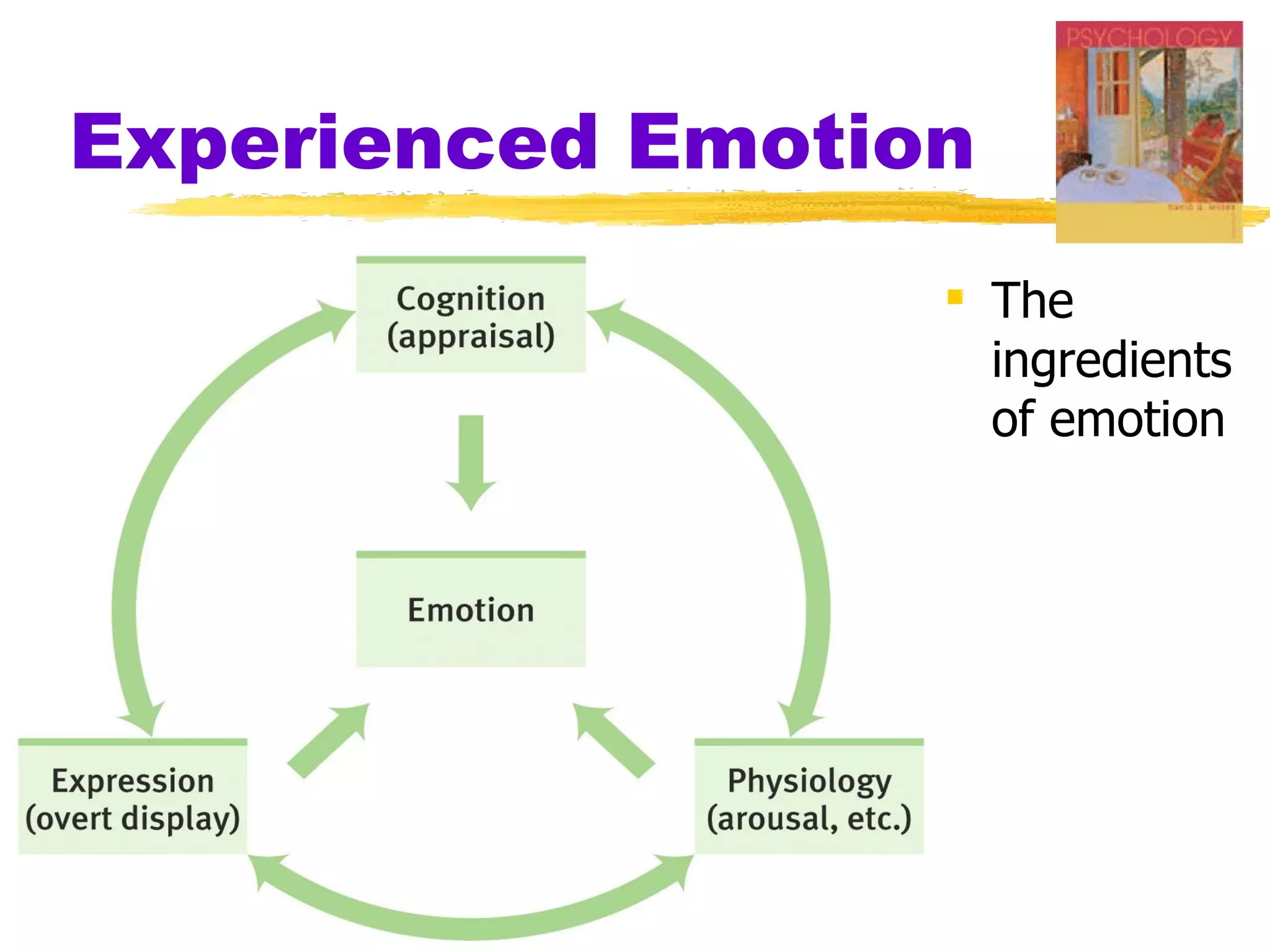
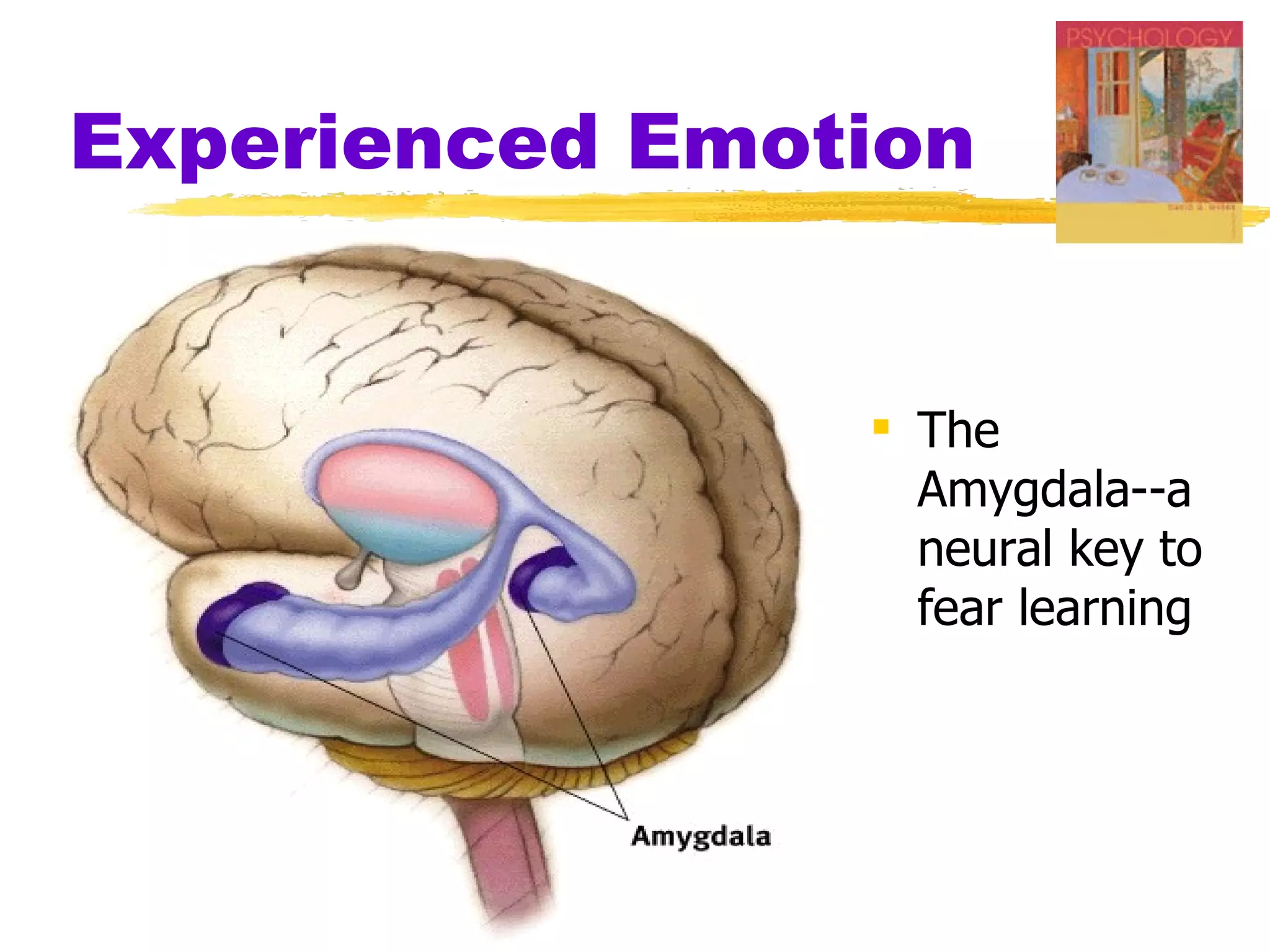
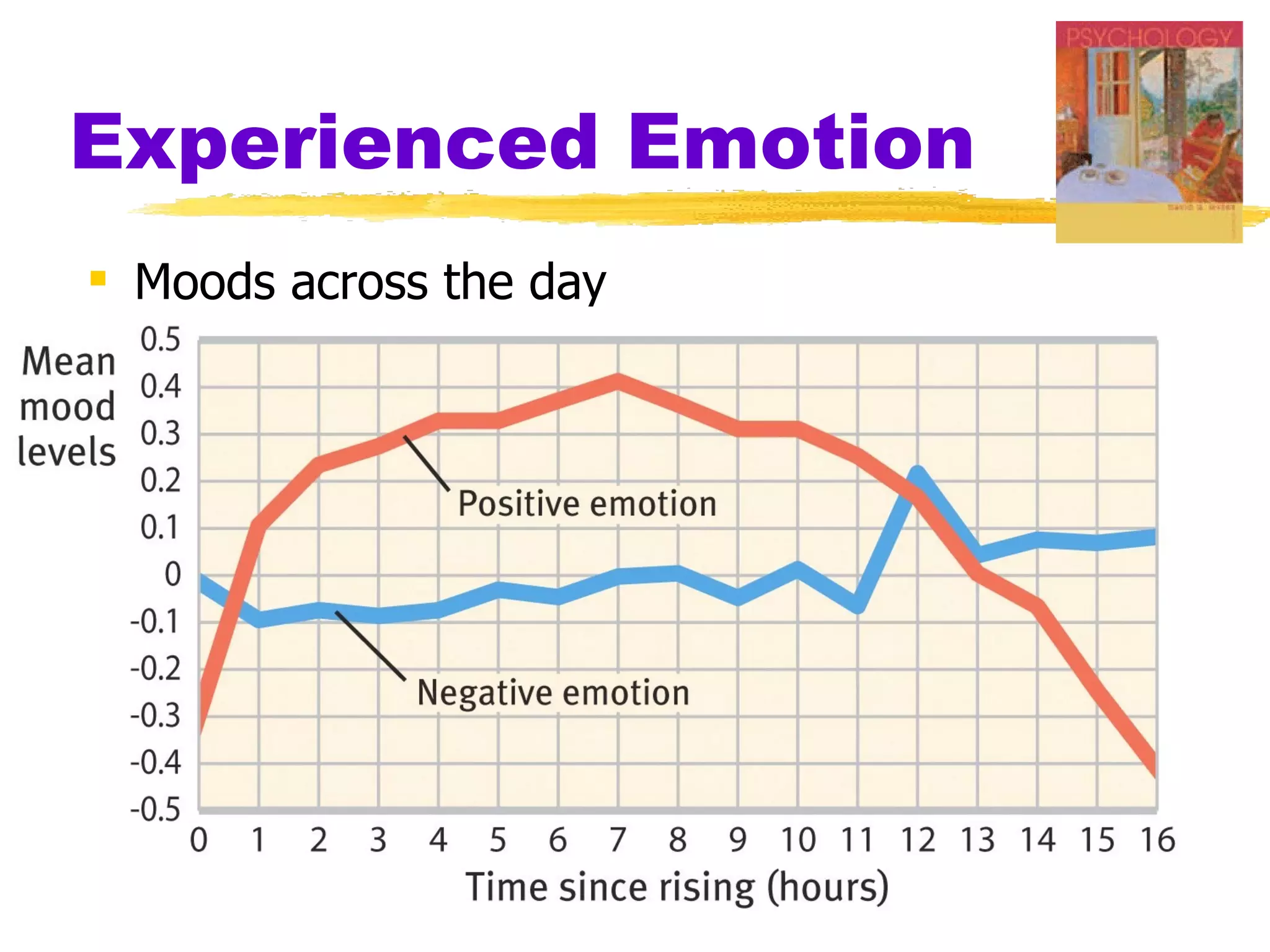
