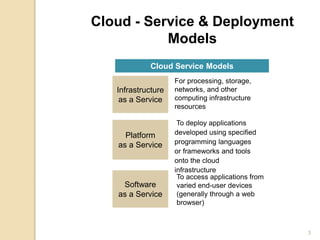
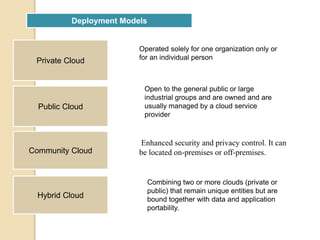
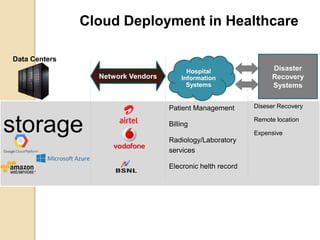
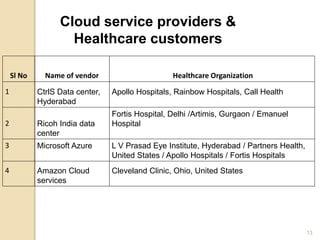
This document discusses cloud computing and its applications in healthcare. It defines cloud computing as a model for accessing computing resources such as hardware and software via a network. There are three main service models for cloud computing: Infrastructure as a Service, Platform as a Service, and Software as a Service. The document also discusses the advantages of cloud computing such as lower costs, interoperability, and increased adoption of electronic medical records. However, security is a main disadvantage since medical information would be stored externally. The document outlines how cloud computing can help with cost reduction, disaster recovery, and storage scalability for healthcare organizations. It provides examples of cloud service providers and healthcare customers that utilize cloud services.