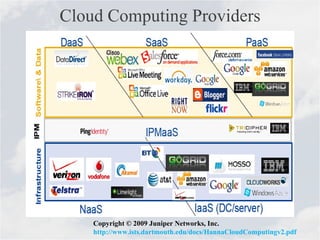
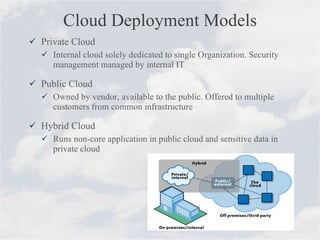
Cloud computing is a model for accessing computing resources over the internet on-demand. There are concerns about security and data protection with cloud services. While cloud computing provides benefits like scalability, cost savings, and mobility, issues include security risks from outages or data breaches, uncertainty around service agreements, and governance challenges with foreign data locations. Standards and best practices can help manage security risks for cloud computing.