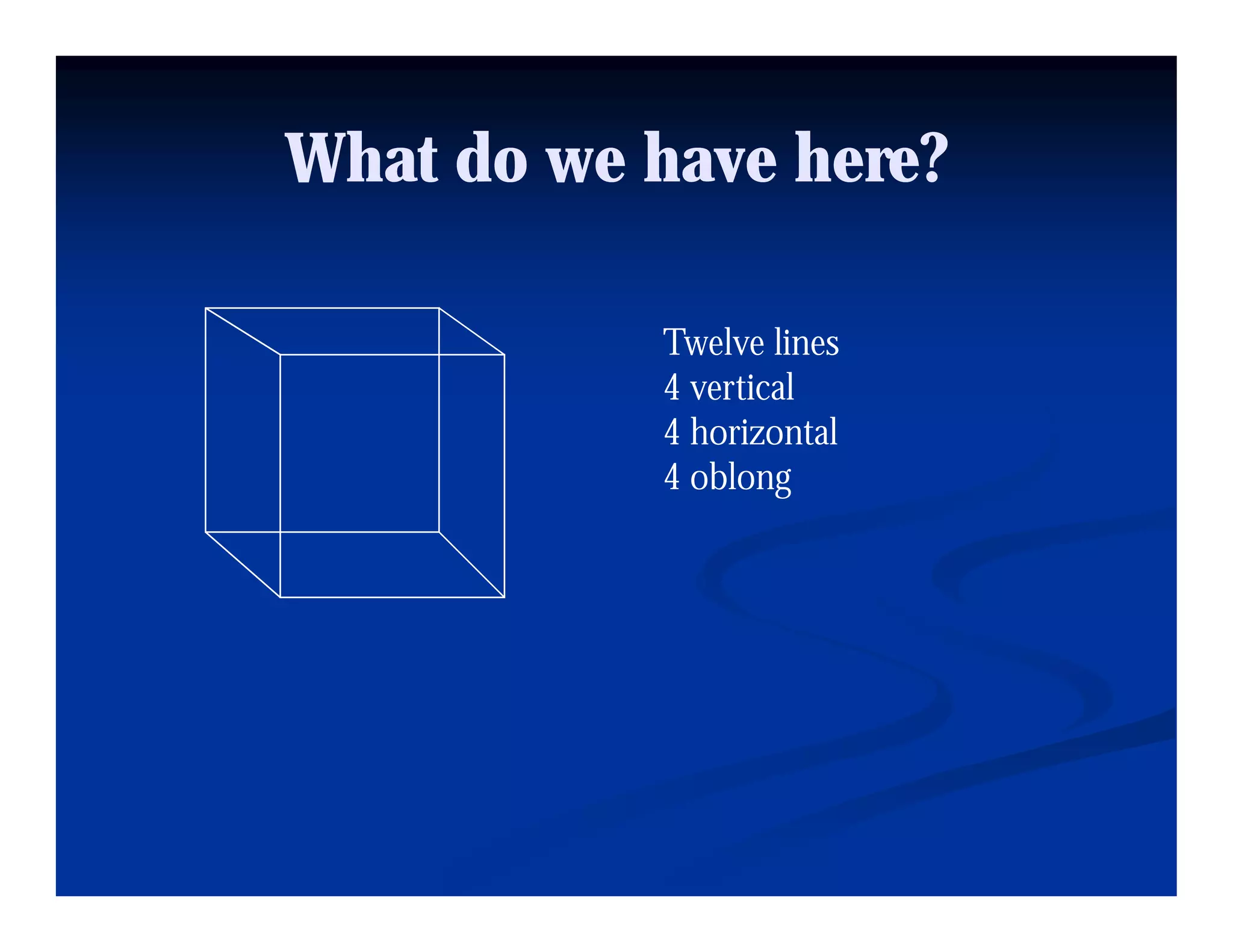
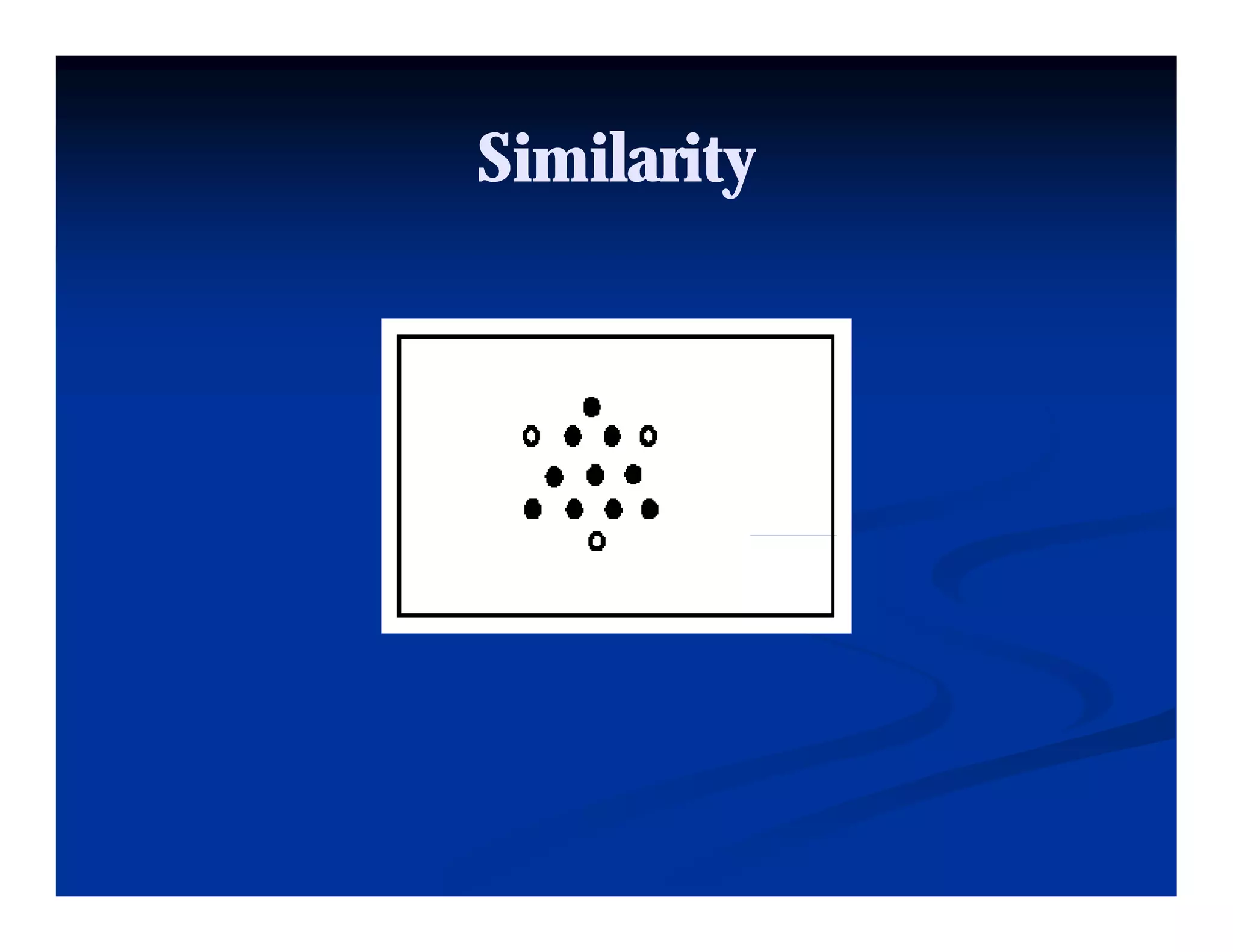
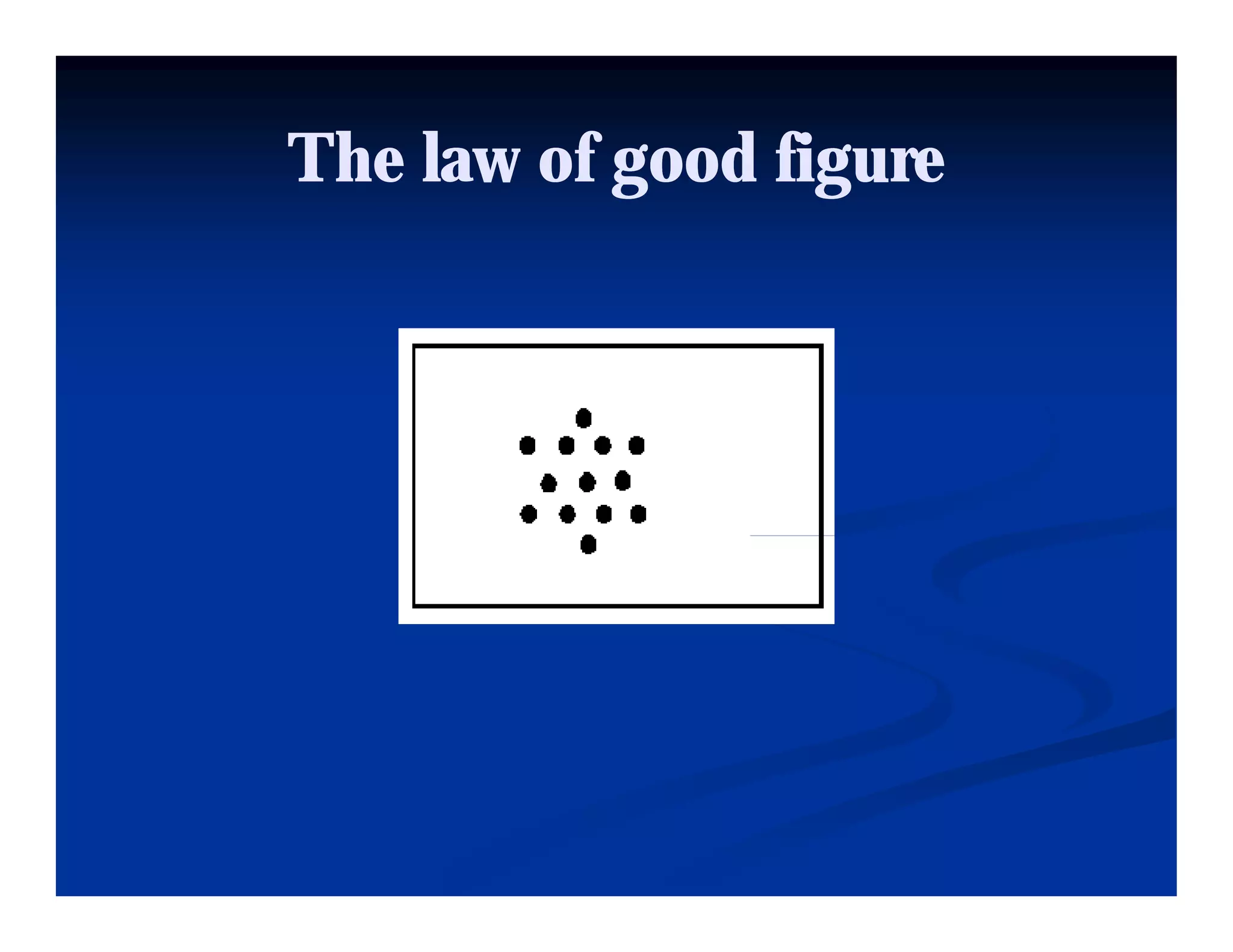
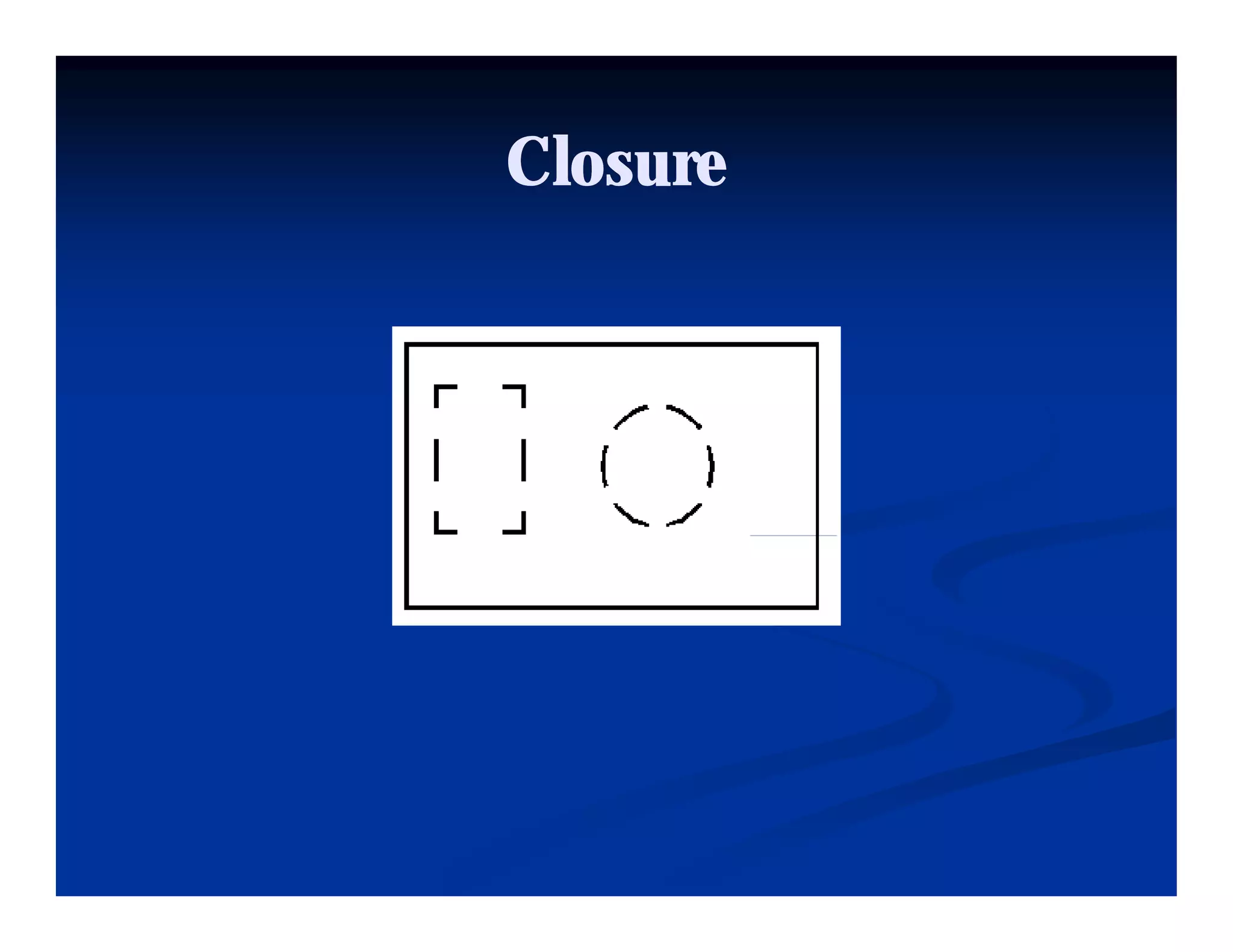
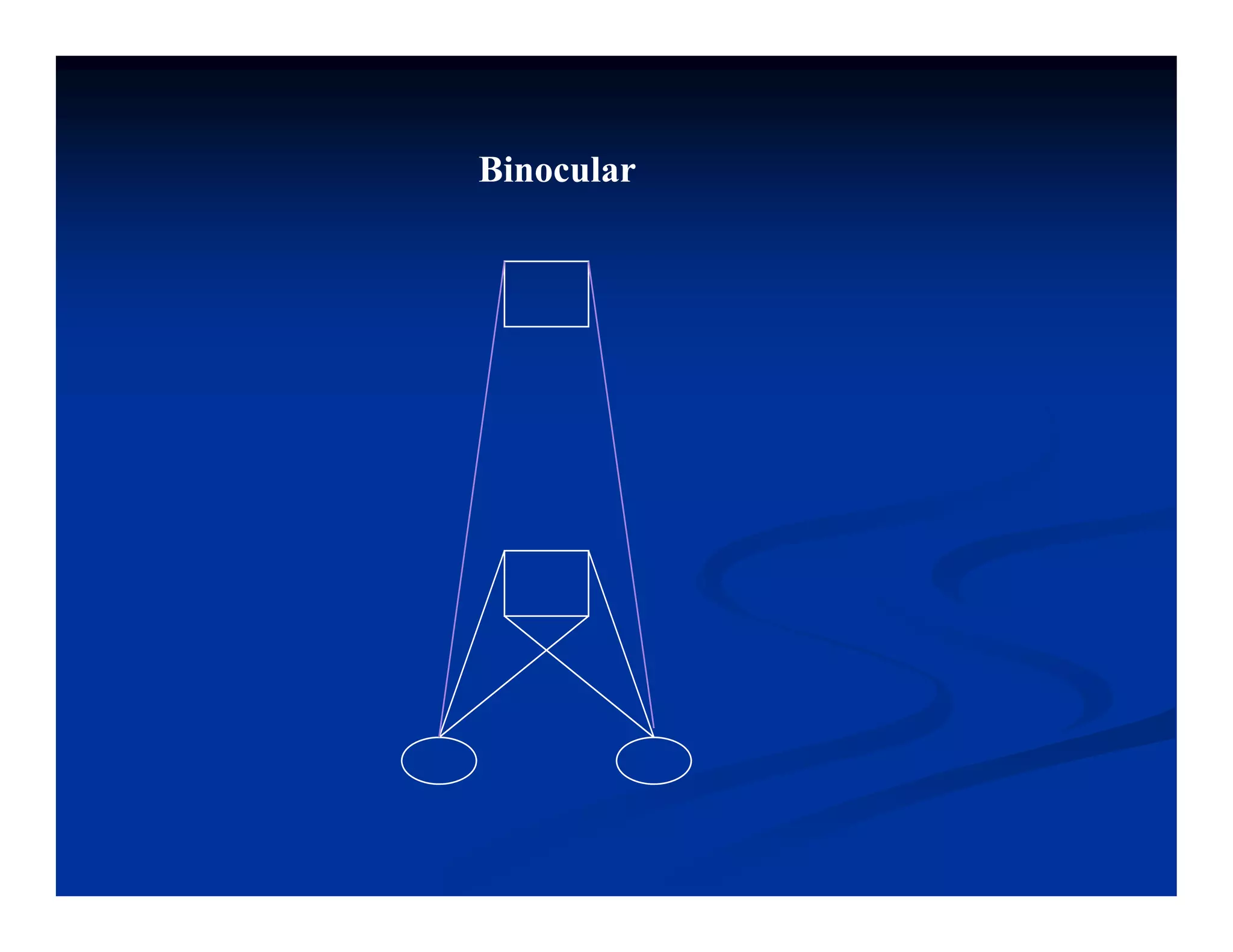