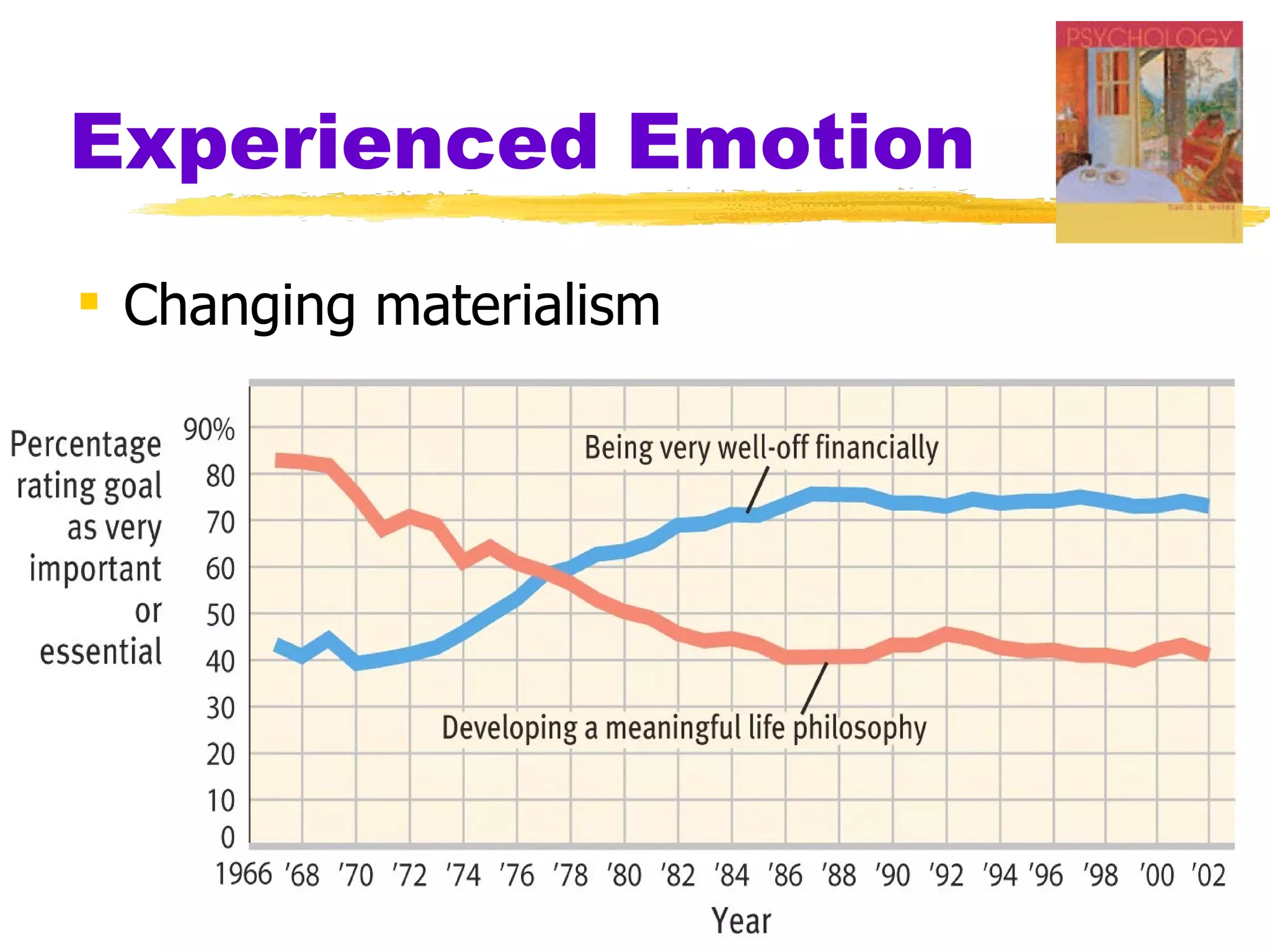
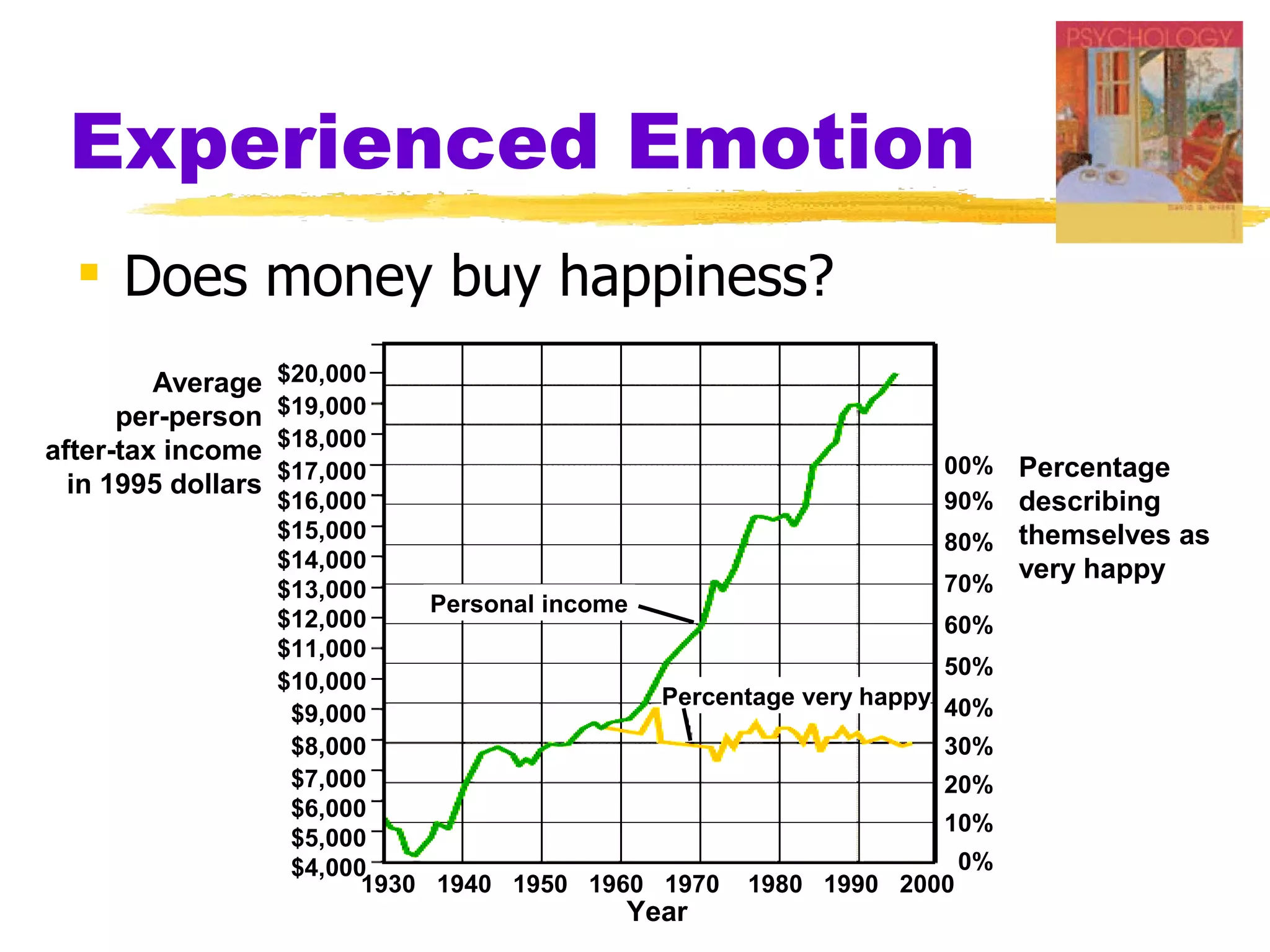
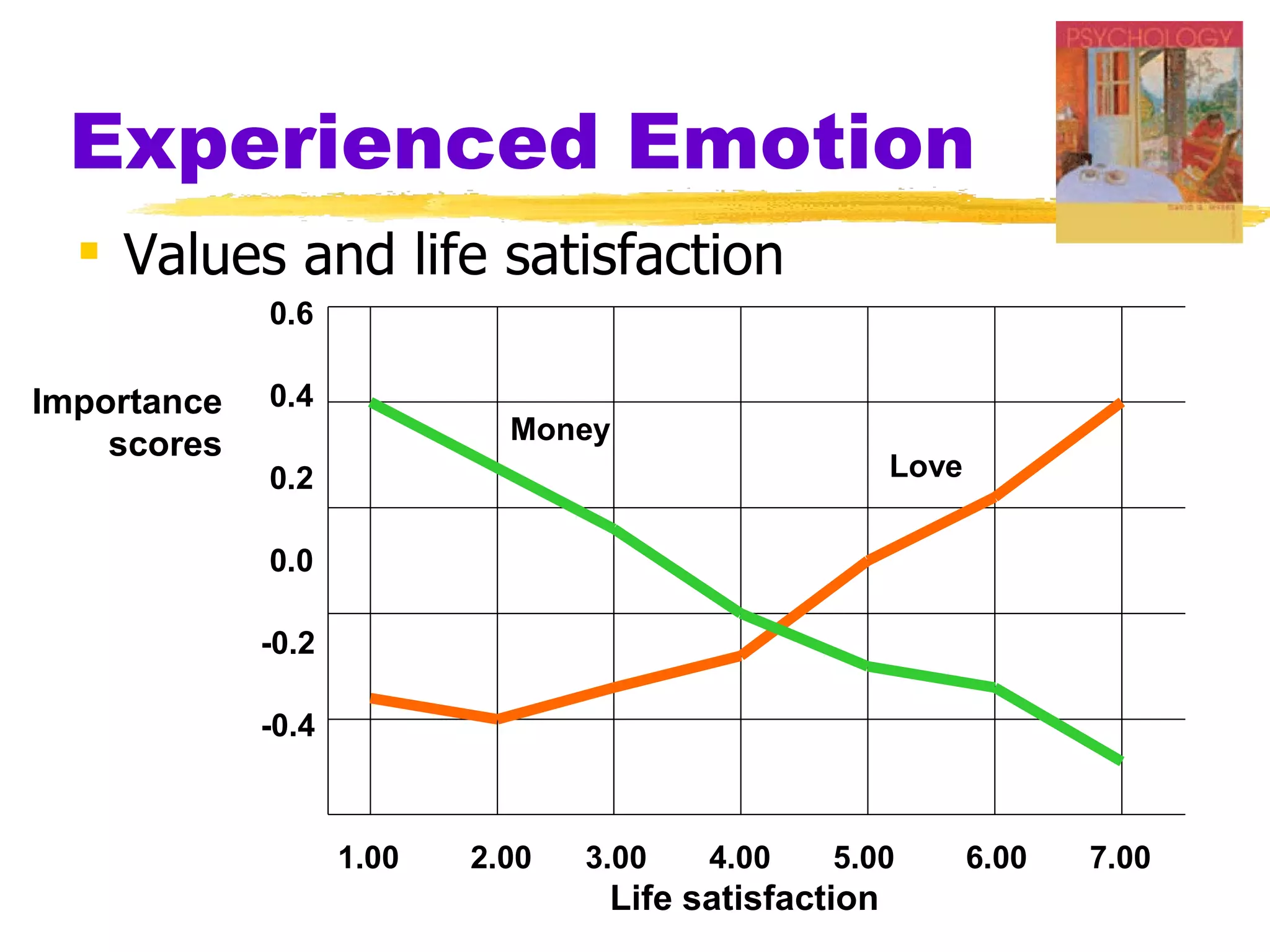
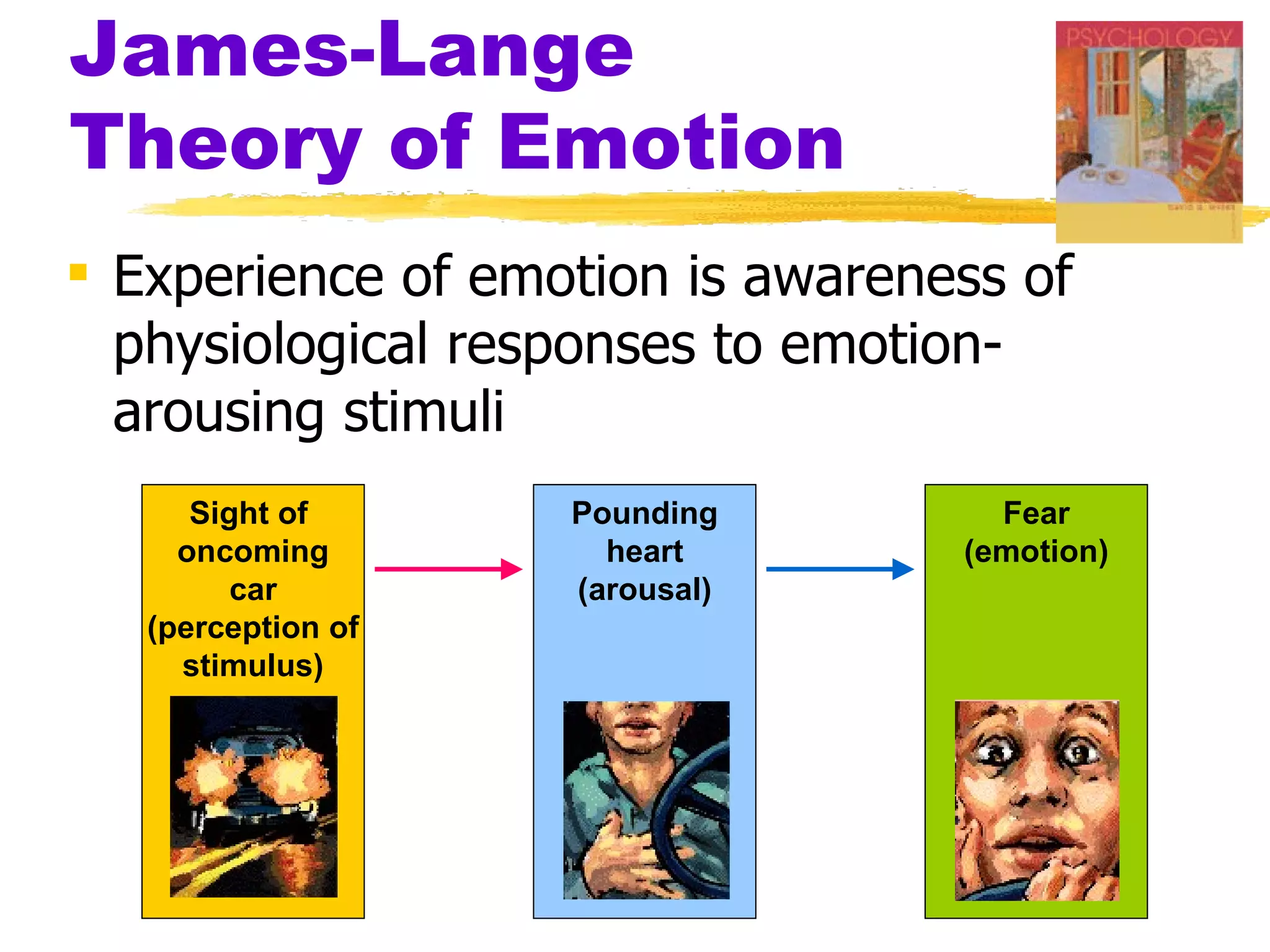
