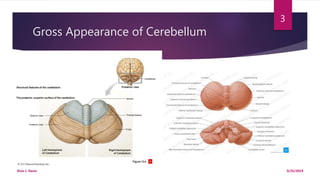
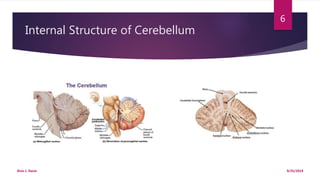
The document discusses the neuroanatomy of the cerebellum, detailing its gross appearance, internal structure, and functional areas. It describes the layering of the cerebellar cortex, the types of cells present, and the mechanisms through which the cerebellum processes motor and sensory information. Additionally, it outlines the pathways through which the cerebellum receives and sends signals to other parts of the nervous system.
















![Intracerebellar Nuclear Mechanisms
The deep cerebellar nuclei receive afferent nervous information from two sources:
(1) the inhibitory axons from the Purkinje cells of the overlying cortex
(2) the excitatory axons that are branches of the afferent climbing and mossy fibers.
Cerebellar Cortical Neurotransmitters
Pharmacologic research has suggested that the excitatory climbing and mossy
afferent fibers use glutamate (gamma aminobutyric acid [GABA]) as the excitatory
transmitter on the dendrites of the Purkinje cells.
9/25/2019Elvis J. Davis
23](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thecerebellum-190925094423/85/The-cerebellum-23-320.jpg)