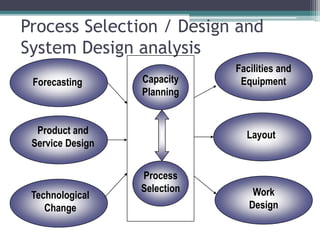
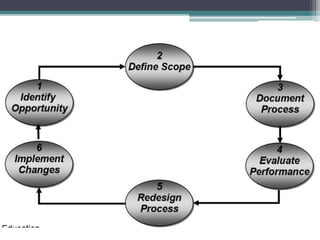
The document discusses process selection, design, and analysis. It describes four main types of production processes: project shops which produce custom goods as needed; job shops which produce custom orders; batch shops which produce goods in batches to fill orders; and assembly lines which connect sequential production steps. The document then outlines the key phases of process design which include forecasting demand, product design, capacity planning, facility layout, and work design. It defines process analysis as documenting processes to understand how work is performed and identify opportunities for redesign, and describes the main steps as identifying opportunities, defining the scope, documenting the current process, evaluating performance, redesigning the process, and implementing changes.