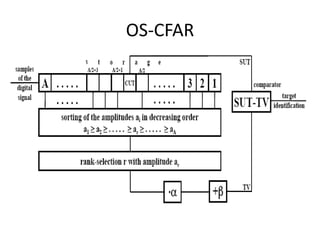
The document discusses different types of Constant False Alarm Rate (CFAR) detection techniques used in radar systems. It describes CAGO-CFAR, OS-CFAR, CASH-CFAR, and MAMIS-CFAR. CFAR aims to maintain a constant false alarm rate despite changing noise, clutter, and interference levels. It does this by setting a threshold based on surrounding clutter levels to detect targets above the threshold. The different CFAR techniques vary in how they calculate the threshold from surrounding clutter.