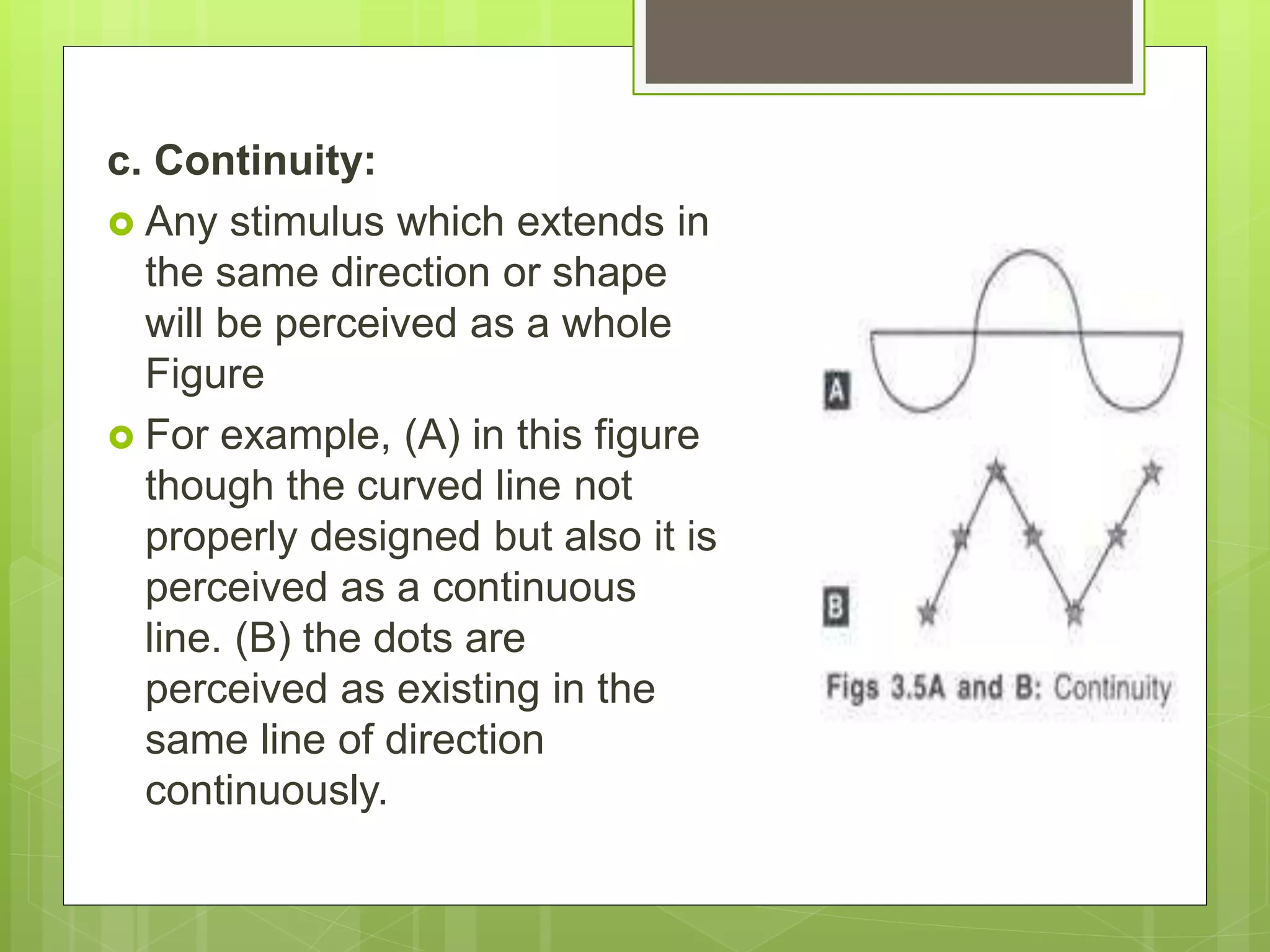
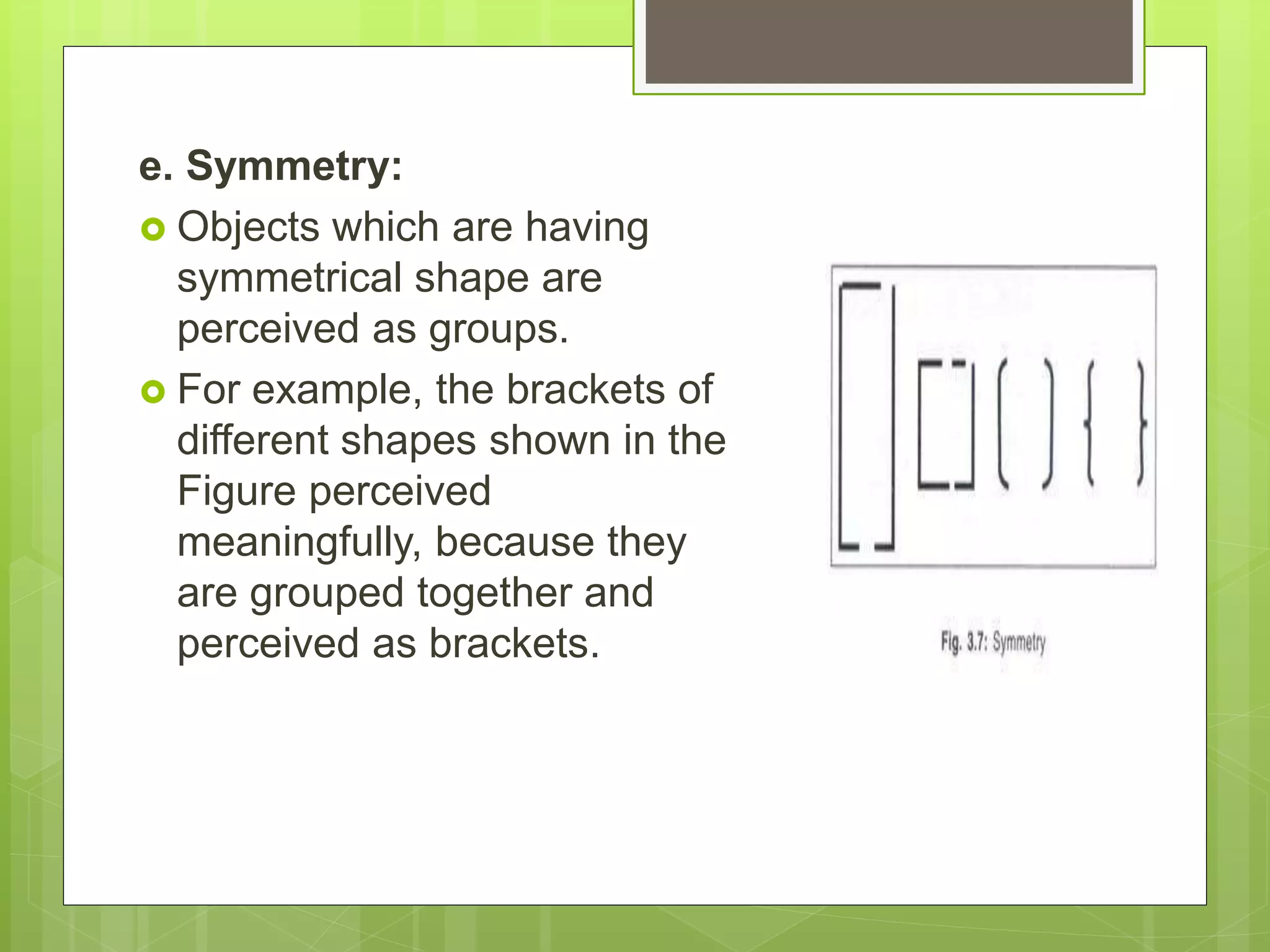
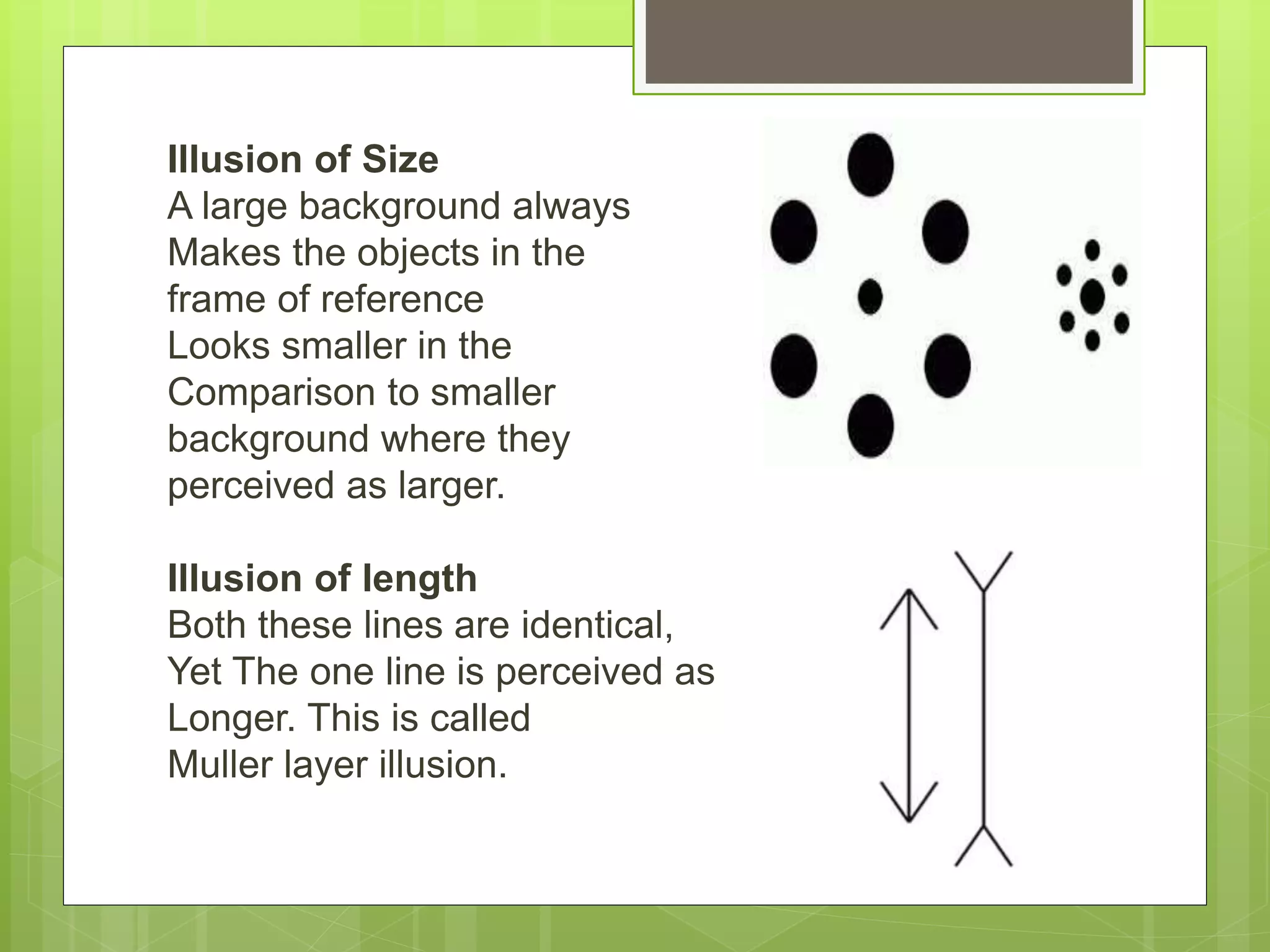
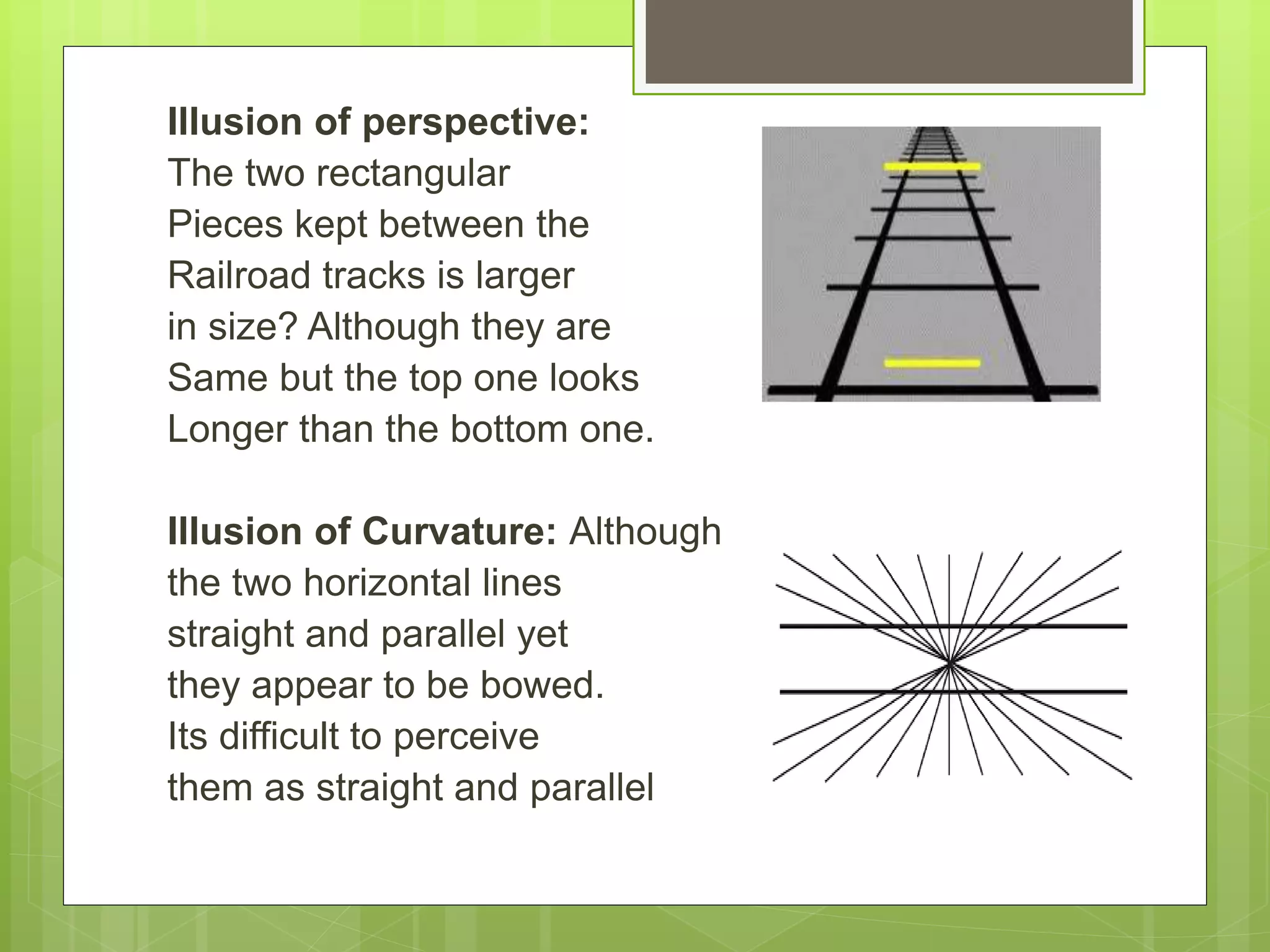
Perception is the organization and interpretation of sensory information to understand one's environment. It involves signals in the nervous system resulting from stimulation of the senses. Perception provides organization and is an information extractor that prepares an individual to respond. It follows principles like figure-ground relationships and grouping stimuli based on proximity, similarity, continuity, closure, and symmetry. Perceptual constancy allows stable perception despite changes to sensory inputs. Depth is perceived through monocular cues like linear perspective and binocular cues like retinal disparity and eye convergence. Factors like senses, brain, memory, interests, needs, and illusions can influence perception. Hallucinations are perceptions without sensory stimuli.