Embed presentation
Downloaded 38 times






![Abbreviated electron configuration
Follow these steps to write abbreviated electron
configurations.
Step 1:Find the symbol for the element on a
periodic table.
Step2: Find the symbol for the closest noble gas
the is located in one row above and put the
symbol in square bracket.
For example for iron the closest noble gas will be
[Ar]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/electronconfiguration-170222170035/85/Electron-configuration-10-320.jpg)
![Step3: Continue writing electron
configuration starting with the period
number of the element followed by s.
For iron abbreviated electron
configuration will be
[Ar]4s2
3d6
18 + 2+ 6= 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/electronconfiguration-170222170035/85/Electron-configuration-11-320.jpg)
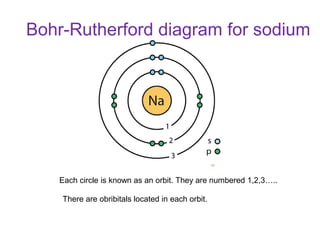
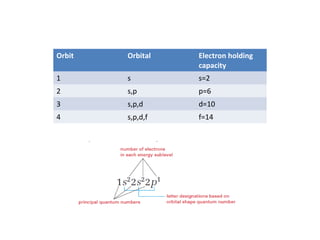
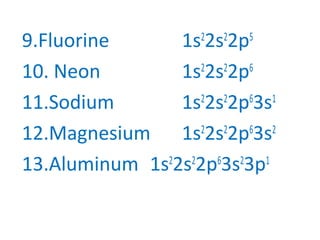
The document discusses electron configurations, which describe the arrangement of electrons in an atom's orbitals. It notes that electrons occupy specific orbitals and that orbitals are grouped into shells. It then provides examples of the full and abbreviated electron configurations for the first 20 elements, showing how many electrons occupy each orbital. The document also outlines the steps for writing abbreviated electron configurations using the noble gas of the same period.









![Abbreviated electron configuration
Follow these steps to write abbreviated electron
configurations.
Step 1:Find the symbol for the element on a
periodic table.
Step2: Find the symbol for the closest noble gas
the is located in one row above and put the
symbol in square bracket.
For example for iron the closest noble gas will be
[Ar]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/electronconfiguration-170222170035/85/Electron-configuration-10-320.jpg)
![Step3: Continue writing electron
configuration starting with the period
number of the element followed by s.
For iron abbreviated electron
configuration will be
[Ar]4s2
3d6
18 + 2+ 6= 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/electronconfiguration-170222170035/85/Electron-configuration-11-320.jpg)