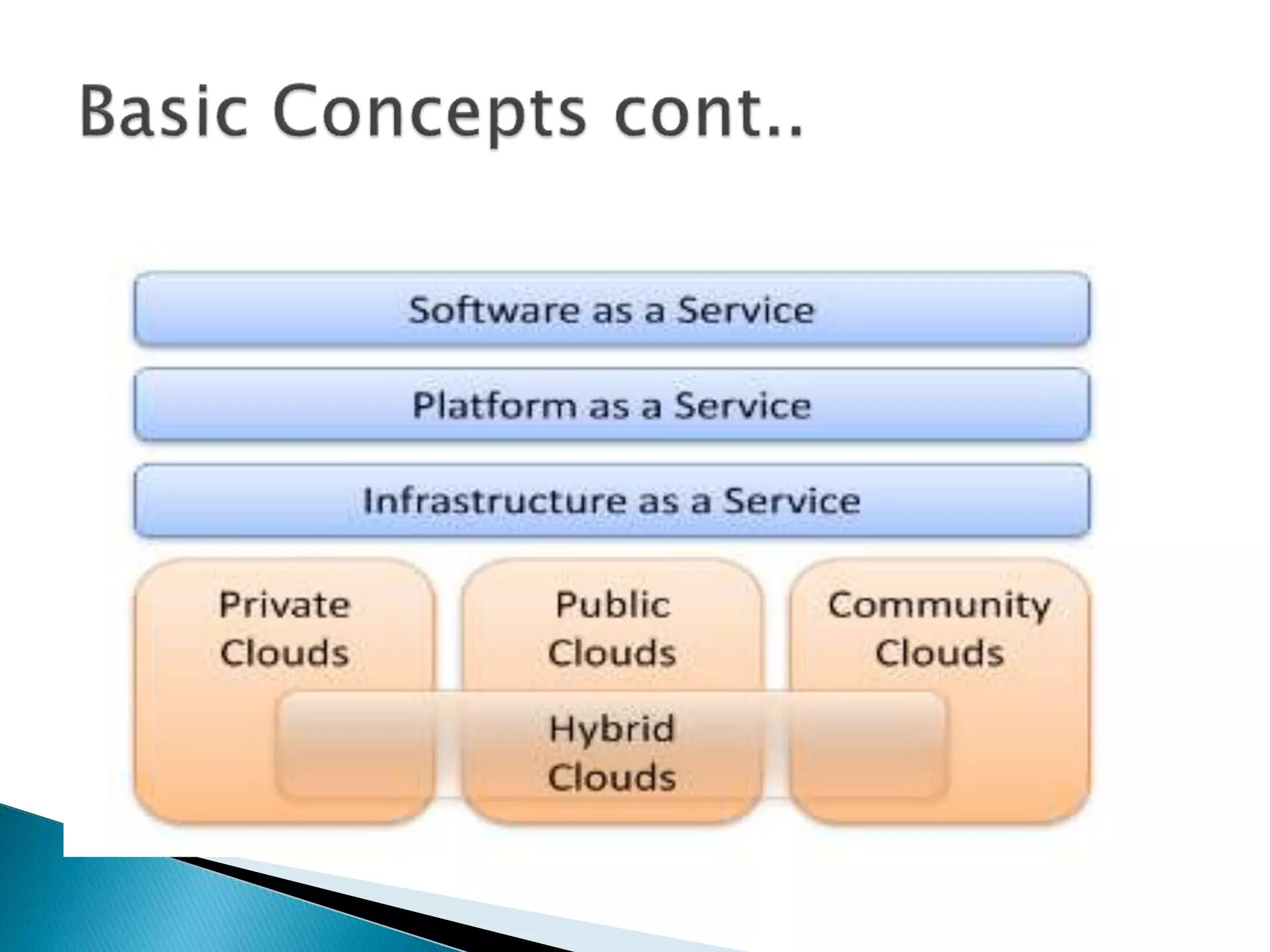
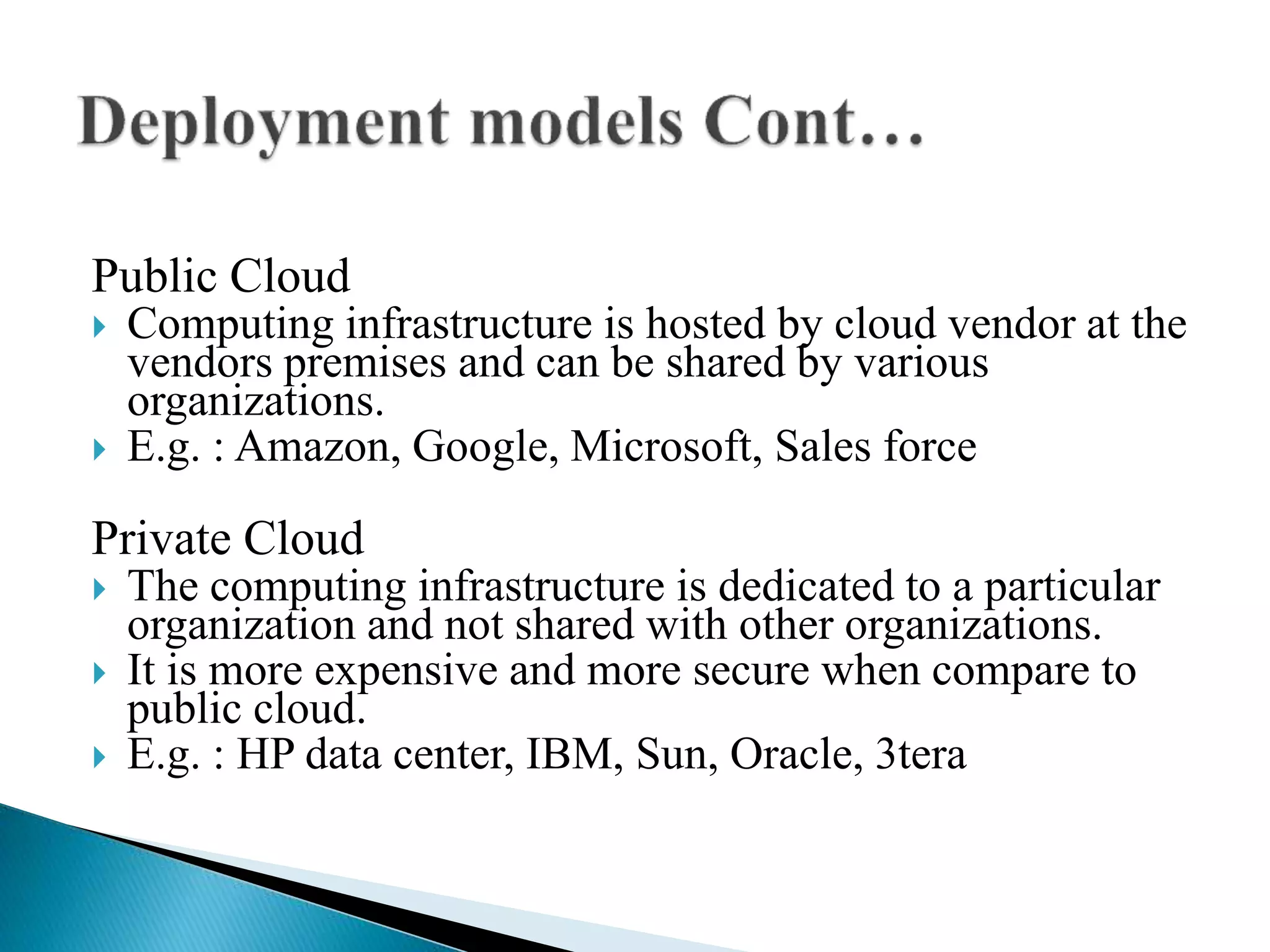
Cloud computing allows users to access shared computer resources like applications, storage, and servers over the internet rather than installing software locally. It provides services through front-end user interfaces while hardware and software infrastructure in the back-end produce these interfaces. There are different cloud service and deployment models including SaaS, PaaS, IaaS, and public, private, hybrid, and community clouds. While cloud computing provides benefits like scalability, cost savings, and flexibility, challenges include security issues, downtime, and lack of control over the infrastructure.