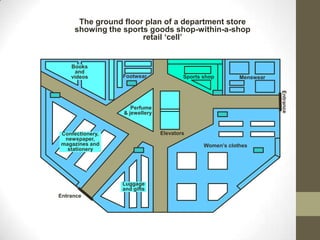
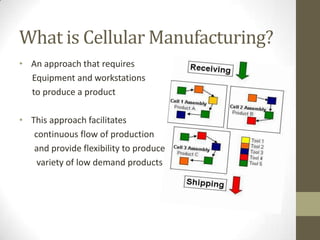
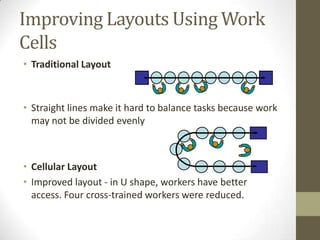
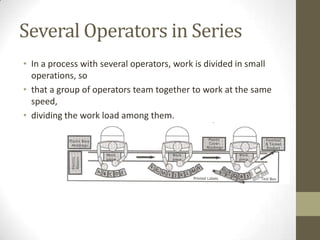
Cellular layout is a facility arrangement where machines are organized to produce specific families of parts, enhancing the flow of production and flexibility. This layout can reduce inventory, labor costs, and improve operational efficiency, while challenges include restructuring existing systems and addressing equipment and management issues. Implementing combined cellular manufacturing further increases adaptability and productivity by optimizing resources across neighboring cells.