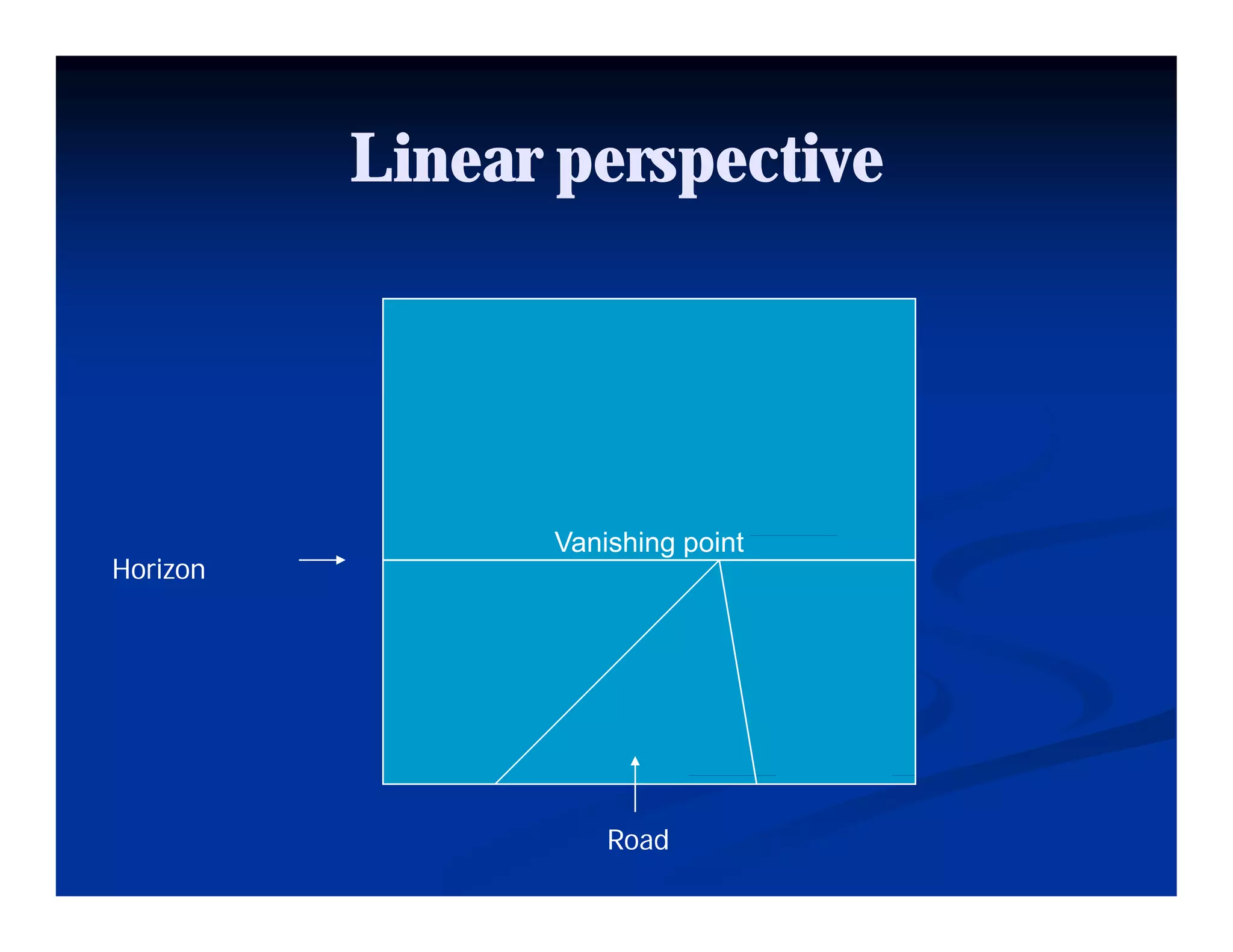
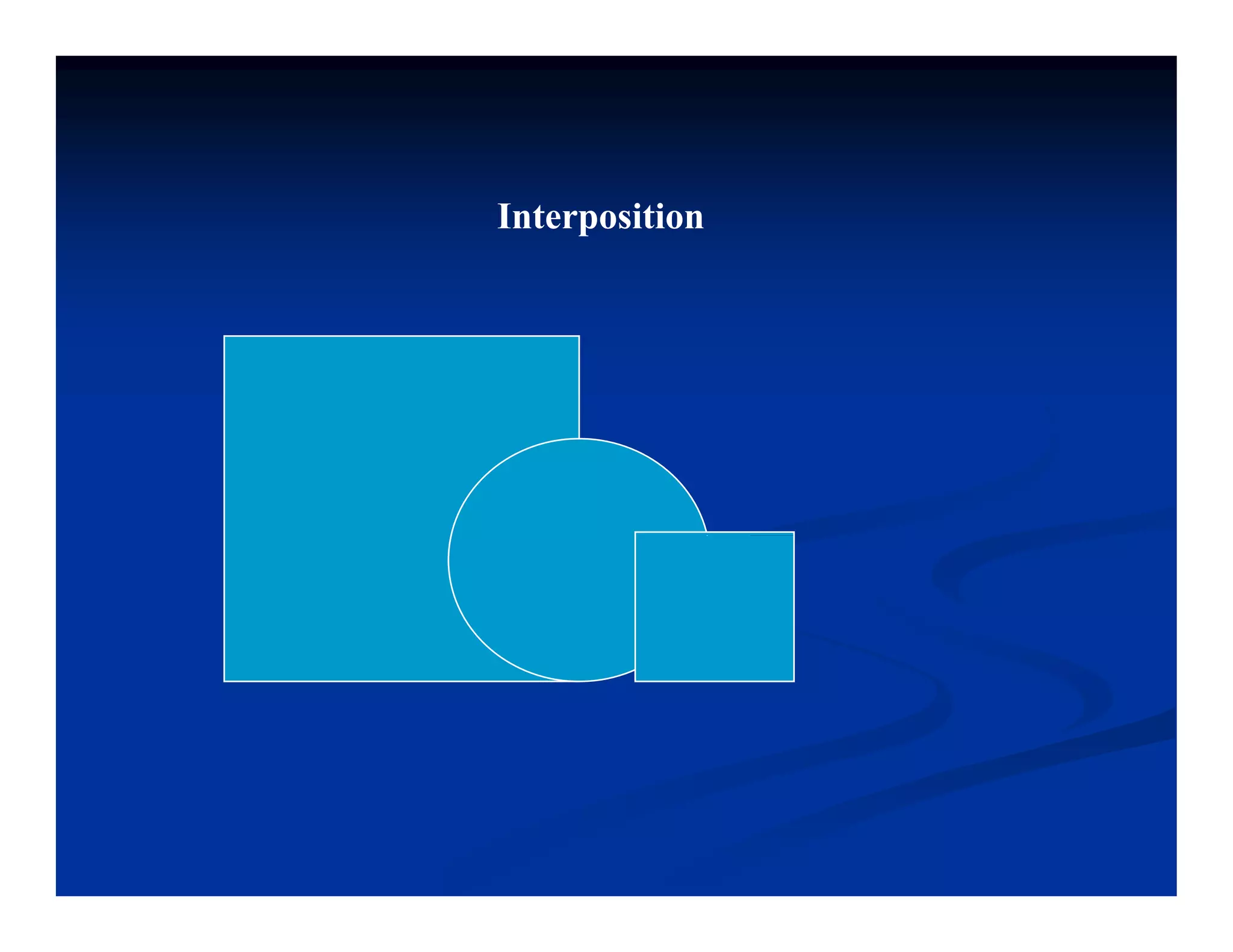
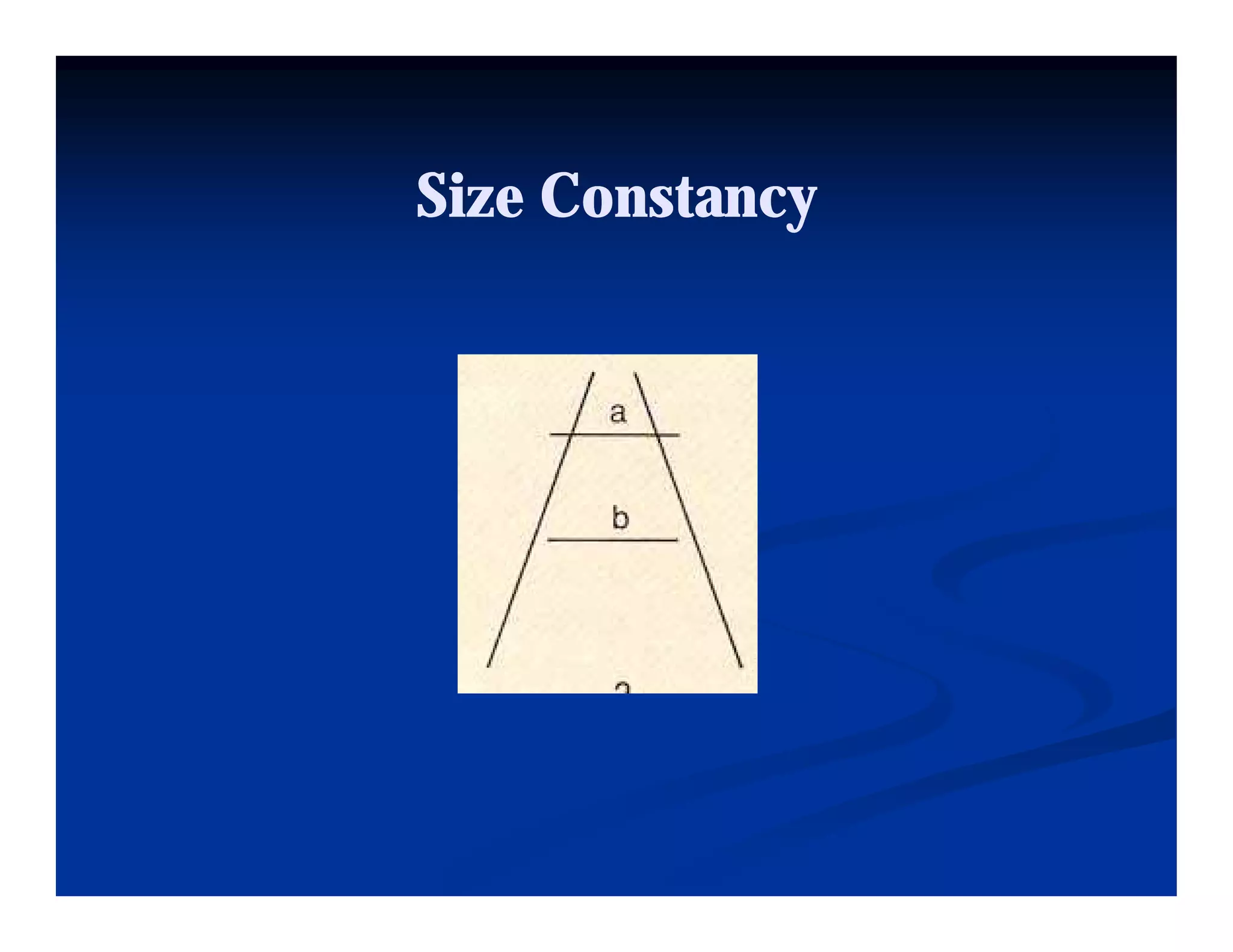
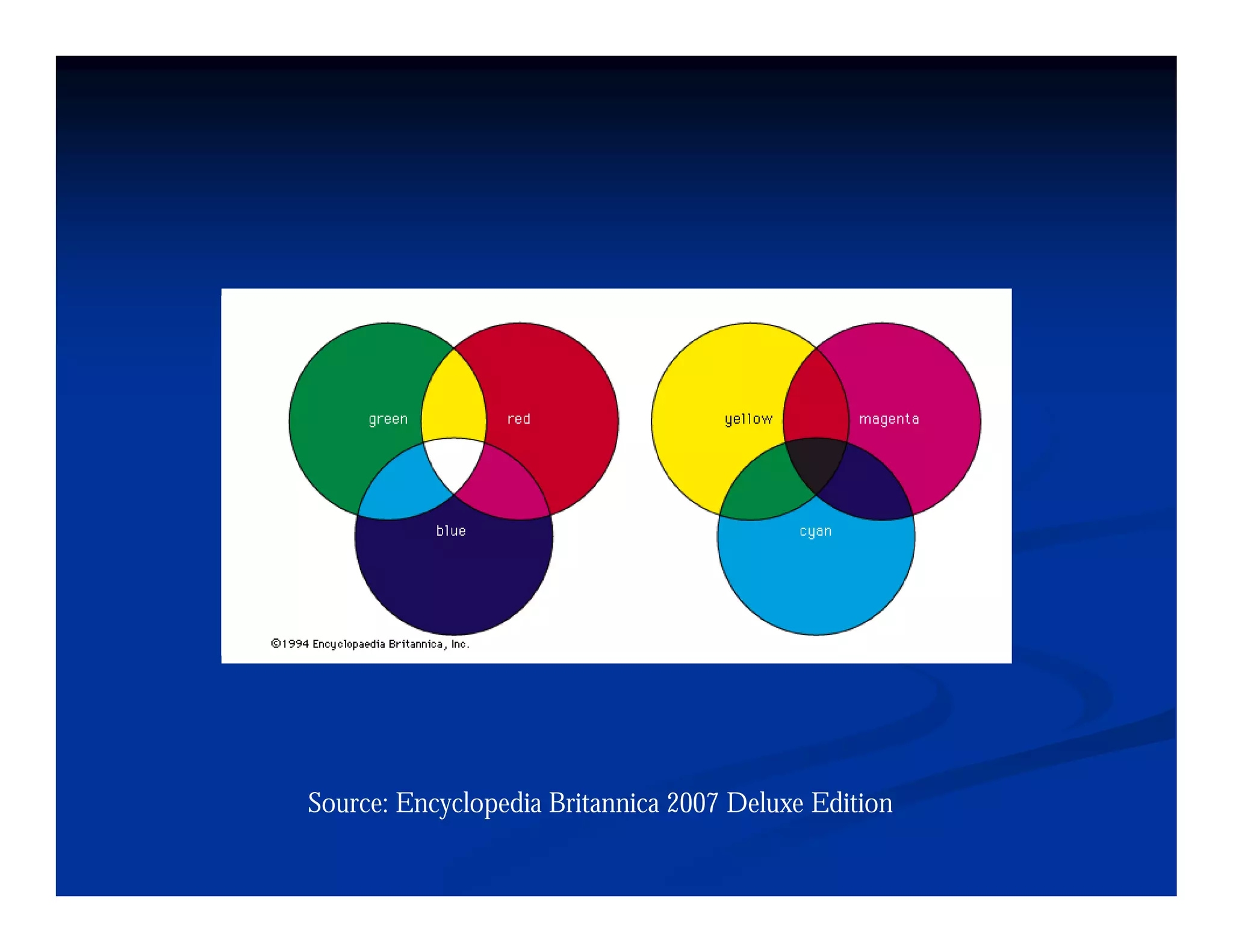
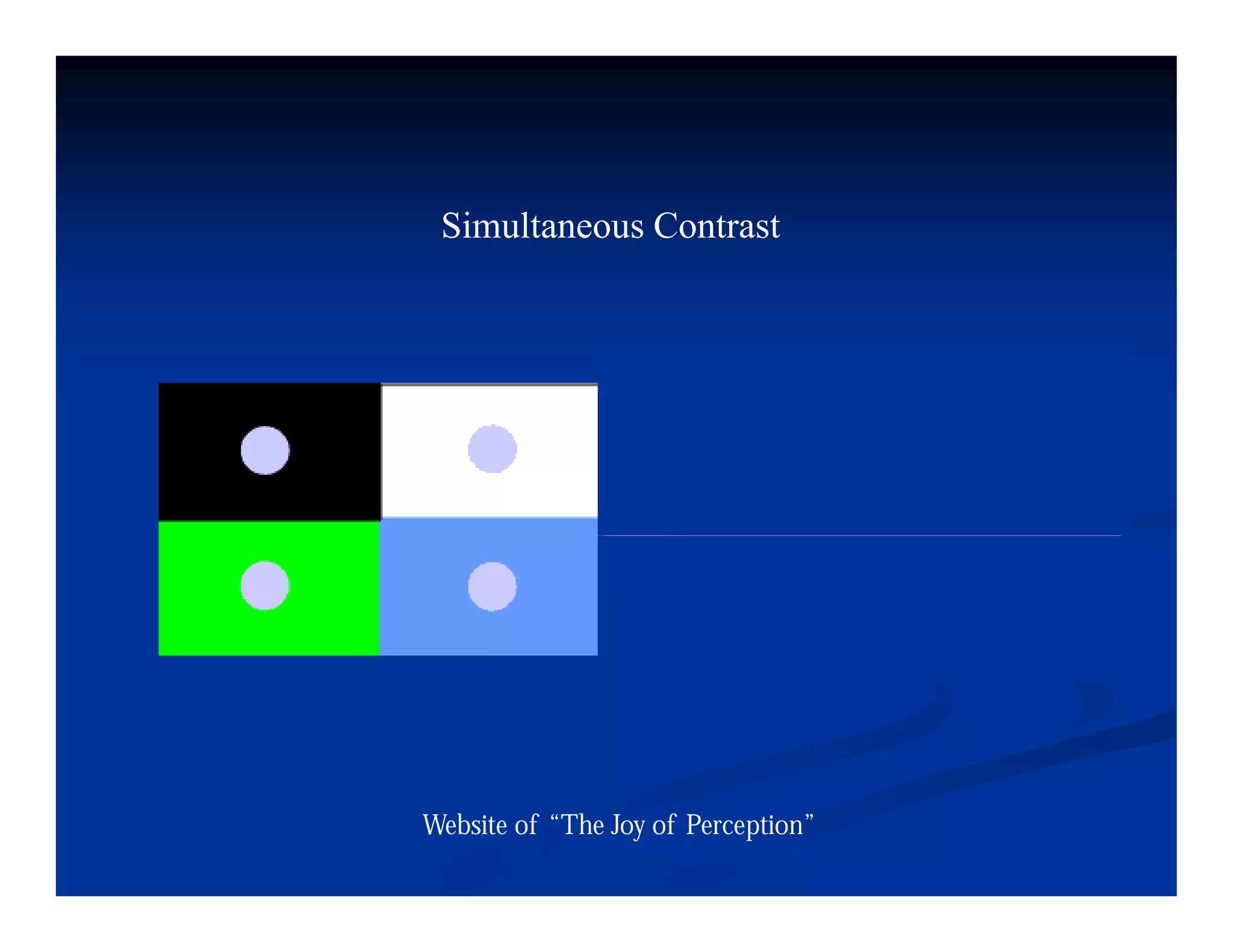
