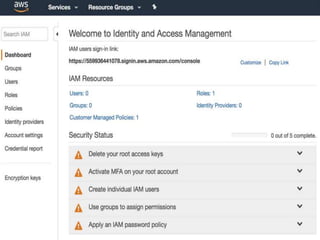
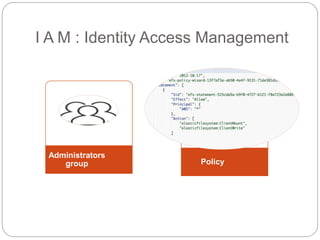
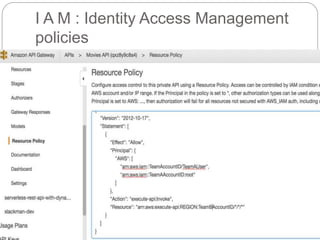
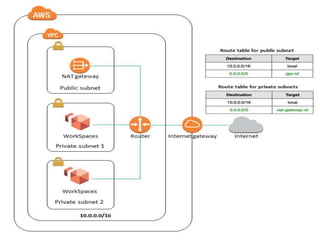
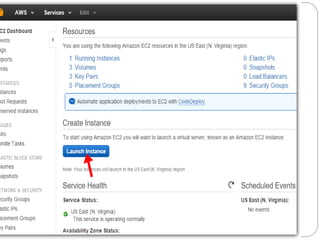
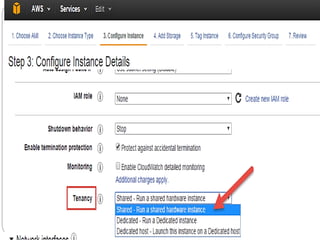
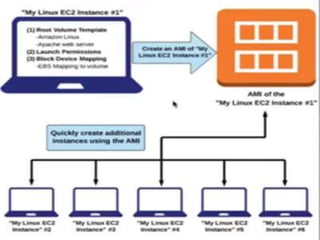
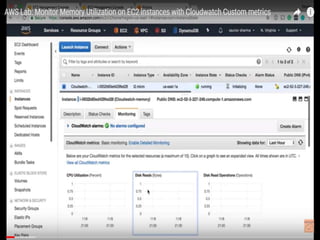
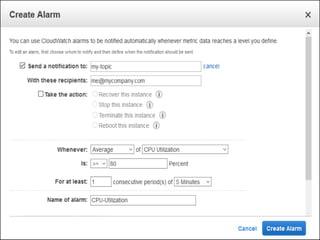
IAM controls access to AWS services and resources by managing users, groups, roles, and policies. VPC allows users to define their virtual networking environment, including subnets and security controls. EC2 provides on-demand scalable compute capacity in the cloud. CloudWatch monitors AWS and application resources, sets alarms, and reacts to changes in metrics and log data.