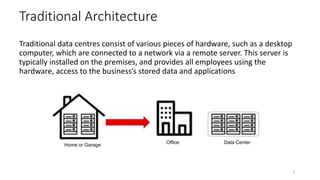
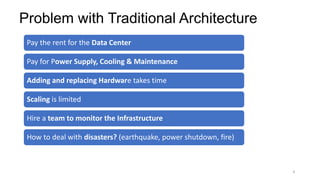
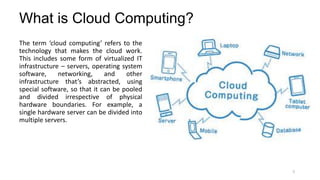
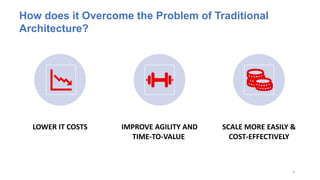
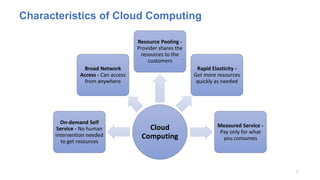
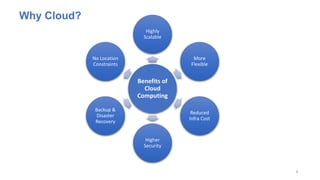
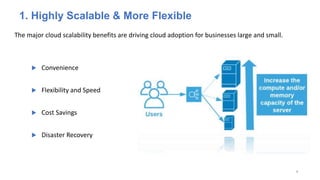
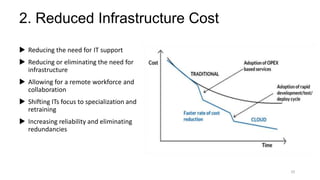
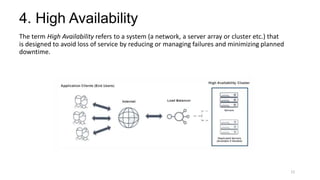
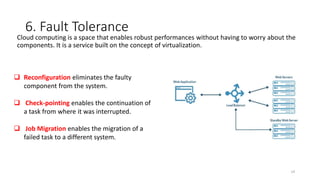
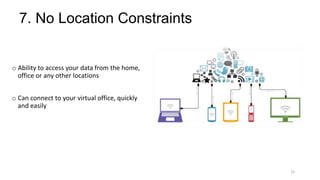
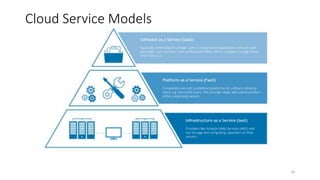
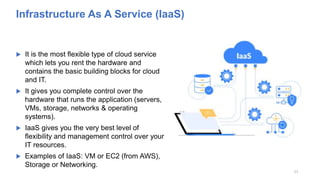
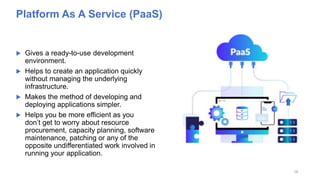
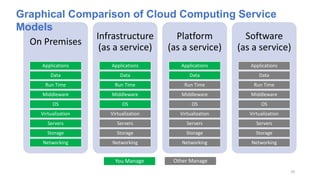
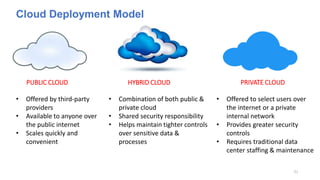
The document discusses cloud computing fundamentals, highlighting the shortcomings of traditional data architecture and the benefits of cloud computing, such as scalability, flexibility, and reduced infrastructure costs. It explains various cloud service models (IaaS, PaaS, SaaS) and deployment models (public, private, hybrid) while emphasizing features like on-demand self-service, resource pooling, and rapid elasticity. The text outlines the advantages of cloud computing in terms of security, disaster recovery, and cost-effectiveness.