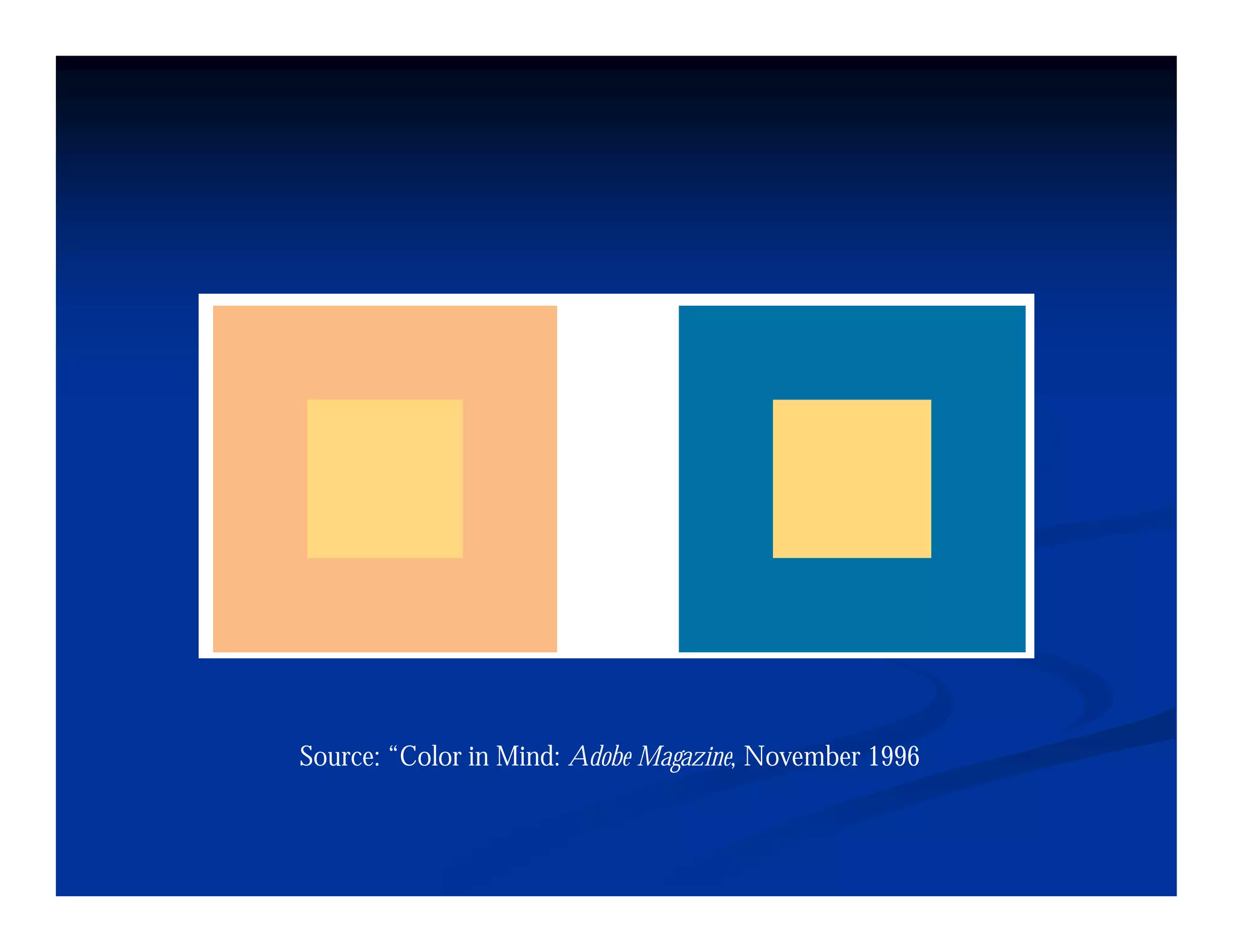
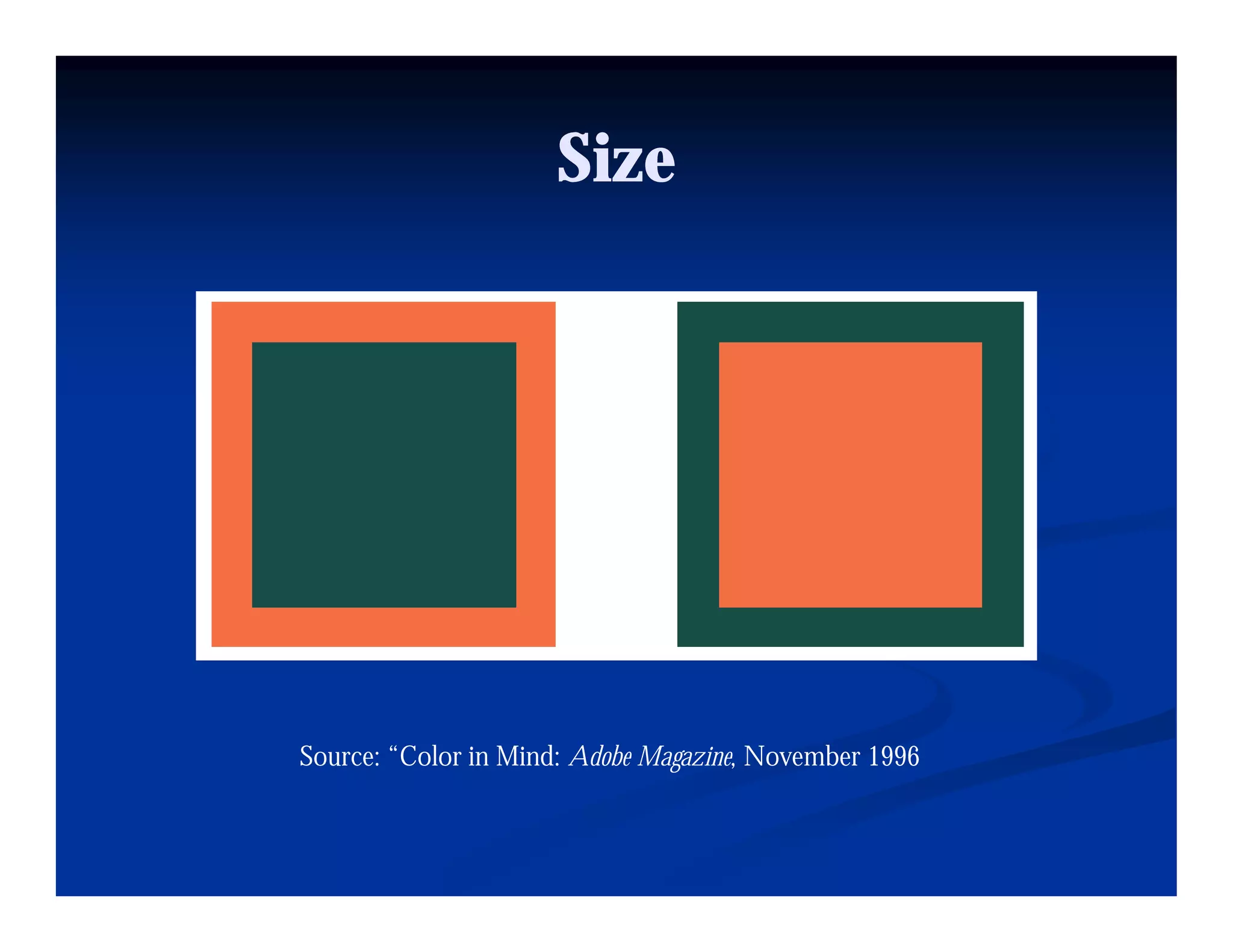
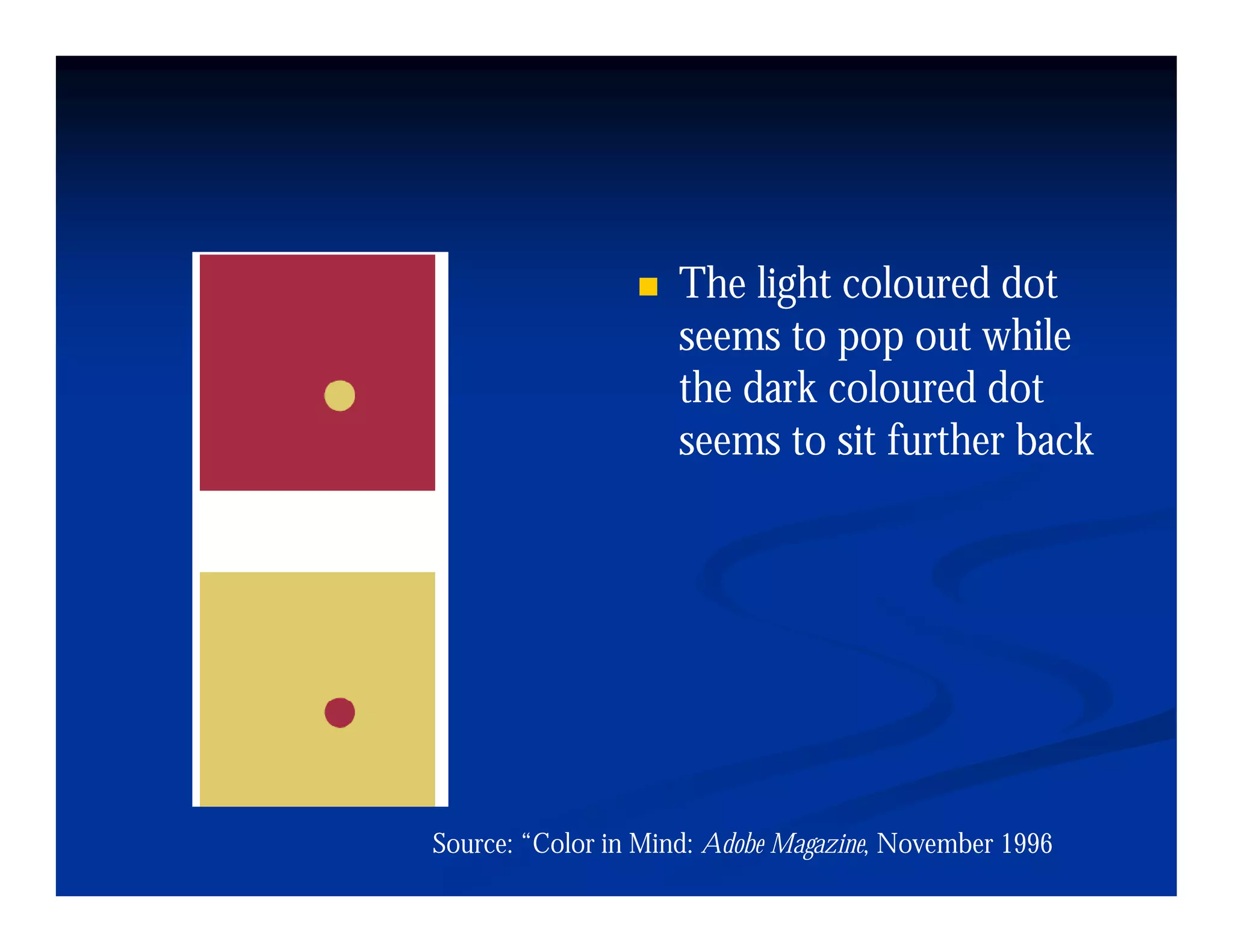
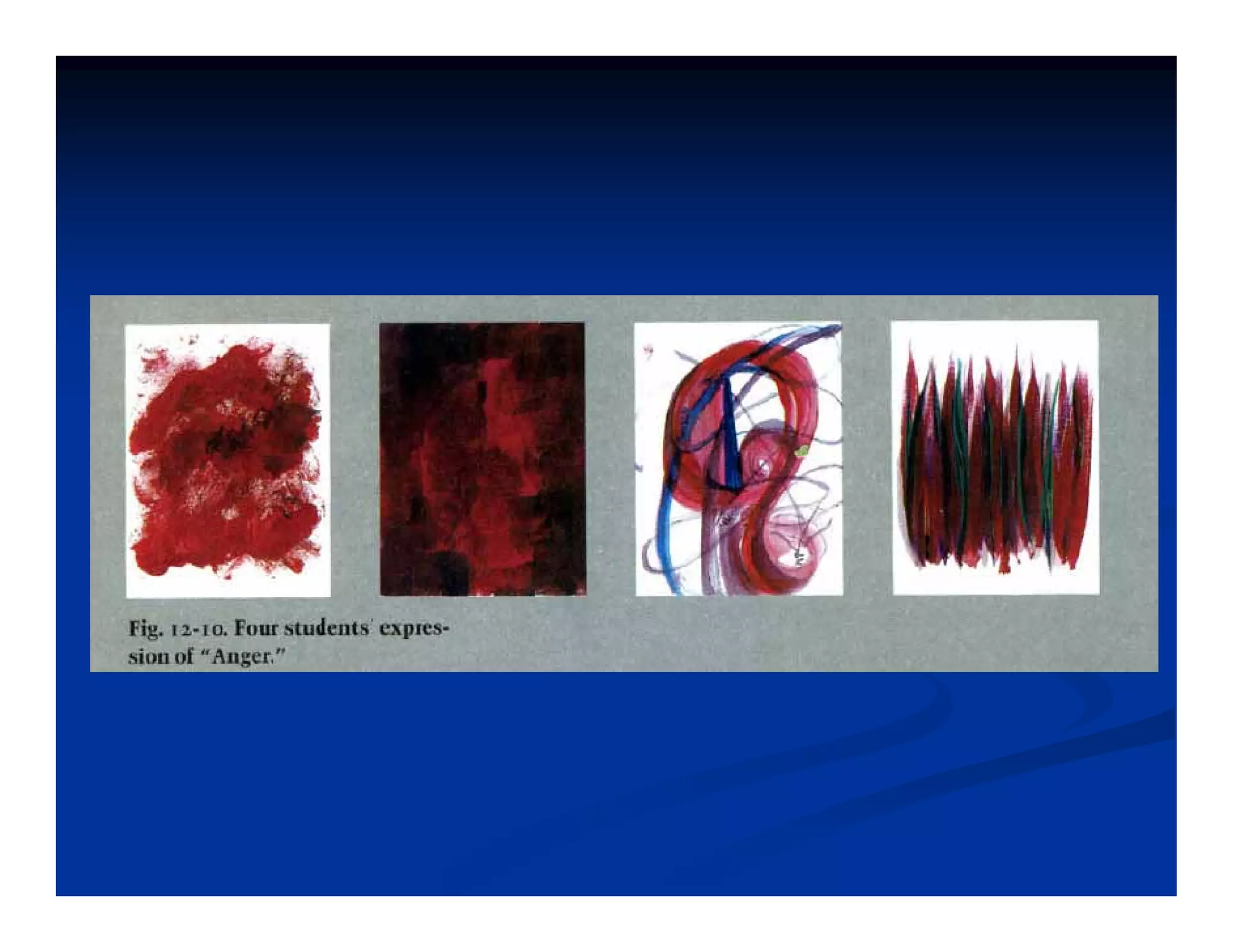
