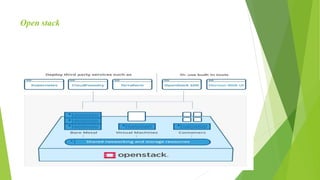
A private cloud provides a proprietary computing environment dedicated to a single business entity. It offers enhanced control and customization compared to public clouds since it is only accessible to one organization. A private cloud can be hosted on a business's local hardware or by a cloud service provider. Benefits include strong security and compliance since sensitive data stays on inaccessible hardware. Private clouds also allow full customization to an organization's specific needs. However, private clouds require large upfront costs and may have issues with underutilization and scalability compared to public clouds.