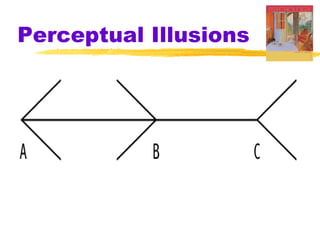
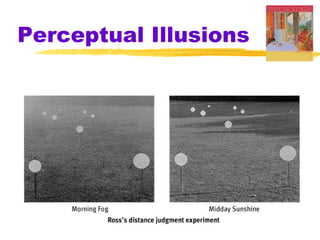
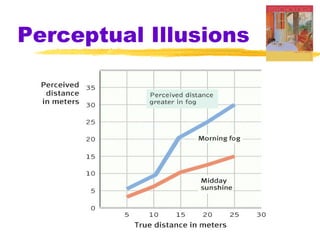
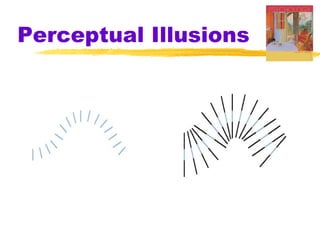
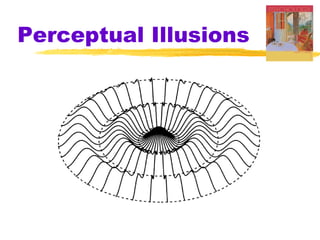
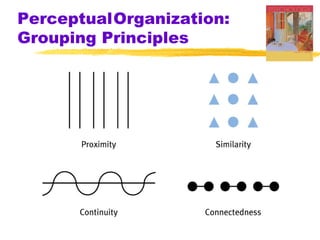
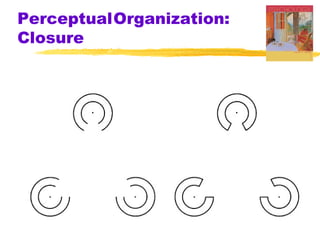
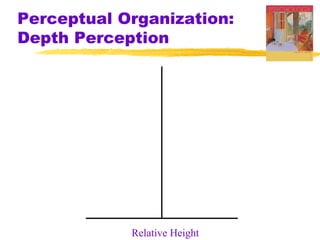
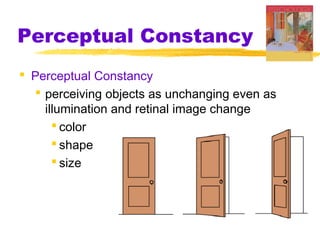
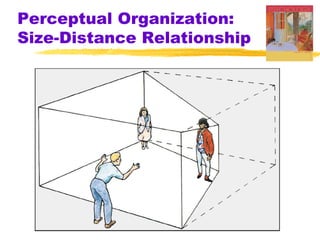
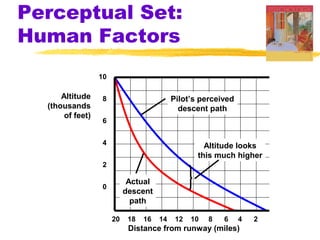
This chapter discusses the topic of perception from Myers' Psychology textbook. It covers selective attention, change blindness, perceptual illusions, and perceptual organization principles including gestalt, grouping, figure-ground, and depth perception using monocular and binocular cues. The chapter also addresses perceptual constancy, adaptation, sets and schemas, and applications to human factors and potential extrasensory perception.