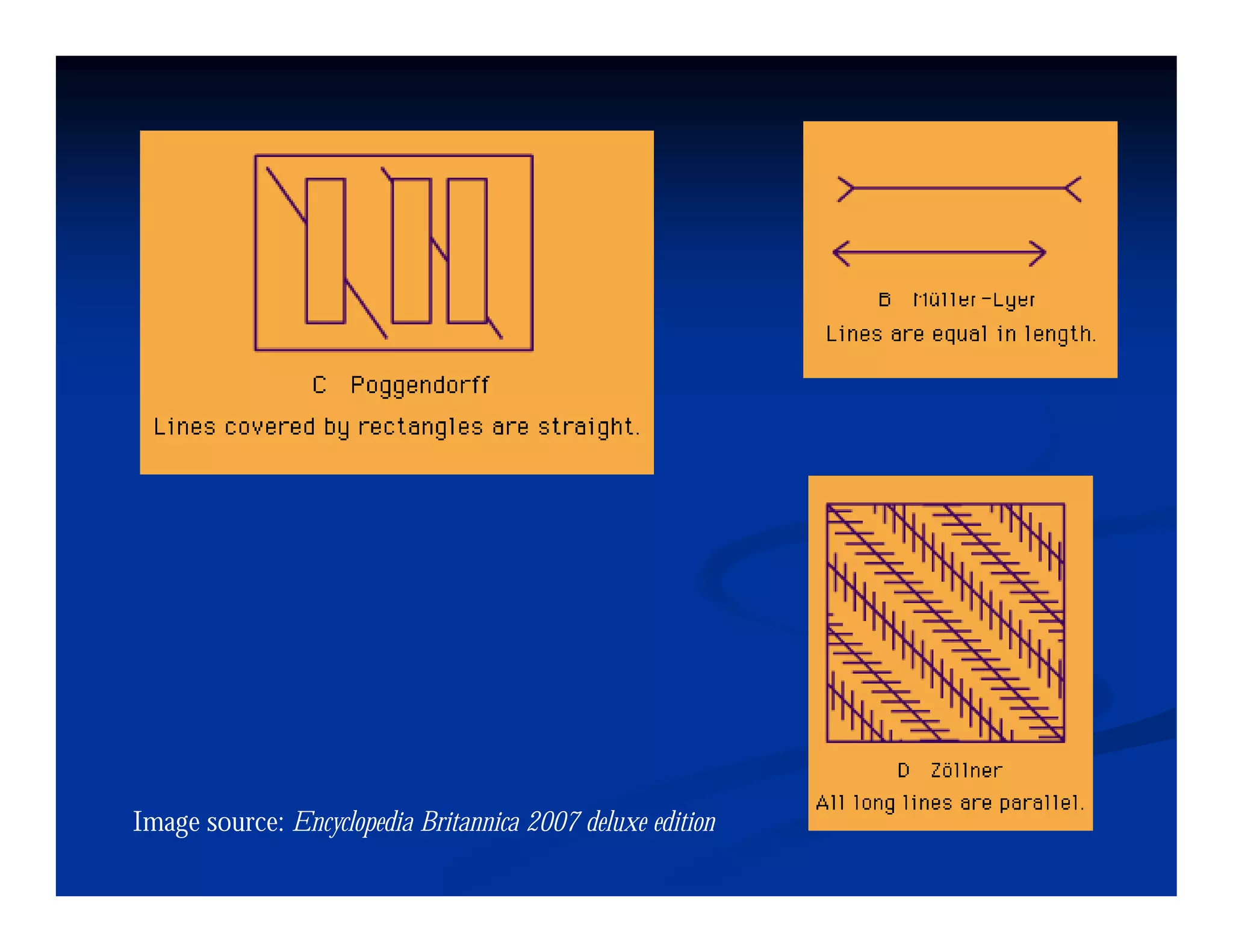
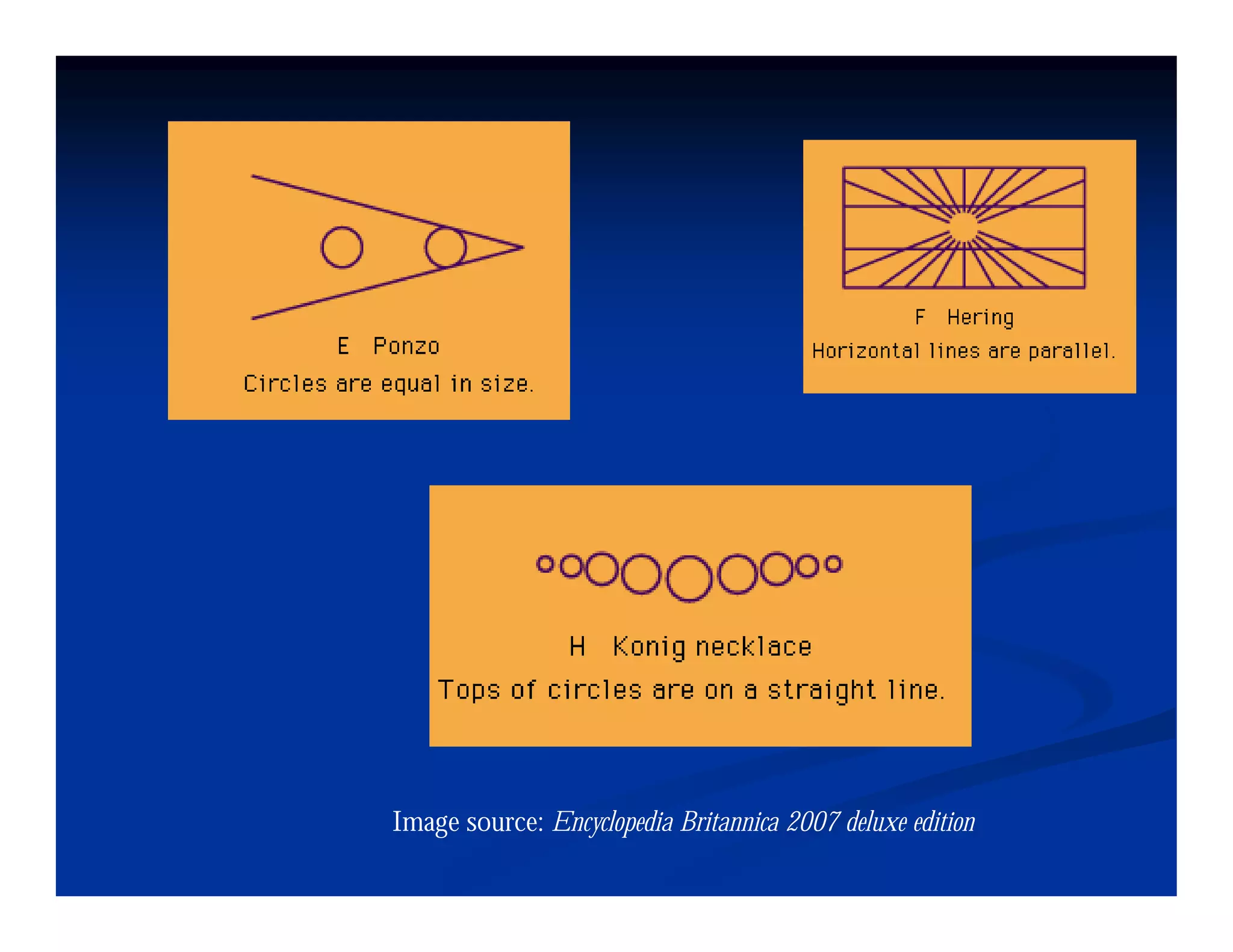
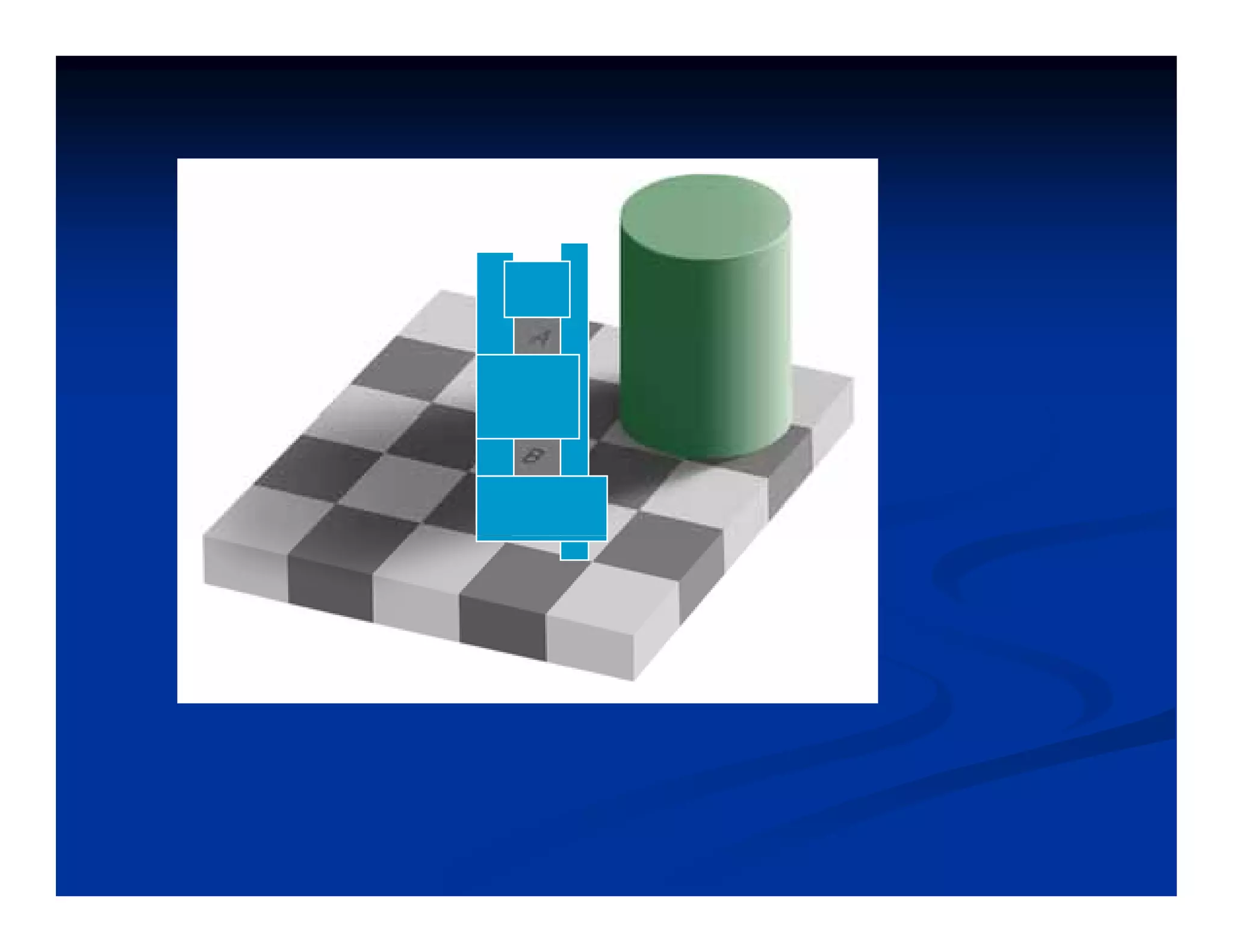
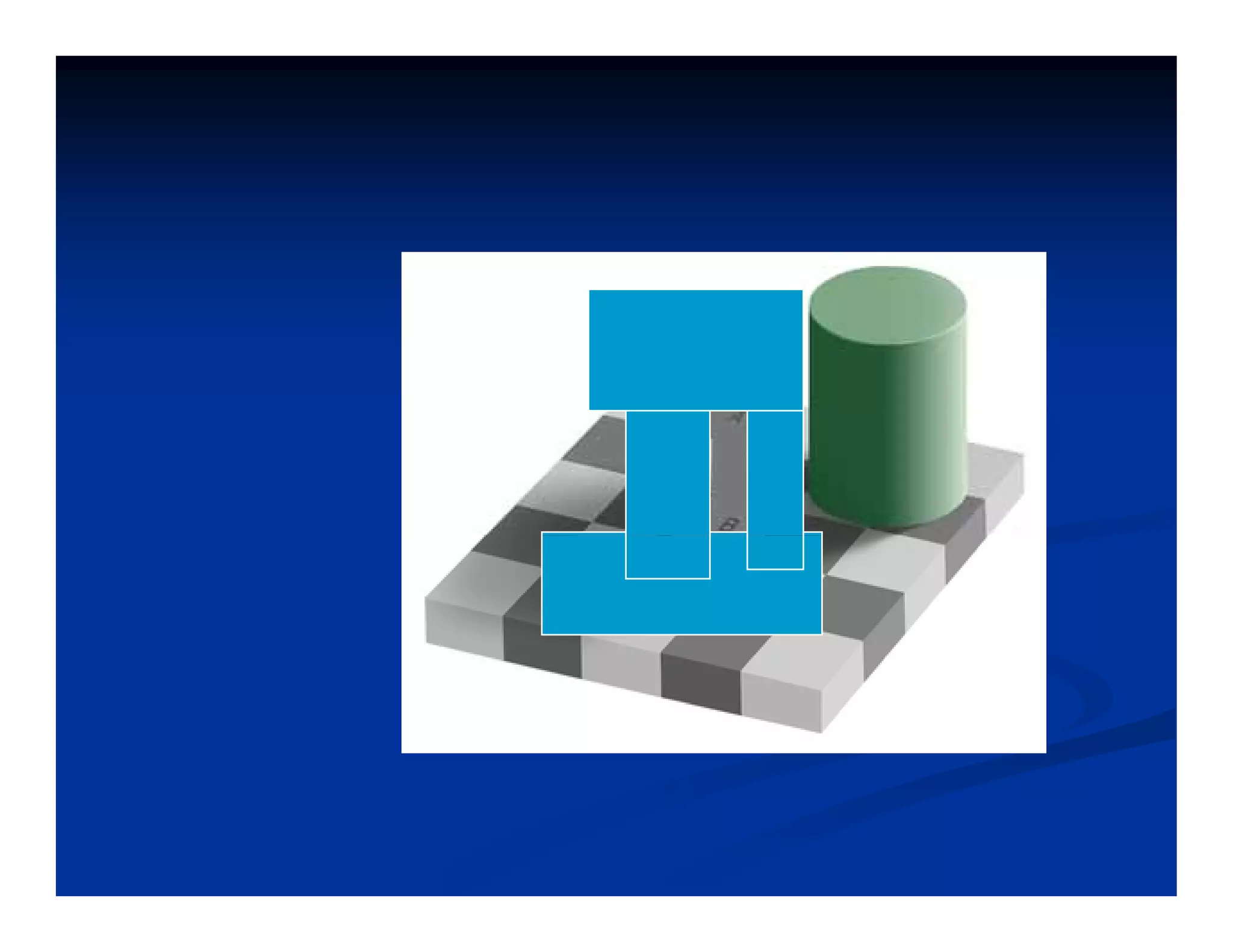
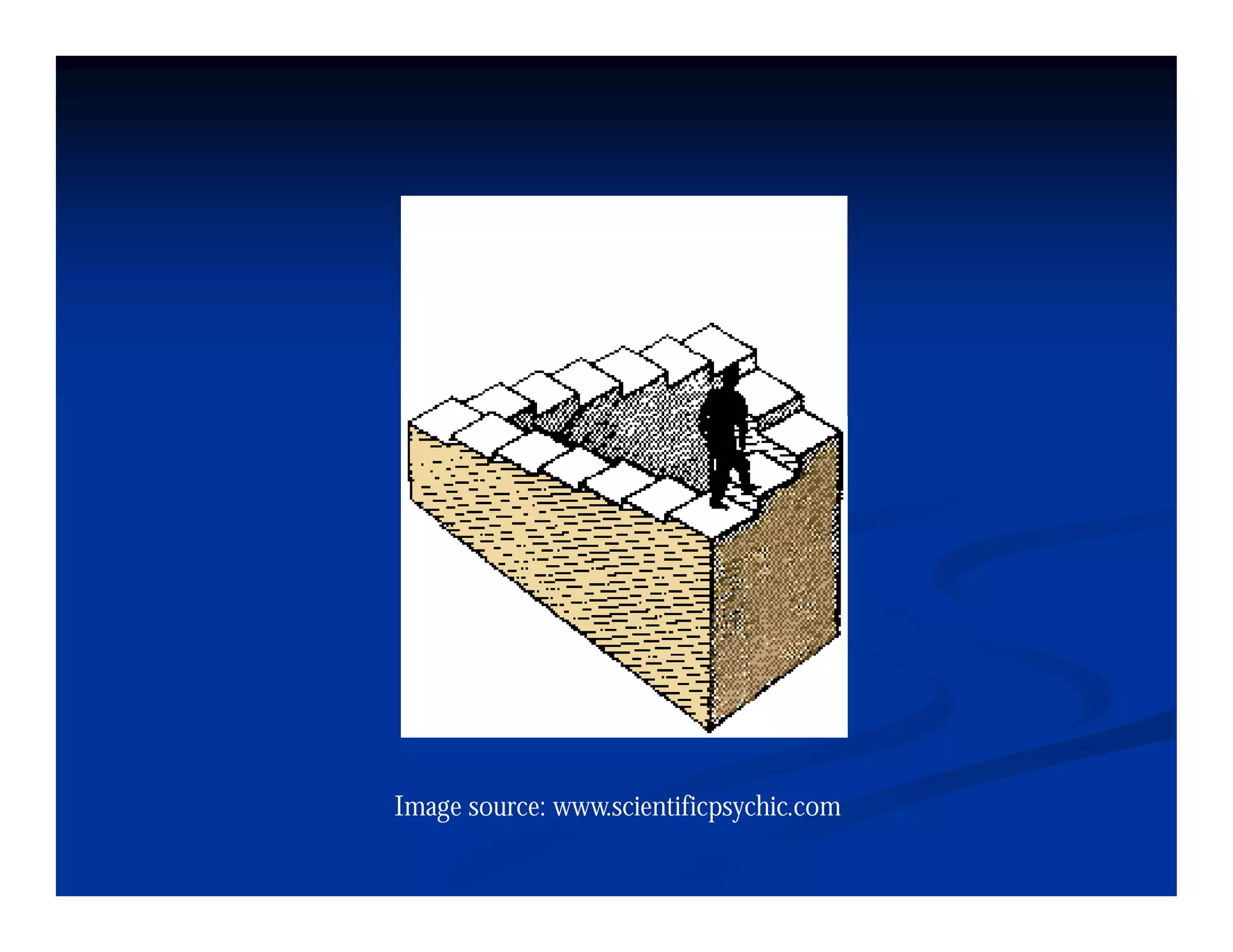
