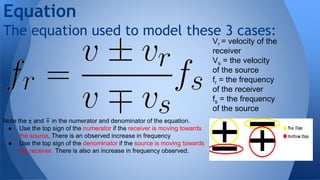
The Doppler effect describes how the frequency of a wave is altered by the motion of the source or receiver. There are three cases: a stationary source with a moving receiver, a stationary receiver with a moving source, and both moving. If the source and receiver move towards each other, frequency increases, and if they move apart frequency decreases. This is demonstrated by the Doppler effect equation. For example, an emergency vehicle's siren appears higher in pitch as it approaches a stationary listener due to the source moving towards the receiver.