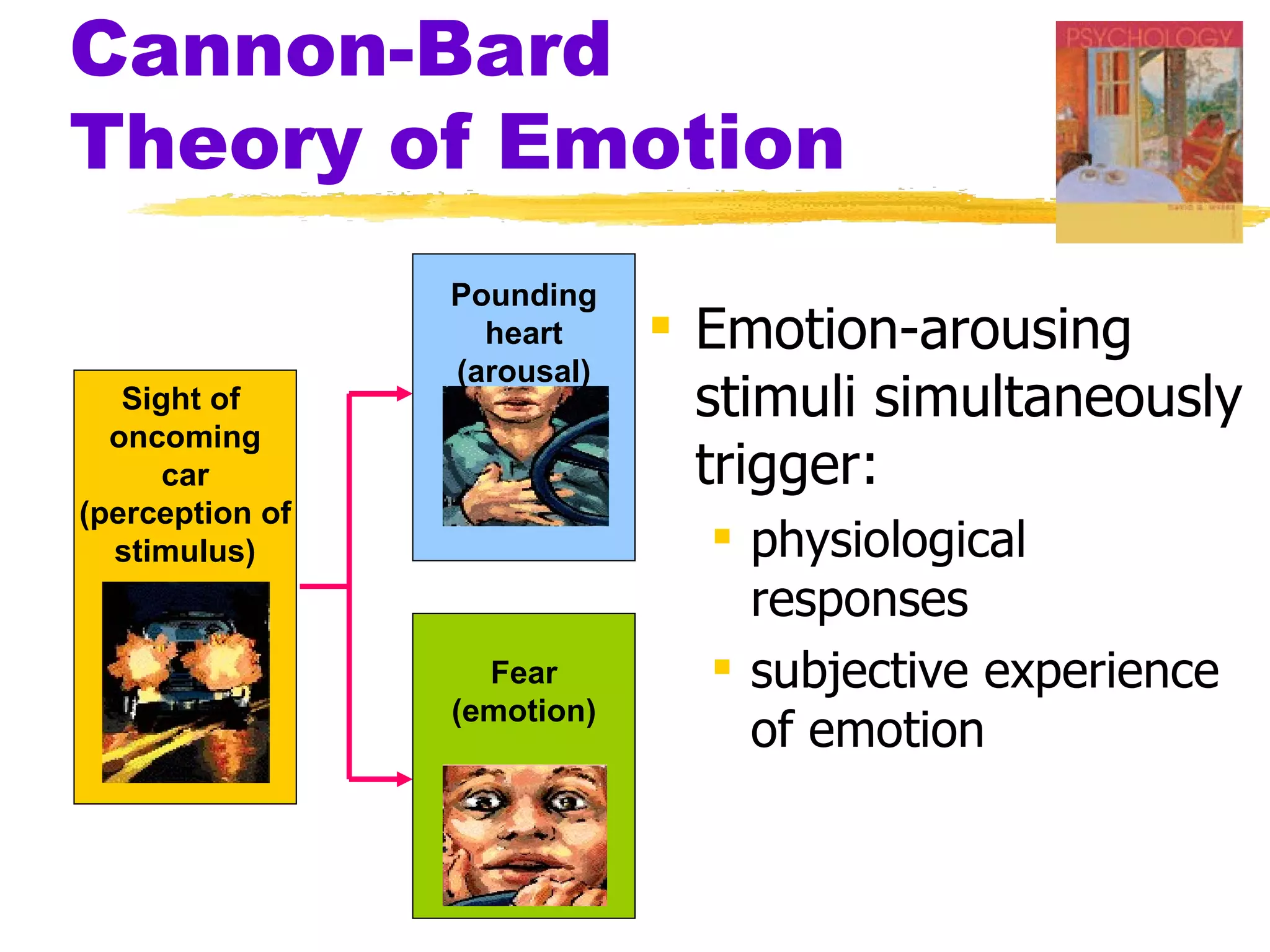
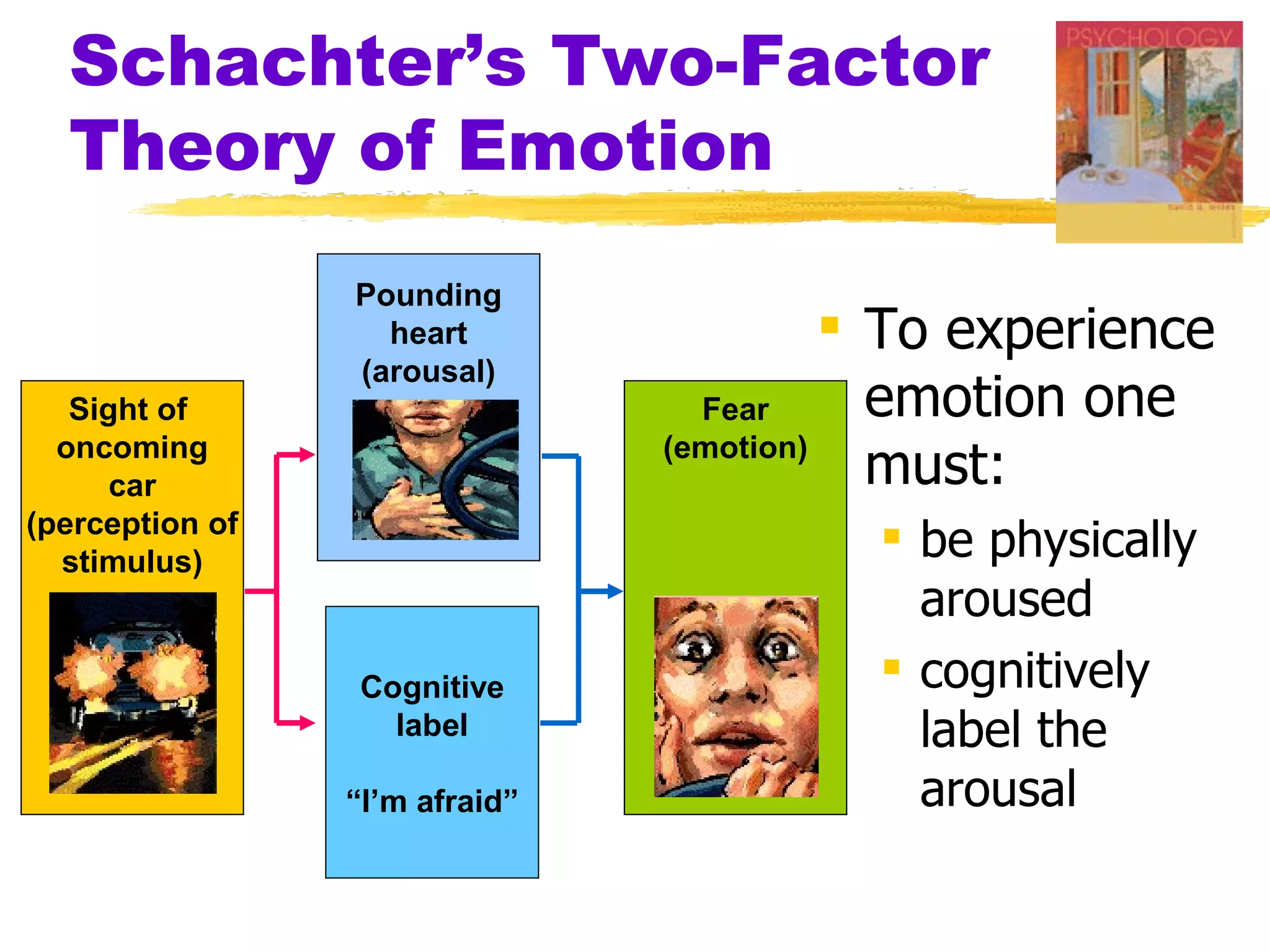
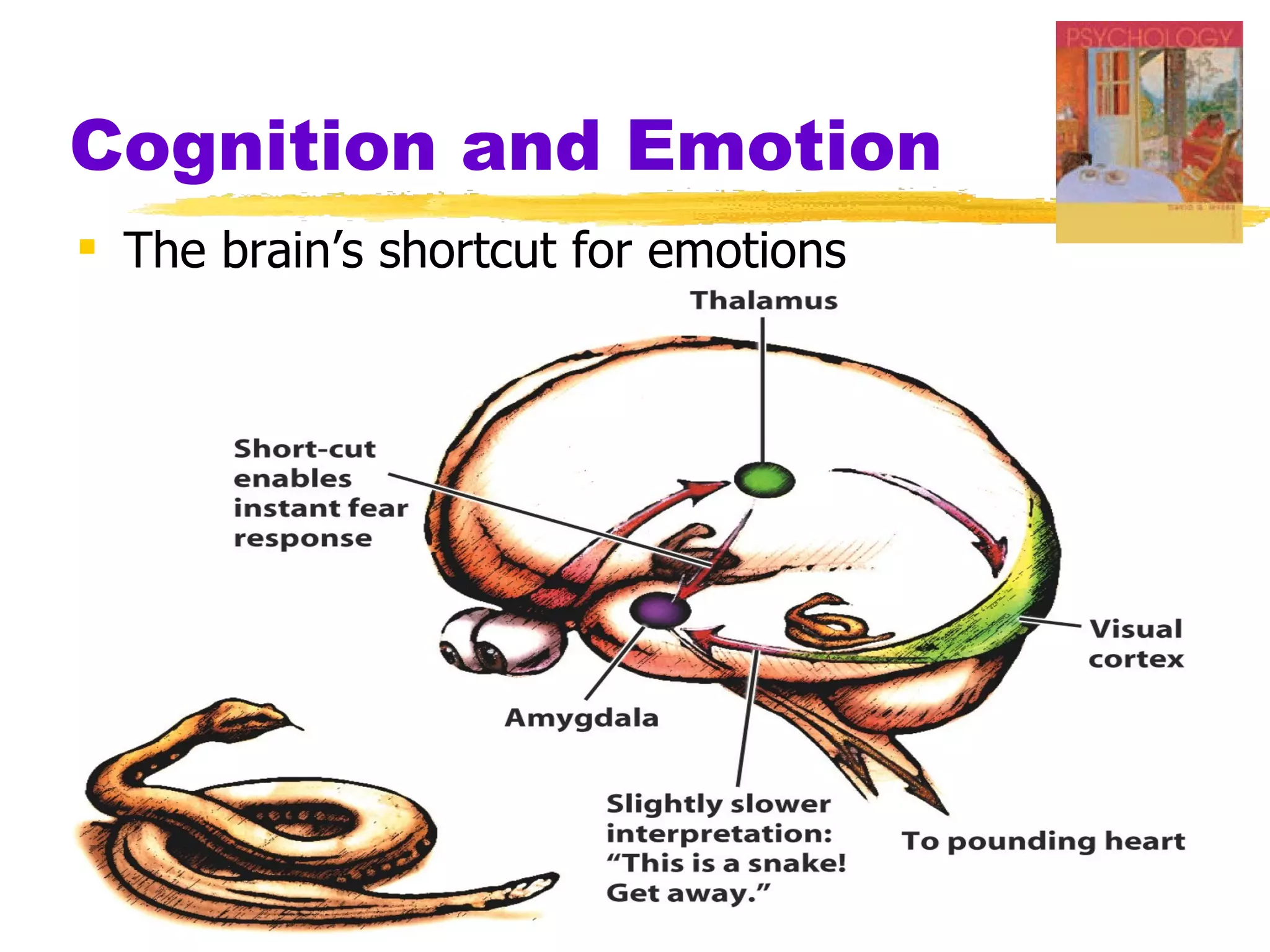