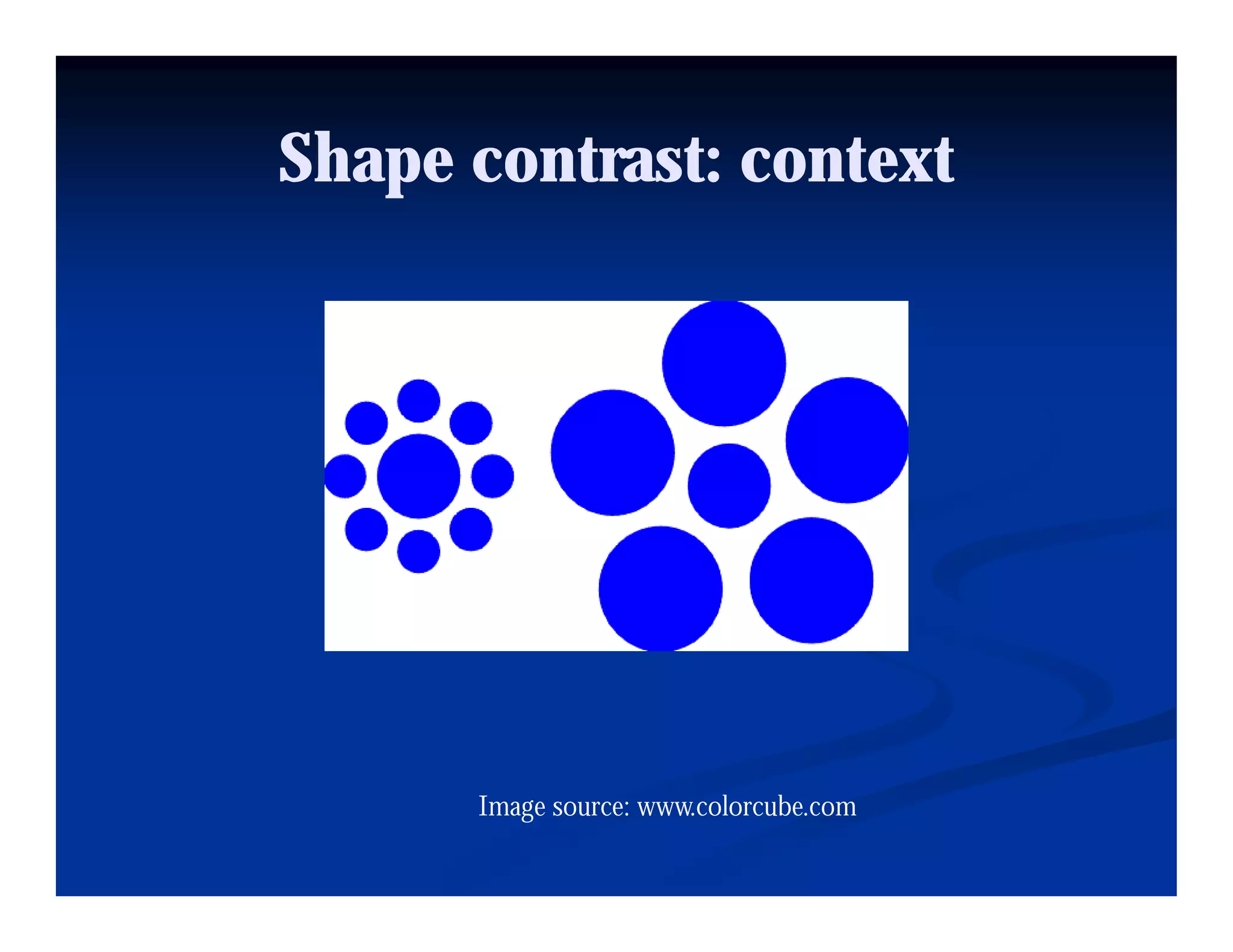
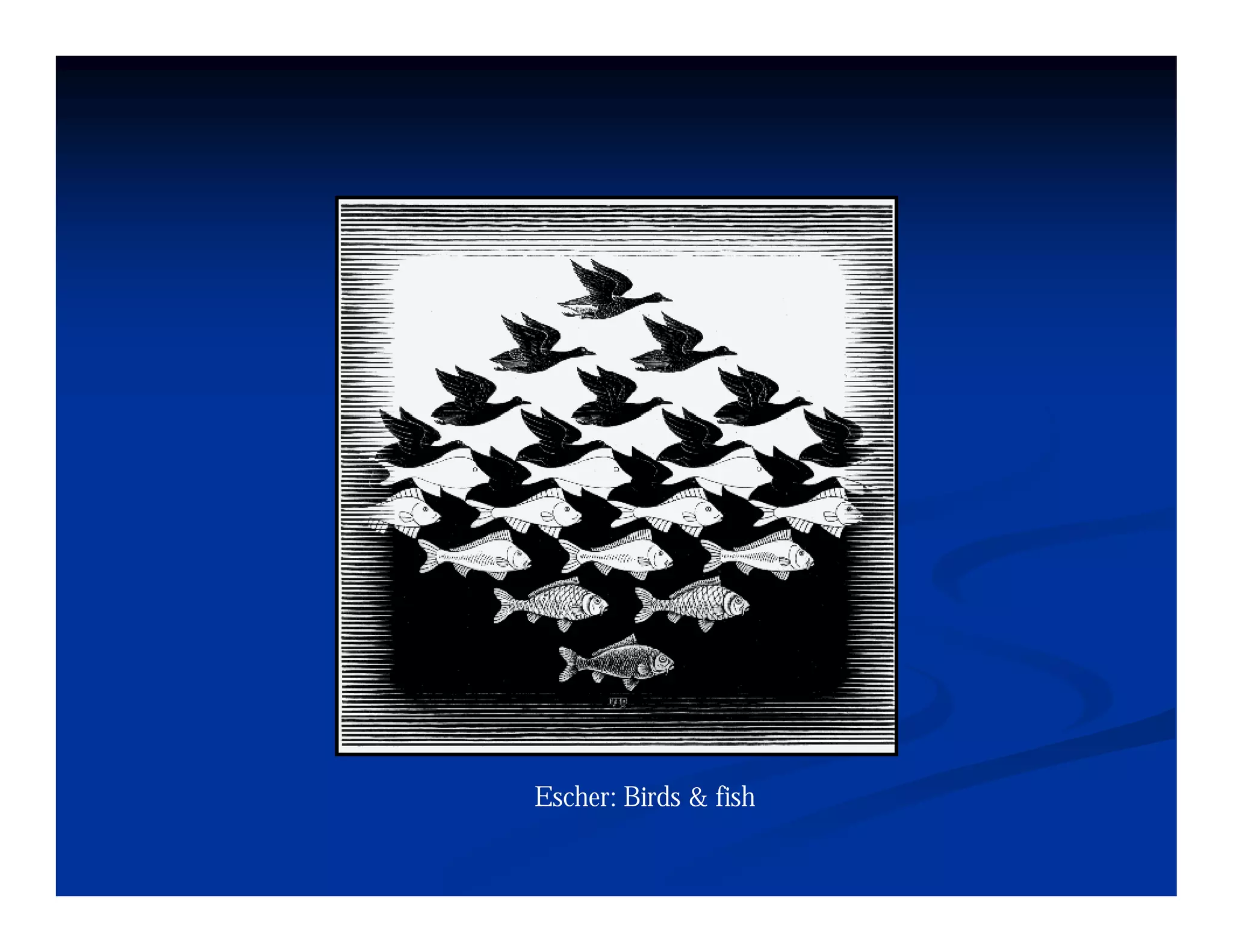
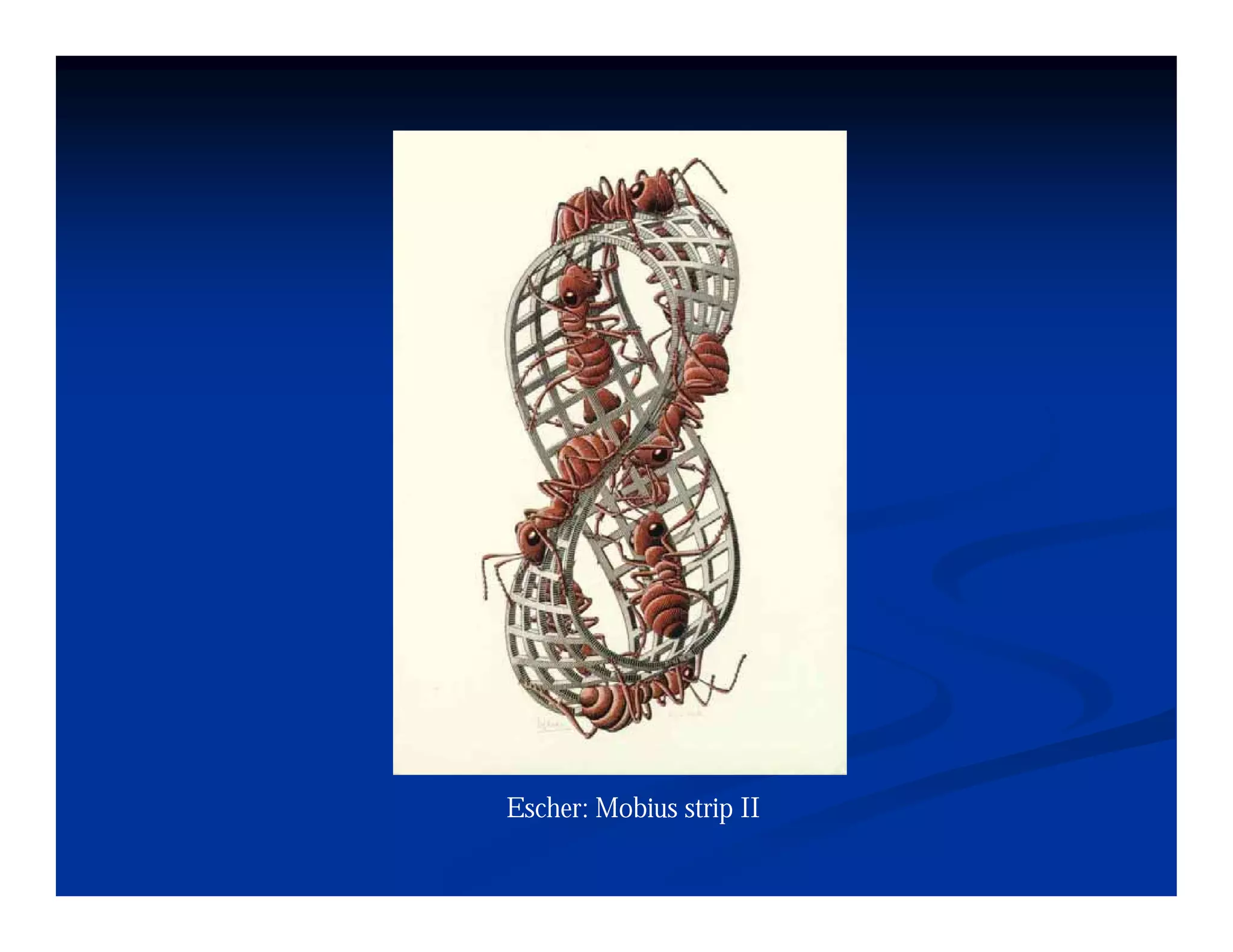
This document discusses visual perception and illusions. It begins by explaining that visual perception involves both biological determinism and learned experiences. It then discusses several concepts related to visual perception, including the Panopticon, emotions communicated through visuals, and how perception involves both sensation and interpretation. The document goes on to explore various visual illusions and paradoxes, how the brain makes inferences to resolve ambiguities, and discusses concepts like attention, filtering, and Gestalt principles of form perception. It analyzes works by several artists and concludes by mentioning references for further information.