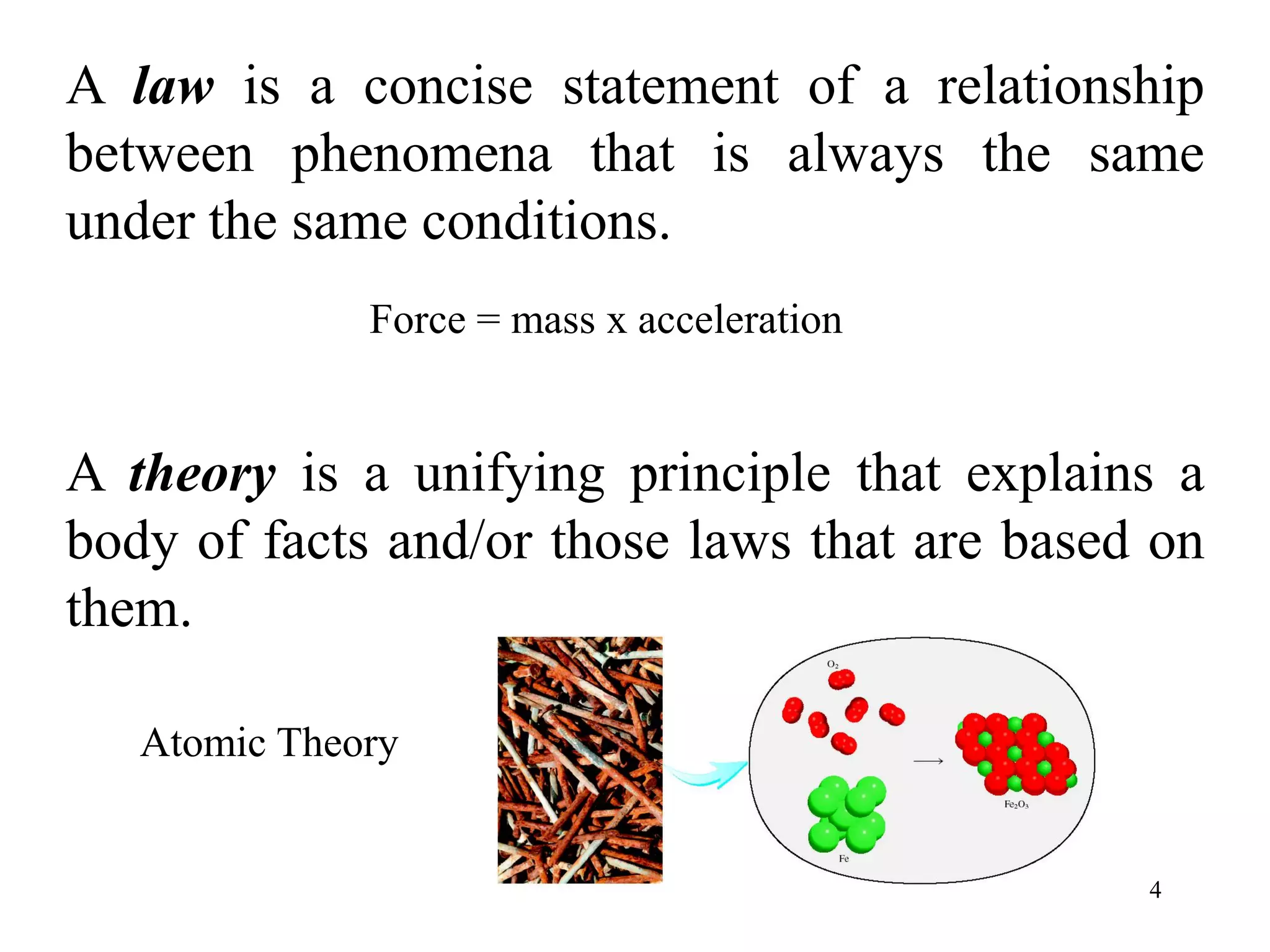
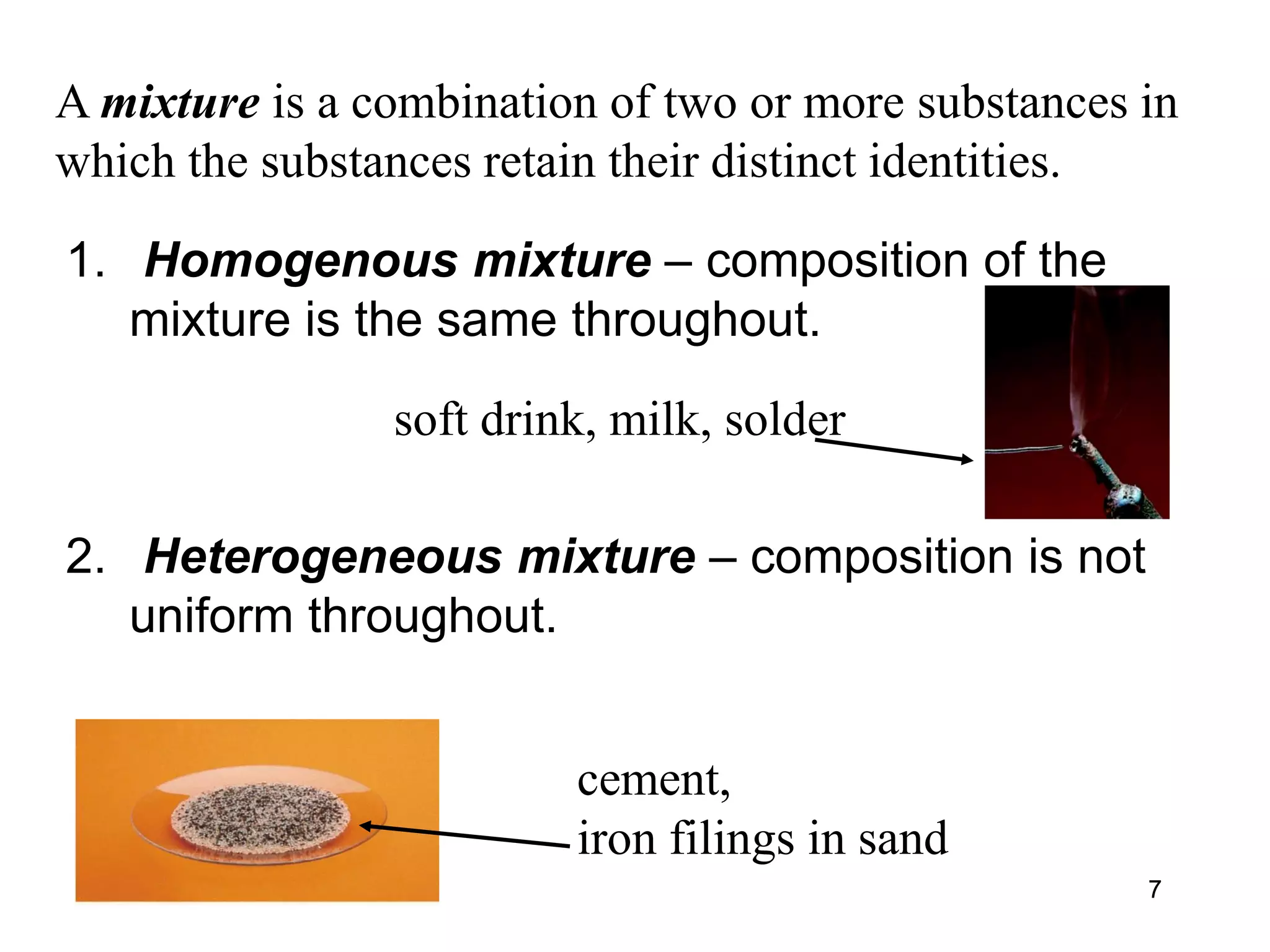
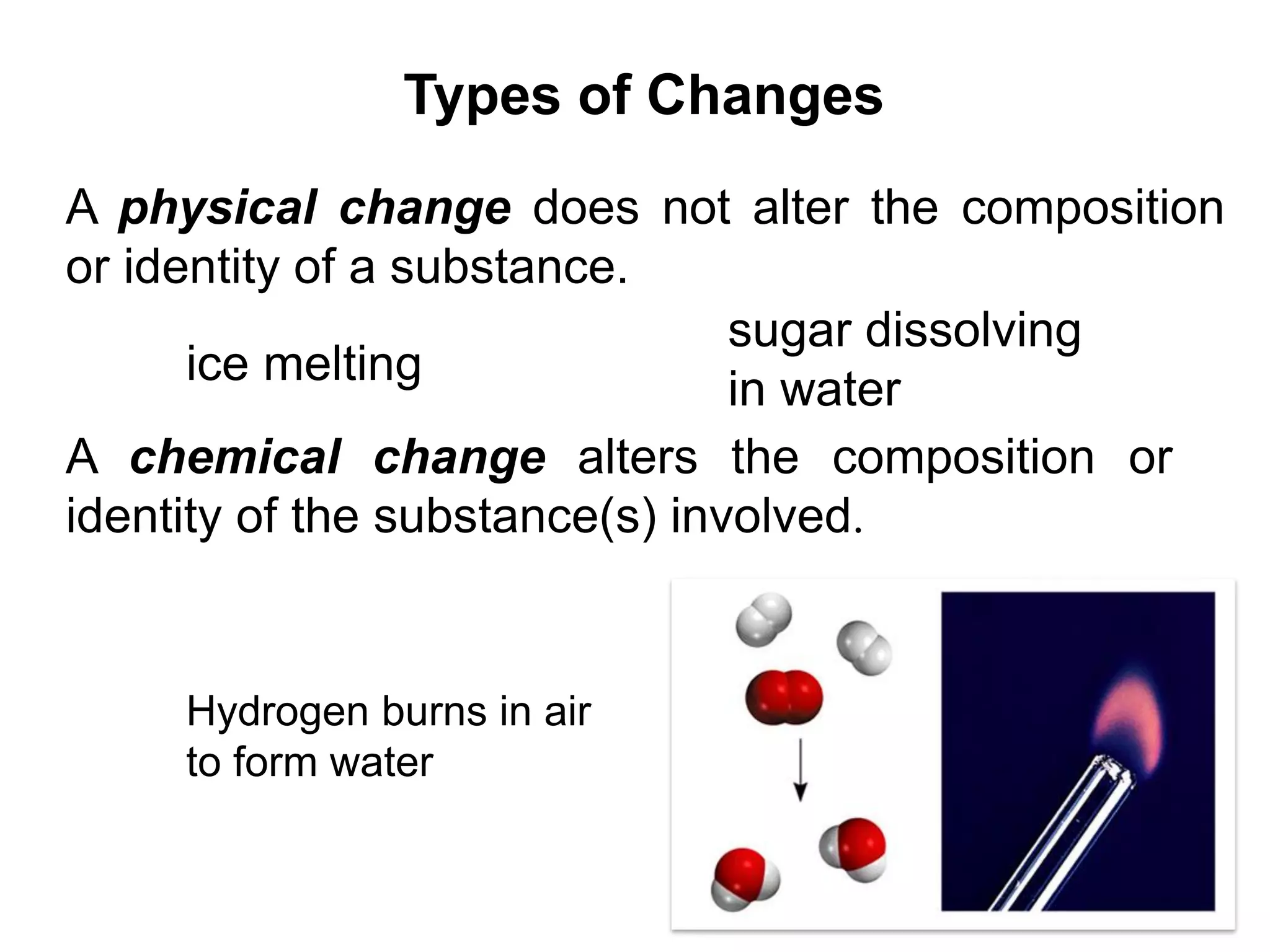
This document provides an overview of basic chemistry concepts. It discusses the following key points in 3 sentences or less:
- Chemistry is the study of matter and the changes it undergoes. Matter can exist in solid, liquid, or gas states. A substance has a definite composition while a mixture combines two or more substances.
