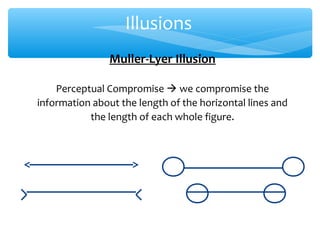
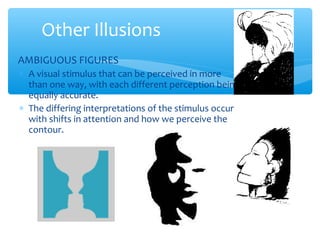
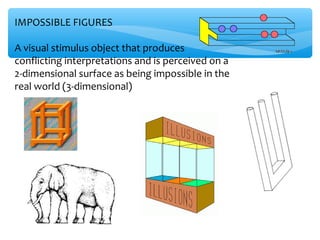
The document discusses perceptual set, which refers to the predisposition to perceive stimuli based on our expectations. Perceptual set can enhance or mislead visual perception. It is influenced by context, past experiences, motivation, emotional state, and cultural factors. The document also discusses distortions of visual perception such as illusions. Illusions demonstrate how reality can be misperceived, such as when perceptual cues conflict (perceptual compromise) or with ambiguous/impossible figures.