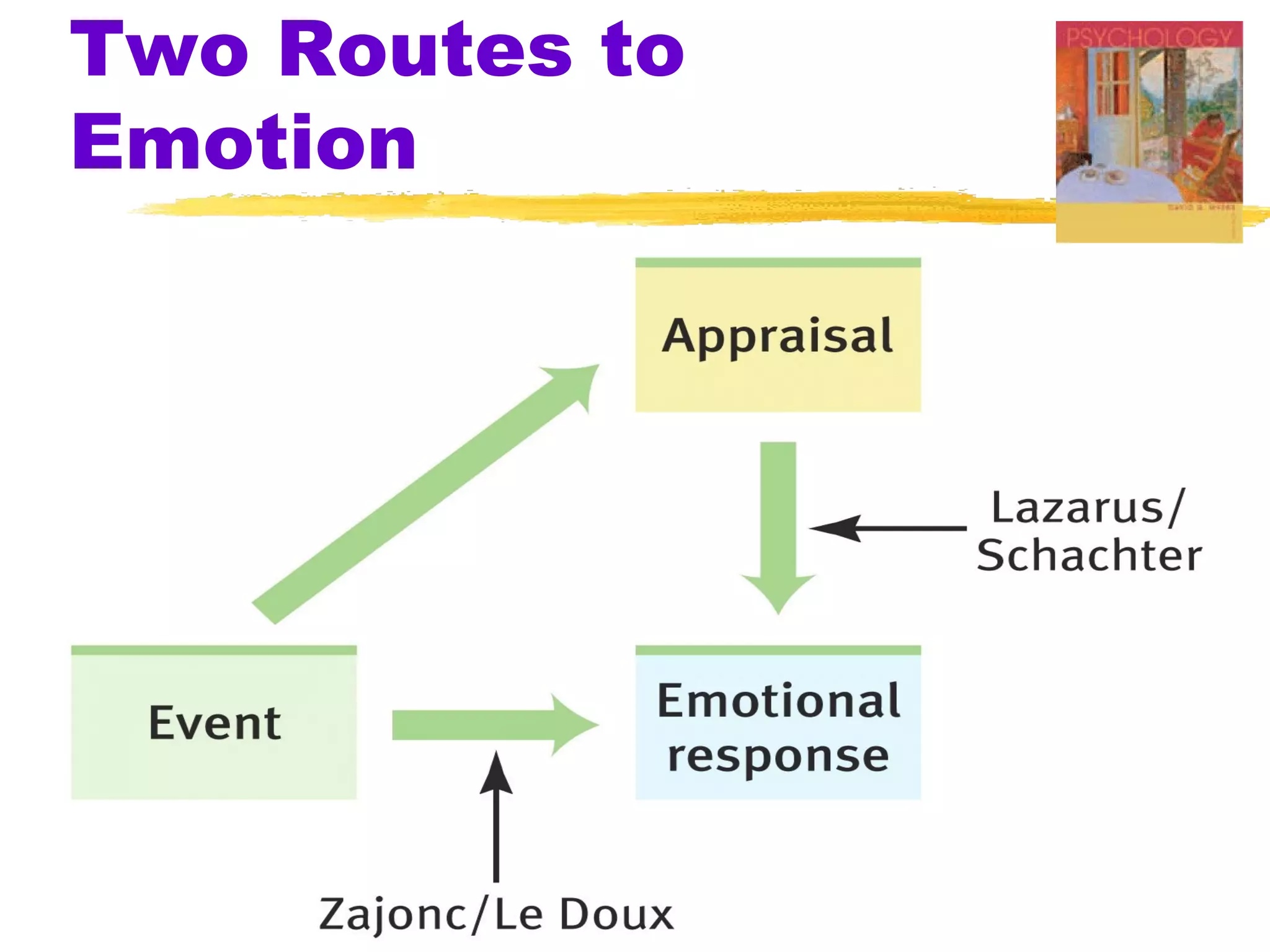
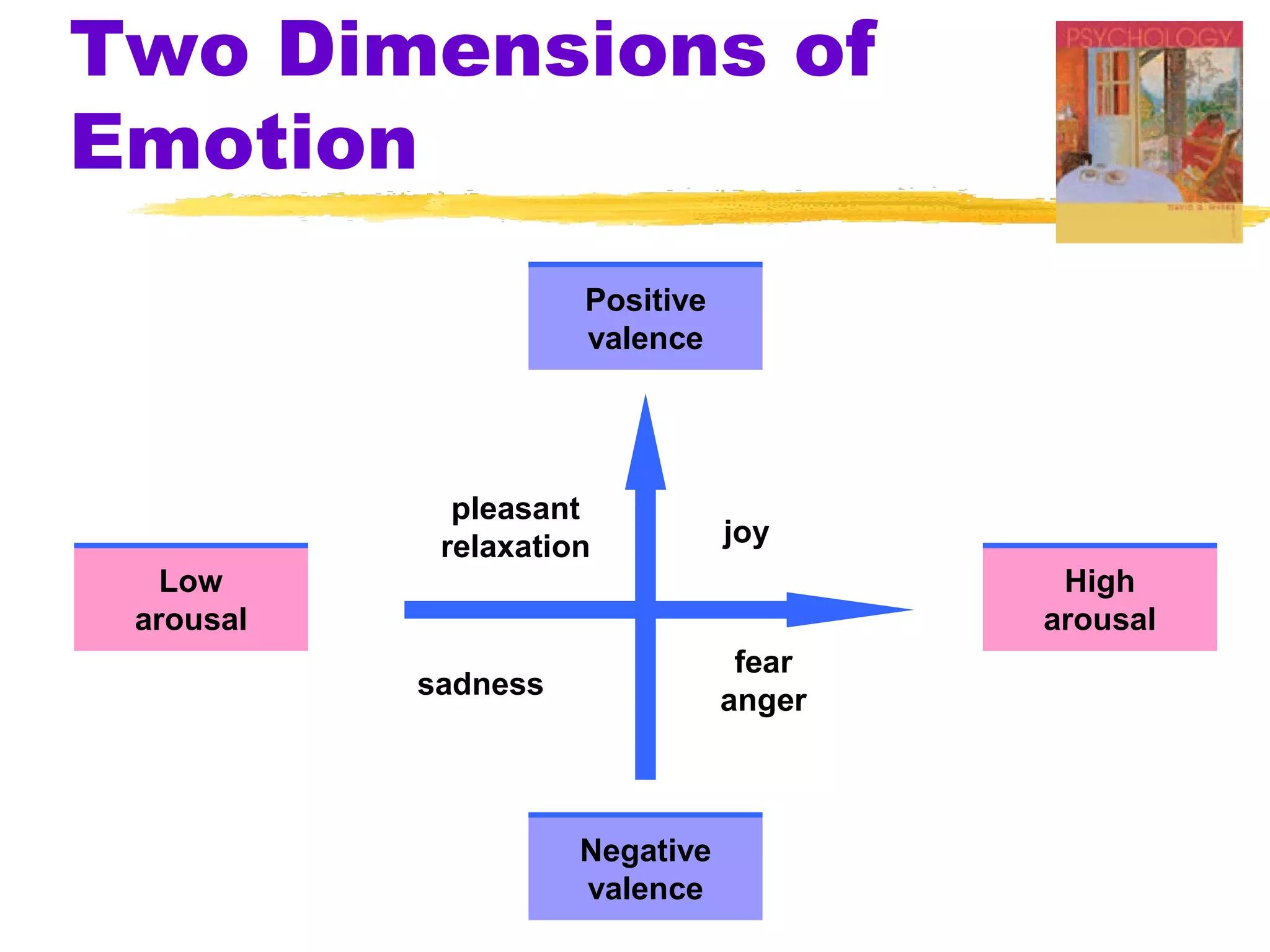
This document summarizes key concepts from Chapter 13 of Myers' Psychology textbook regarding emotion. It discusses theories of emotion such as the James-Lange theory, Cannon-Bard theory, and Schachter's two-factor theory. It also covers topics like expressed emotion, experienced emotion, moods, subjective well-being, and factors related to happiness. The document provides an overview of the physiological, cognitive, and social aspects of emotion.