- An element is a substance that cannot be broken down further, with over 100 known elements. Compounds are formed from chemical combinations of elements. Physical changes do not alter substance composition while chemical changes do.
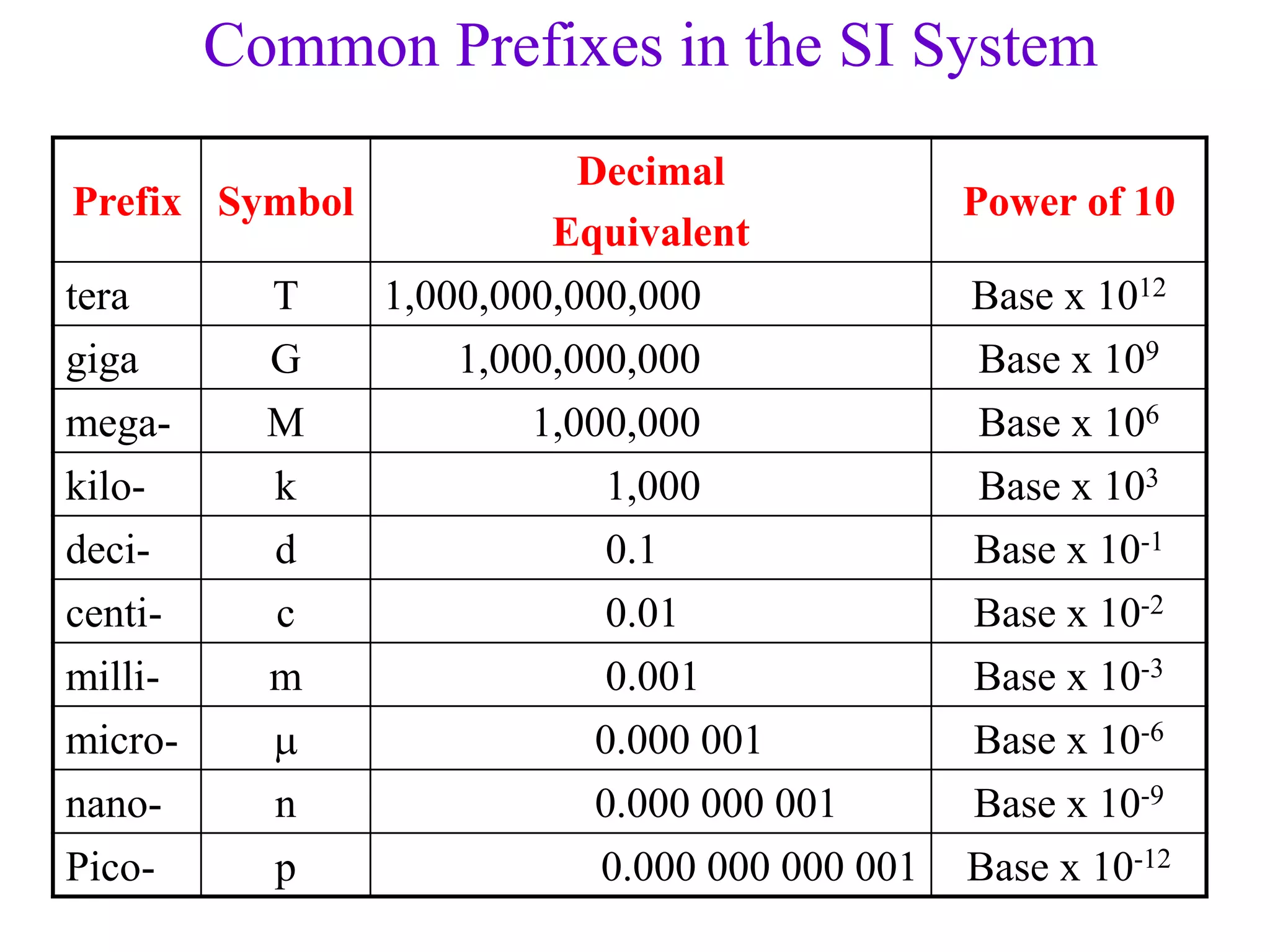
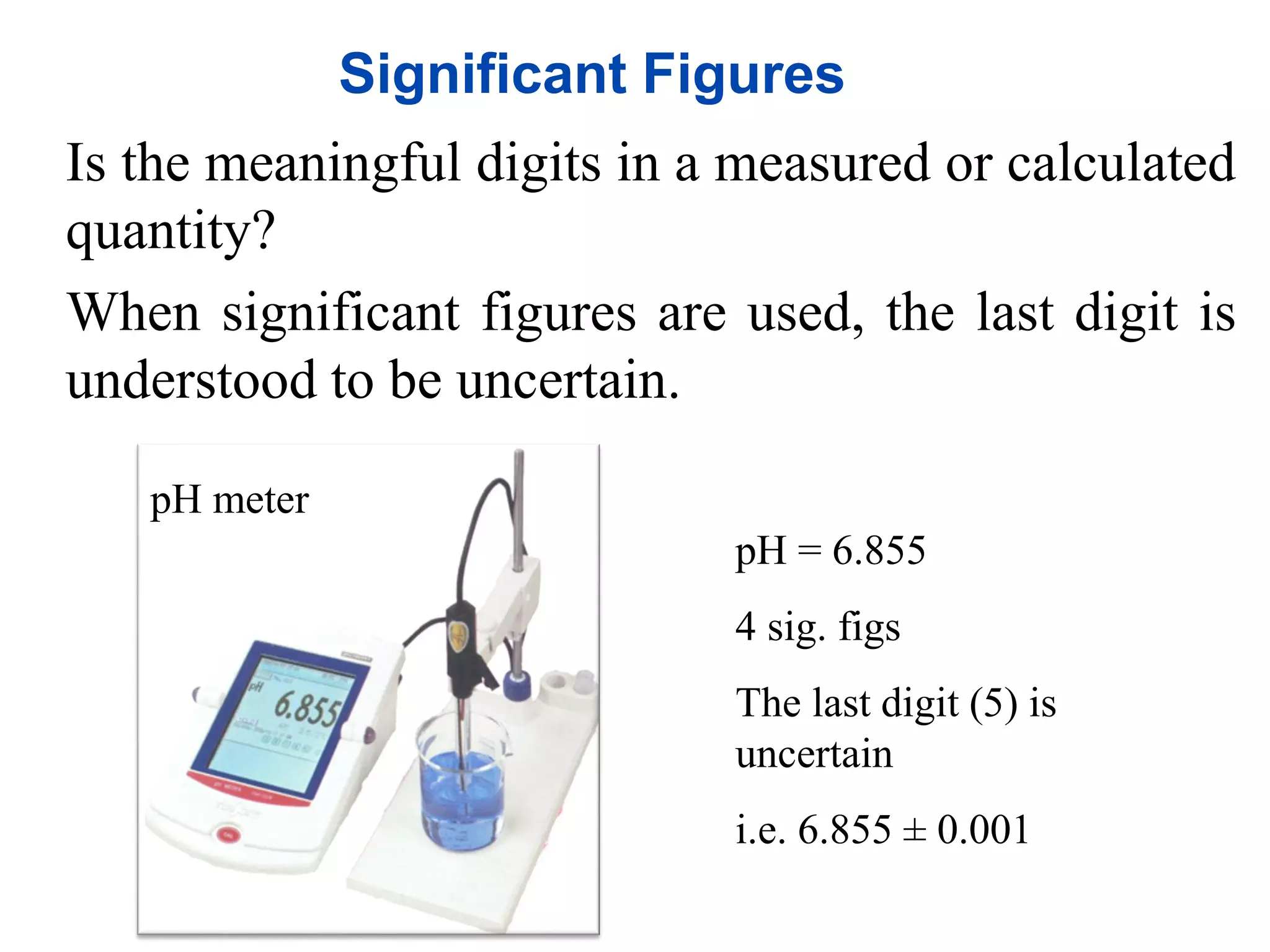
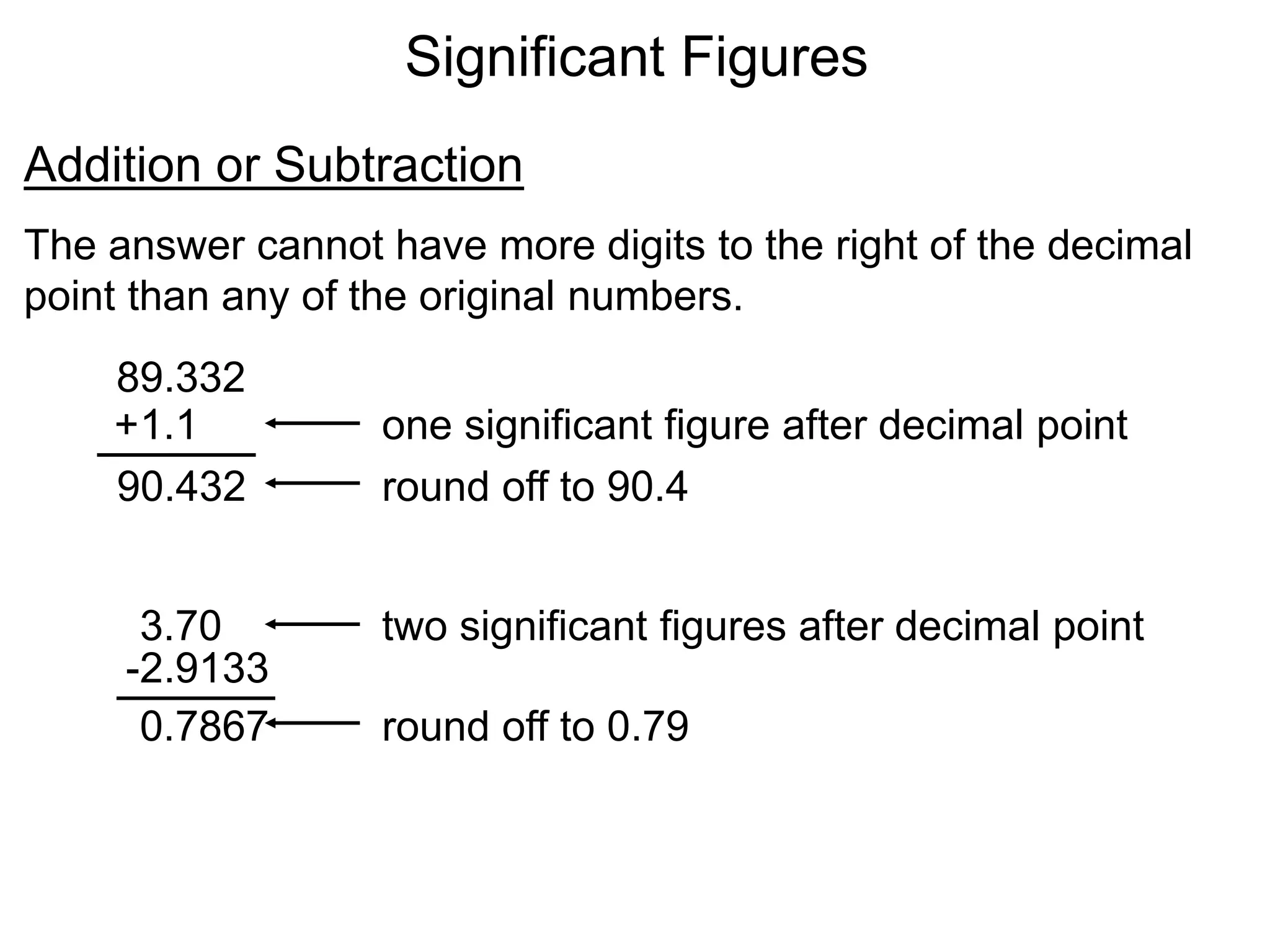
- Measurements in chemistry rely on devices like rulers, balances, and thermometers. The standard metric units and prefixes like milli and kilo are used to quantify measurements, properties