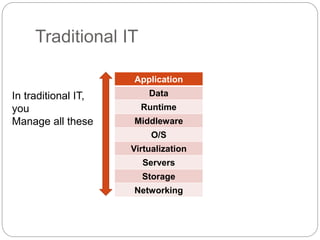
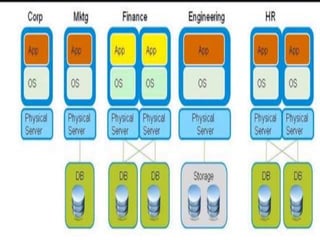
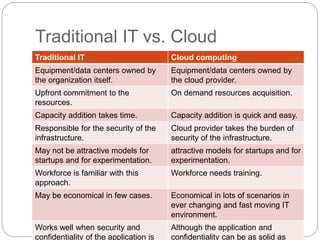
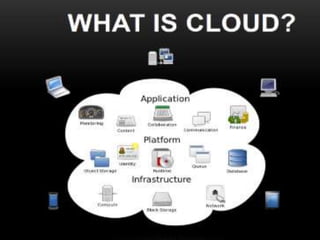
This document provides an overview of traditional IT and cloud computing. It discusses how traditional IT involves organizations owning and managing their own infrastructure, software, and data. It then contrasts this with cloud computing, where resources are provided as a service by cloud providers over the internet on demand. Some key benefits of cloud computing mentioned include rapid scalability, lower upfront costs, and a workforce that requires less maintenance of physical infrastructure.