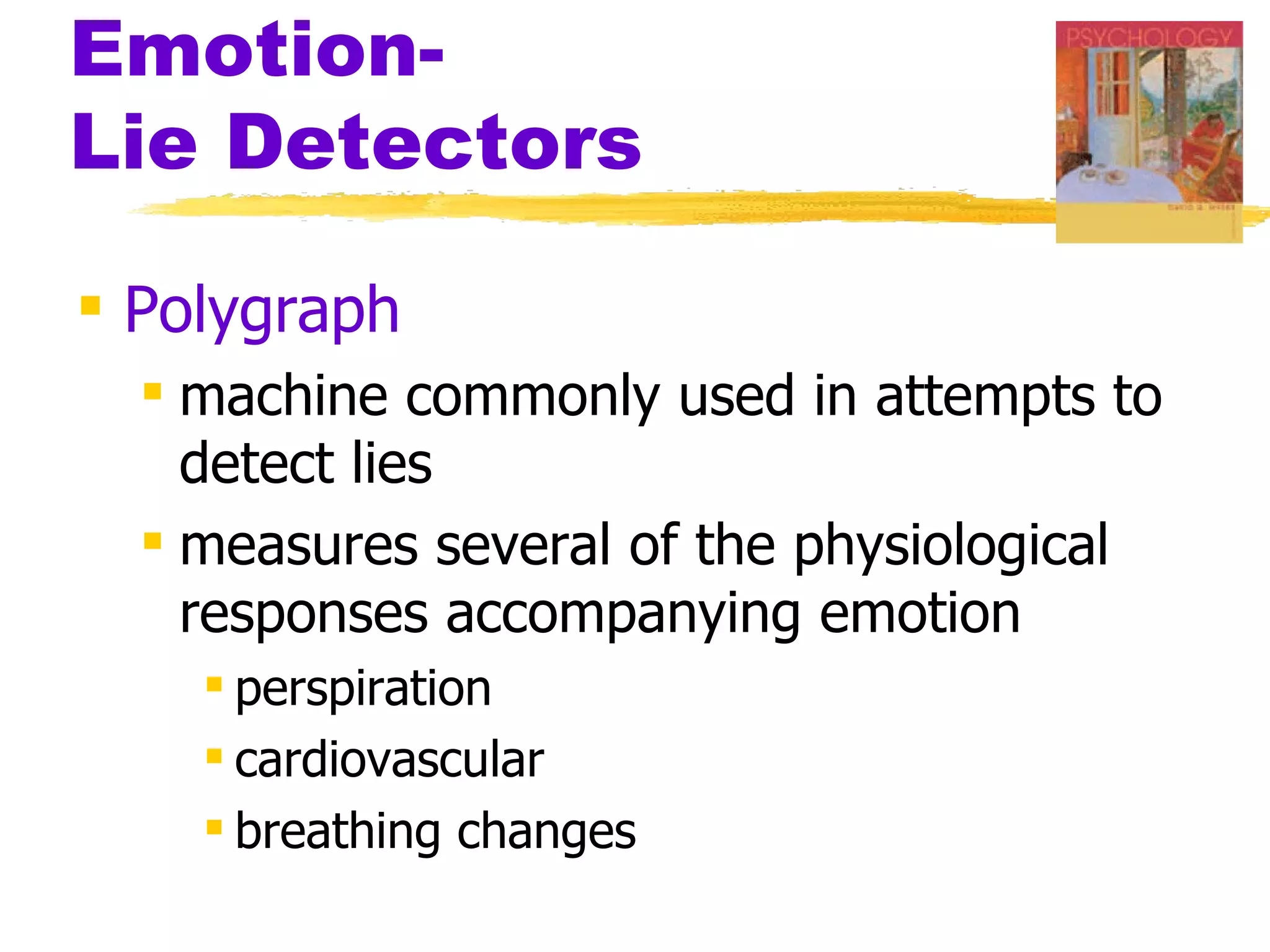

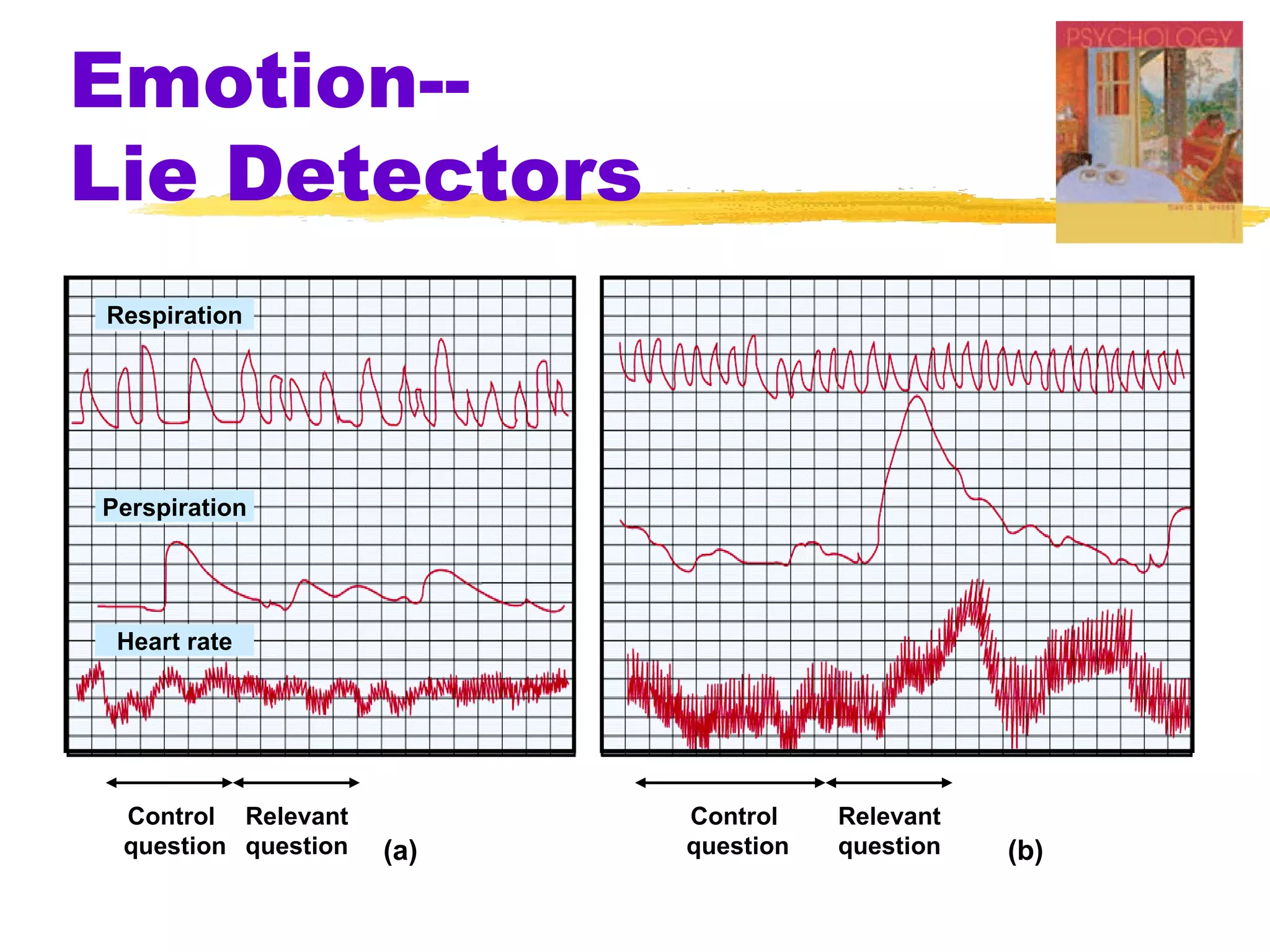
![Emotion--Lie Detectors
Control Question
Up to age 18, did you ever physically
harm anyone?
Relevant Question
Did [the deceased] threaten to harm
you in any way?
Relevant > Control --> Lie](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ch13ppt-100425183651-phpapp02/75/Ch13-ppt-14-2048.jpg)