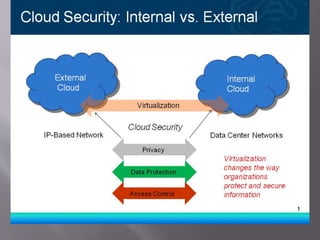
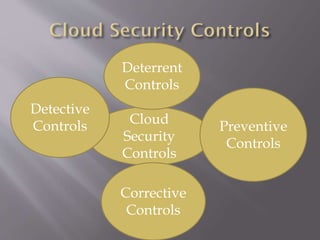
Cloud computing relies on sharing computing resources over the internet rather than local servers. It delivers services like servers, storage, and applications through the internet. Cloud security refers to policies, technologies, and controls to protect data, applications, and infrastructure in cloud computing. There are security issues faced by both cloud providers and their customers. Virtualization in cloud infrastructure also brings unique security concerns for customers due to the altered relationship between the OS and hardware.